The Official Roles Assigned to the Five Zang and Six Fu Organs in Ancient Chinese Medicine
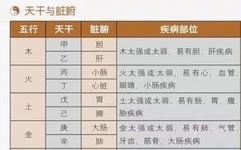
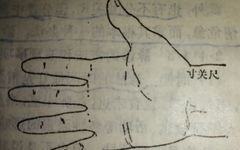
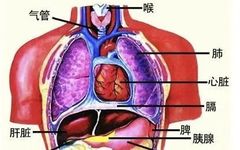
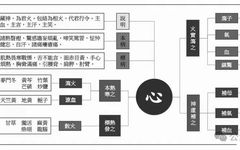
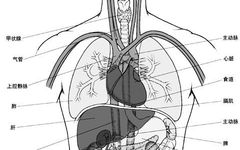
The core theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) revolves around the Five Zang and Six Fu organs. The Five Zang refers to the liver (Gan), heart (Xin), spleen (Pi), lungs (Fei), and kidneys (Shen); while the Six Fu includes the gallbladder (Dan), small intestine (Xiao Chang), stomach (Wei), large intestine (Da Chang), bladder (Pang Guang), … Read more