Ginseng, as a representative of traditional Chinese medicine, has a history of nearly four thousand years of application in China, and has been regarded by renowned medical experts throughout history as the “king of herbs.” Many classic medical texts record the efficacy and functions of ginseng. It is also well-known as a powerful tonic. Let us explore the efficacy and functions of ginseng in detail.
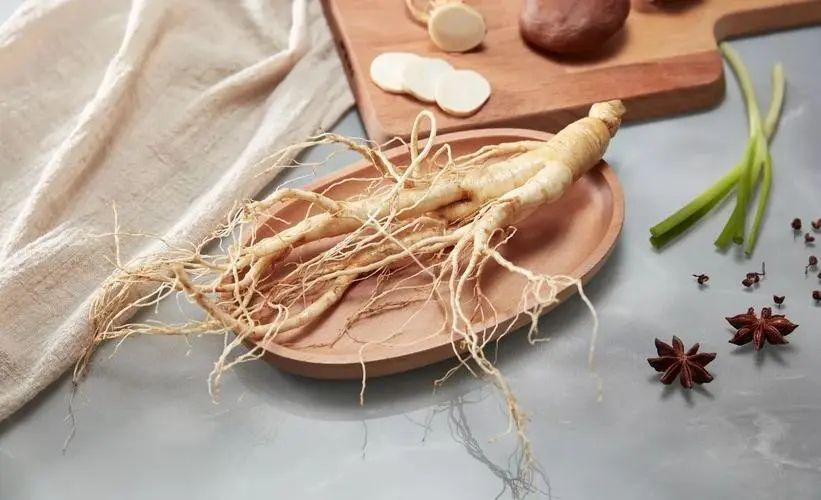

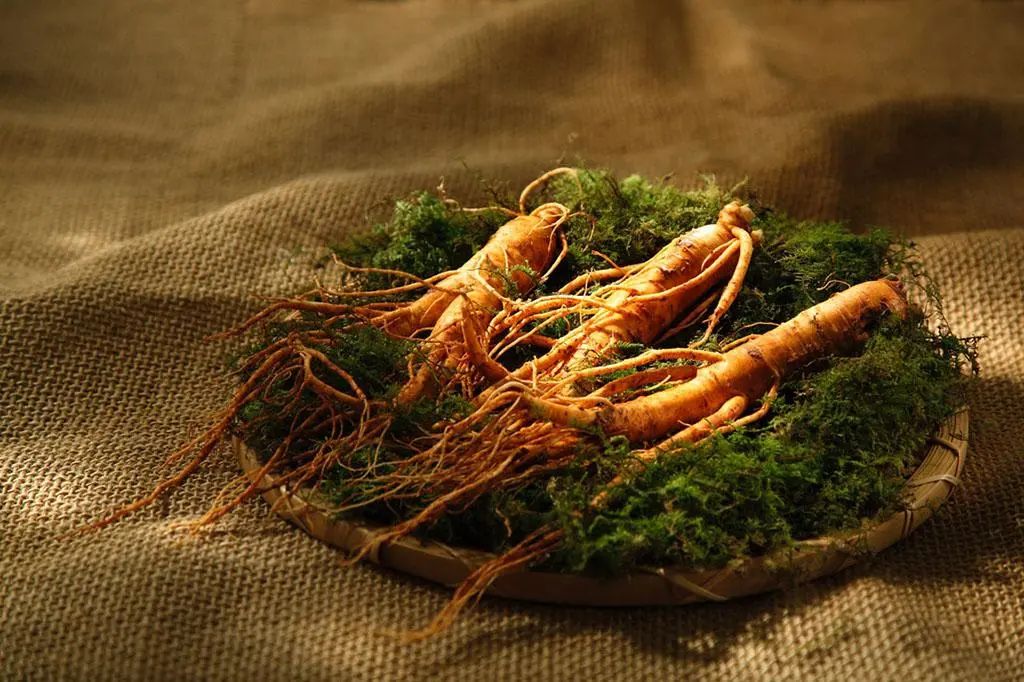
Ginseng is also known by various names such as Ren Shen, Gui Gai (《Ben Jing》), Tu Jing, Shen Cao, Huang Shen, Xue Shen (《Wu Pu Ben Cao》), Di Jing (《Guang Ya》), Bai Chi Chu (《Ben Cao Tu Jing》), Hai Yu, Jin Jing Yu Lan, Hai Er Shen (《Gang Mu》), Bang Chui (《Liaoning Major Medicinal Materials》). The medicinal part is the root of the plant belonging to the Araliaceae family.

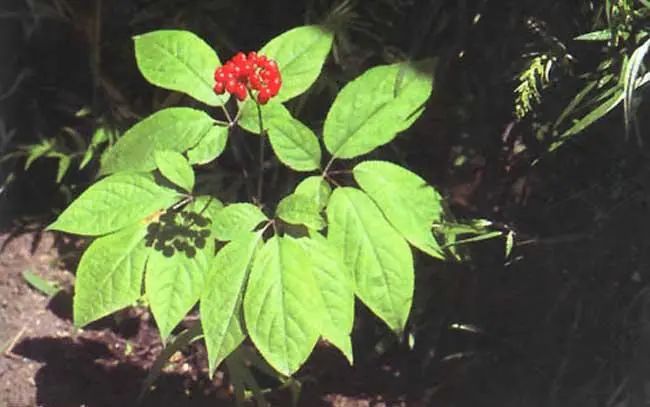
The plant is a perennial herb, reaching up to 60 centimeters in height. The main root is thick, fleshy, and cylindrical, often branched. The upper part of the root that branches is commonly referred to as “Ling Ti” or “Heng Ti”; those that do not branch or branch at the lower part are called “Ben Ti” or “Gu Ti”; the fibrous roots are long with numerous small wart-like structures; the stem has stem scars and sometimes produces adventitious roots. The stem is erect, green, slender, and smooth. The leaves are whorled at the top of the stem, with the number varying according to the age of the plant. Initially, there is one 3-foliate leaf, two-year-olds have one 5-foliate palmate leaf, three-year-olds have two 5-foliate palmate leaves, and four-year-olds have three leaves, increasing yearly to a maximum of six leaves; the leaves have long petioles; the leaflets are oval or obovate, with the smaller leaflets at the base measuring 2-3 cm long and 1-1.5 cm wide; the upper leaflets are 4-15 cm long and 2.2-4 cm wide; the tips are gradually pointed, the base is wedge-shaped, extending downwards, with finely serrated edges, and the upper side has erect stiff hairs along the leaf veins, while the underside is hairless; the petioles can be up to 2.6 cm long. The total flower stalk emerges from the center of the leaf petiole at the top of the stem, measuring about 7-20 cm long, with an umbellate inflorescence containing a dozen or several dozen pale yellow-green flowers, usually blooming in the fourth year; the flowers have pedicels, are bisexual and male; the calyx is green and 6-lobed; there are 6 petals with pointed tips; there are 5 stamens; the ovary is inferior, with 2 chambers, and the style is separate in bisexual flowers, while in male flowers, it forms a hollow tubular structure. The fruit is a drupe, kidney-shaped, turning bright red when mature, with one seed in each chamber. The seeds are white, flat, and oval-shaped, with one side truncated. The flowering period is from June to July, and the fruiting period is from July to September.

Meridian Affinity: Spleen, Lung, Heart.
Taste and Properties: Sweet, slightly bitter, neutral.
Precautions: Should not be used with Li Lu.
Main Functions and Indications: Greatly tonifies Yuan Qi, restores pulse, stabilizes collapse, tonifies Spleen and benefits Lung, generates fluids, calms the spirit. It is used for deficiency leading to collapse, cold limbs, weak pulse, Spleen deficiency with poor appetite, Lung deficiency with cough and asthma, fluid damage with thirst, internal heat with diabetes, prolonged illness with weakness, palpitations and insomnia, impotence, and cold in the palace; heart failure, cardiogenic shock.
Dosage: 3-9g, decocted separately and added to soups; wild mountain ginseng can be ground into powder and taken, 2g at a time, twice a day.
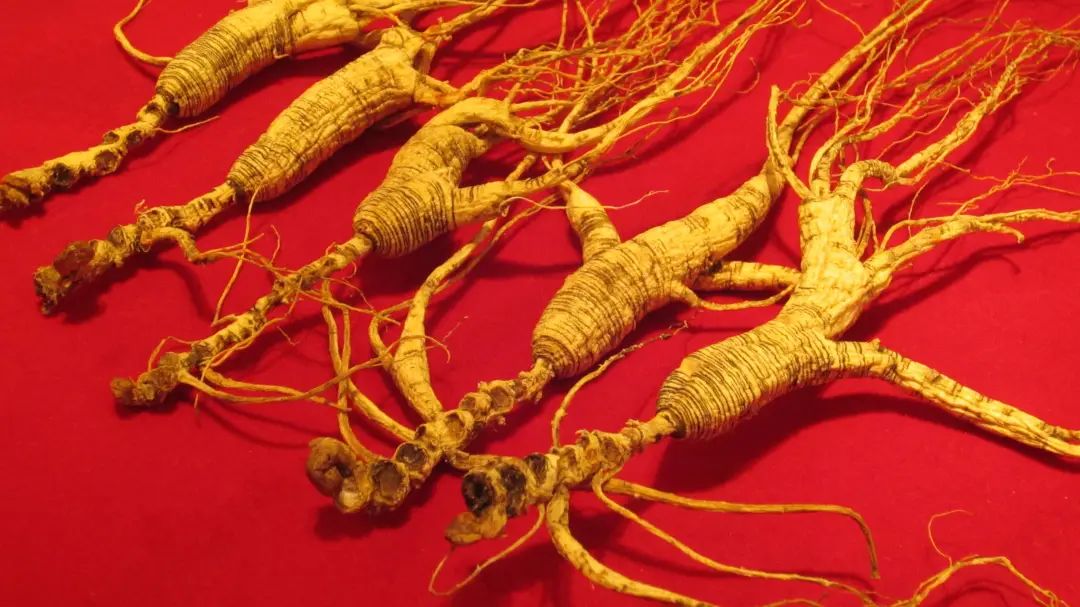

The Efficacy and Functions of Ginseng
1. Enhances immunity. Ginseng contains various important nutrients, such as ginsenosides, ginseng acid, and ginseng polysaccharides, which are believed to enhance the body’s immune function and improve resistance to diseases. Long-term use of ginseng can strengthen the immune system and enhance the body’s resistance to various diseases. 2. Promotes blood circulation. The effective components rich in ginseng can dilate blood vessels, promote blood circulation, and enhance cardiovascular function. Good blood circulation helps supply sufficient oxygen and nutrients to all tissues and organs, maintaining normal metabolism and function. 3. Improves mental state. Ginseng has a certain stimulating effect, promoting the excitement of the nervous system, improving mental state, and enhancing cognitive ability and coping skills. Long-term use of ginseng can alleviate mental fatigue and lack of concentration, improving work and study efficiency. 4. Anti-aging. The antioxidants abundant in ginseng can neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing damage to cells and delaying cellular aging and decline, maintaining skin elasticity and youthfulness. Ginseng can also regulate the endocrine system, balance hormone levels, and combat the aging process. 5. Enhances physical strength and endurance. Ginseng can improve physical strength and endurance, enhancing muscle strength and endurance, and improving athletic ability. This is particularly important for those who need to work and exercise at high intensity for extended periods; long-term use of ginseng can increase the body’s endurance and anti-fatigue capacity. 6. Promotes digestion and absorption. The effective components in ginseng can promote gastrointestinal motility, increase gastric juice secretion, improve digestive function and absorption capacity, and enhance the utilization of nutrients from food. For those with gastrointestinal issues, moderate consumption of ginseng can alleviate symptoms such as stomach pain and indigestion.

Selected Formulas
① For treating Qi deficiency of Ying and Wei, weak organs, abdominal distension, loss of appetite, intestinal rumbling and diarrhea, nausea and vomiting: Ginseng (remove the skin), Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes), Fu Ling (Poria, remove the skin), Gan Cao (Licorice, roasted) in equal parts. Grind into a fine powder, take 6g each time, boil with one cup of water until reduced to 70%, and take orally at any time, adding a little salt; white soup can also be used. Regular use warms the Spleen and Stomach, enhances appetite, and dispels cold and dampness. (《Ju Fang》 Four Gentlemen Decoction)
③ For treating chronic cough due to Lung deficiency: 2 liang of ginseng powder, 1 liang of roasted deer antler glue (ground). Take 9g each time, with a cup of mint and soybean soup, a little green onion, boil once or twice, pour into a cup, and sip warm when coughing. (《Shi Liao Ben Cao》)
⑤ For treating Yang deficiency with asthma, spontaneous sweating, night sweats, shortness of breath, and dizziness: 5 qian of ginseng, 1 liang of cooked Fu Zi. Divide into four doses, each with 10 slices of fresh ginger, 2 cups of water, boil to 1 cup, and take warm away from meals. (《Ji Sheng Fang》)
⑥ For treating heart Qi deficiency with palpitations and spontaneous sweating: 1 pig kidney, boiled with 2 cups of water until reduced to 1.5 cups, finely chop the kidney, add 0.5 liang of ginseng and 0.5 liang of Dang Gui (Angelica, remove the skin and take the middle section). Cut and boil until reduced to 80%, eat the kidney and take the juice. If there is leftover kidney, dry the two medicinal residues and grind into fine powder, making pills the size of a wutong seed, taking 30-50 pills each time. (《Bai Yi Xuan Fang》)
⑧ For treating diabetes with excessive thirst: equal parts of ginseng and Trichosanthes root. Grind into powder, mix with honey to form pills the size of a wutong seed, taking 30 pills each time, with Mai Dong (Ophiopogon) soup. (《Ren Zhai Zhi Zhi Fang》 Yu Hu Wan)
⑩ For replenishing after bleeding: 2 liang of ginseng (remove the skin), 5 jujubes. Take with 2 cups of water, boil to 1 cup. Sip slowly, and after taking, sleep well to eliminate all diseases. (《Shi Yao Shen Shu》 Du Shen Decoction)
⒁ For treating chest obstruction and fullness in the heart, Qi stagnation in the chest, and fullness under the ribs: 3 liang each of ginseng, Gan Cao (Licorice), Gan Jiang (Dried Ginger), and Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes). Combine these four ingredients with 8 liters of water, boil to obtain 3 liters, take 1 liter warm, three times a day. (《Jin Gui Yao Lue》 Ginseng Decoction)
WeChat has been updated! If you neither starred me, nor liked or “looked at” my articles, the system will assume you do not need to receive updates on herbal knowledge, and ultimately, you will not receive our article updates.
End of the article. Thank you for your patience in reading. If you find it good, please click “ like” and “
like” and “ look” at it.
look” at it.
As the ancient saying goes, “When three people walk together, there must be a teacher among them.” For the convenience of mutual integration and exchange of knowledge among practitioners of traditional Chinese medicine, a group for herbal knowledge is being established. If you wish to join, please add the editor on WeChat and indicate your identity. The editor invites you to join the group.


