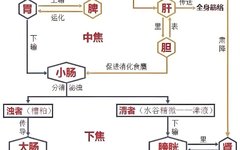
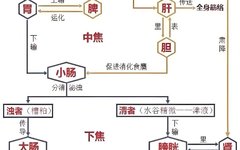
Traditional Chinese Medicine: Hard Stool Like Sheep Feces, Yin Deficiency and Dry Intestines? Share a Formula of Two Herbs to Nourish Yin, Moisten the Intestines, and Promote Bowel Movement
Constipation is a common ailment among many women and middle-aged individuals, characterized by hard stools resembling sheep feces, difficulty in bowel movements, and often accompanied by heat in the palms and soles, poor sleep, and frequent dreams leading to insomnia. Many have tried various oral laxatives and external treatments like glycerin suppositories or even enemas, … Read more