Functions of the Five Zang and Six Fu Organs in Traditional Chinese Medicine
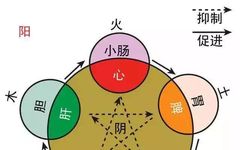
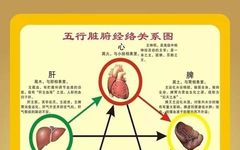
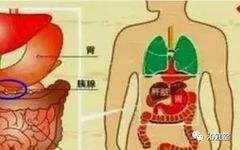
⭕ The human body contains a total of five Zang (organs) and six Fu (hollow organs). The five Zang organs are: Xin (Heart), Gan (Liver), Pi (Spleen), Fei (Lung), Shen (Kidney); the six Fu organs are: Dan (Gallbladder), Wei (Stomach), Da Chang (Large Intestine), Xiao Chang (Small Intestine), San Jiao (Triple Burner), Pang Guo (Bladder). … Read more