Seasonal Health Preservation in Traditional Chinese Medicine
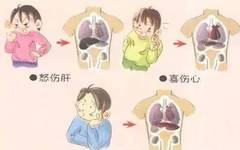
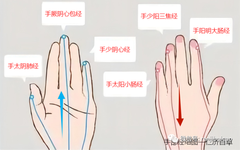
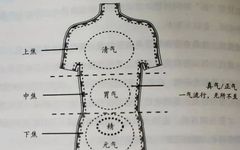
In the universe, human life activities are closely related to nature. This perspective, which examines the physiological phenomena of the human body in conjunction with the natural world, is a unique aspect of ancient Chinese culture known as the “Correspondence between Heaven and Man”. Therefore, the Huangdi Neijing states: “Between heaven and earth, within the … Read more