A Beginner’s Guide to Traditional Chinese Medicine: An Easy-to-Understand Explanation of the Six Fu Organs (Including: The True Interpretation of Pulse Diagnosis for Beginners)
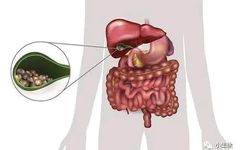
1. Gallbladder The gallbladder is the foremost of the six fu organs and belongs to the extraordinary organs. It is shaped like a pouch, resembling a gourd, and is attached to the liver’s small lobe. The gallbladder is yang and belongs to wood, while the liver is yin and also belongs to wood. The gallbladder … Read more