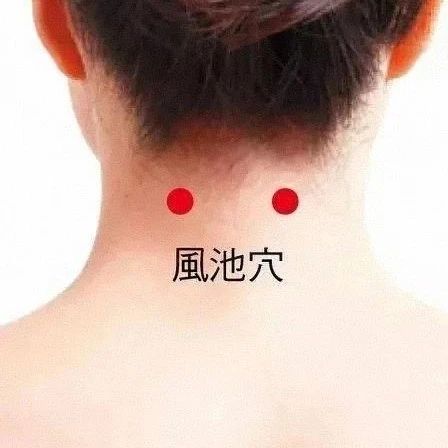
Moxibustion or Massage of Fengchi Point Can Improve Vision
Fengchi Point / 1 Fengchi – Awakens the Mind and Opens the Senses, Enhances Hearing and Vision The Fengchi point, also known as Refu point, is located at the nape of the neck, just below the occipital bone, aligned with the Fengfu point, in the depression between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the upper trapezius muscle. … Read more