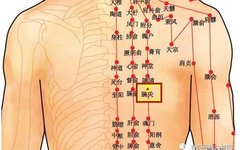
Effective Powder Formulas for Treating Low Back Pain with 100% Efficacy
Formula One: Low Back Pain Formula Ingredients: Huang Qi (Astragalus) 15-30g, Dang Gui (Angelica Sinensis) 12g, Chuan Xiong (Ligusticum Chuanxiong) 8g, Chi Shao (Red Peony) 10g, Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia) 15g, Sheng Ma (Cimicifuga) 5-8g, Wu Yao (Lindera) 8-12g, Di Long (Earthworm) 10g. Dosage: One dose per day, decocted in water, taken three times daily. … Read more