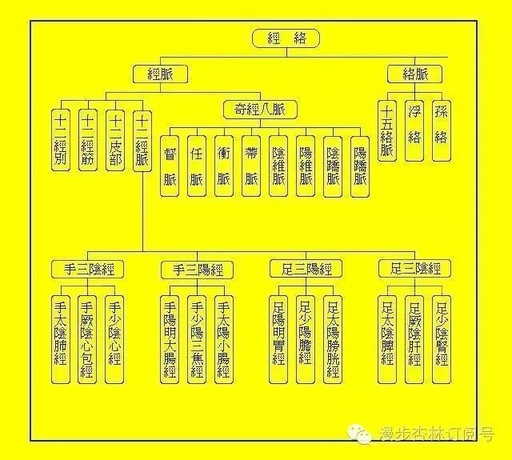
The Six Fu Organs: What Are the Roles of the Gallbladder, Stomach, Small Intestine, and Large Intestine?
The Six Fu organs refer to the gallbladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, bladder, and San Jiao (Triple Burner). Among them, the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and bladder are known as the “transformation Fu” because they are responsible for the conduction and transformation of substances. The physiological function of the Six Fu organs: The … Read more