
Recently, many users have reported,
why they are not receiving our articles?
Actually, it is because the public account no longer pushes content based on time.
Therefore, we need you to click on “View”,
or set the medical news app as a “Star”,
so hurry up and take action!
Source: Shanghai Medical News
With seasonal changes and alternating temperatures, people are prone to colds. If you don’t want to go to the hospital, what methods do you usually choose to combat a mild cold that affects your daily life? Making ginger and brown sugar tea is simple and convenient, bringing warmth to your heart; brewing a packet of granules, such as Ban Lan Gen (Isatis Root), Xiao Chai Hu (Minor Bupleurum), or Lianhua Qingwen (Lianhua Qingwen Granules), choosing Chinese medicine can provide psychological comfort even if it doesn’t work immediately. However, these practices may not only be unhelpful but could also worsen the cold. In medicine, it is essential to differentiate and treat based on the syndrome, rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), colds are mainly divided into Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat types. These two types differ significantly in pathogenesis, symptoms, and medication choices. Wind-Cold colds are caused by the invasion of Wind-Cold pathogens, leading to the failure of Lung Qi to disperse. Wind-Heat colds are caused by the invasion of Wind-Heat pathogens, resulting in the disharmony of Lung Qi.
How to distinguish between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat colds?
1. Judging by pathogenesis. When Wind and Cold pathogens invade the body together, it is classified as Wind-Cold syndrome; when Wind and Heat pathogens invade together, it is classified as Wind-Heat syndrome. Therefore, Wind-Cold colds are more common in winter, while Wind-Heat colds are often seen in summer, but this is not absolute. The pathogenesis of Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat colds is influenced not only by the season but also by individual constitution, lifestyle habits, and other factors.
2. Judging by symptoms.
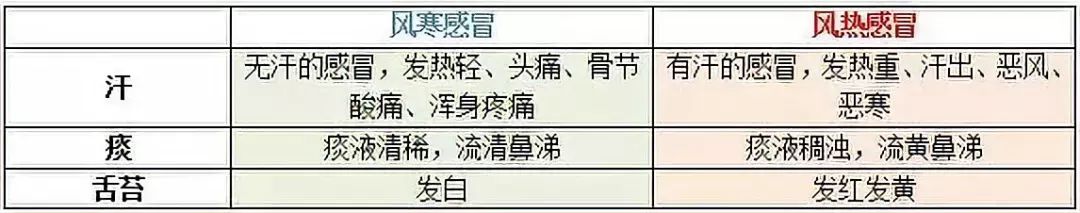
How to choose the appropriate medication?
For Wind-Cold colds, the main treatment should focus on warming and dispersing the exterior, commonly using Ma Huang (Ephedra), Jing Jie (Schizonepeta), Fang Feng (Siler), and Su Ye (Perilla Leaf) as dispersing and cold-resolving herbs. For Wind-Heat colds, the main treatment should focus on cooling and dispersing the exterior, commonly using Ju Hua (Chrysanthemum), Bo He (Mint), and Sang Ye (Mulberry Leaf) as heat-clearing and detoxifying herbs.
Commonly Used Chinese Patent Medicines
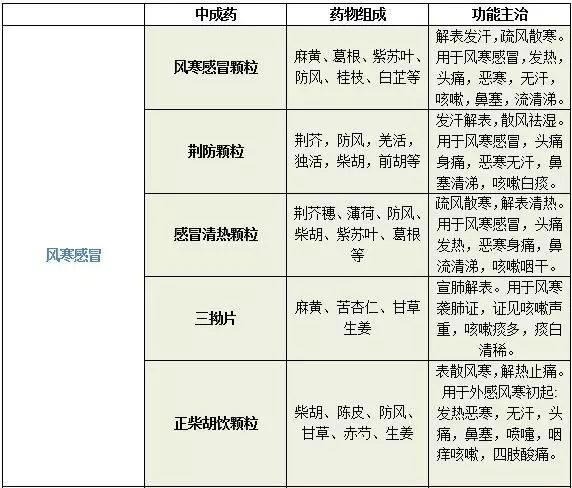
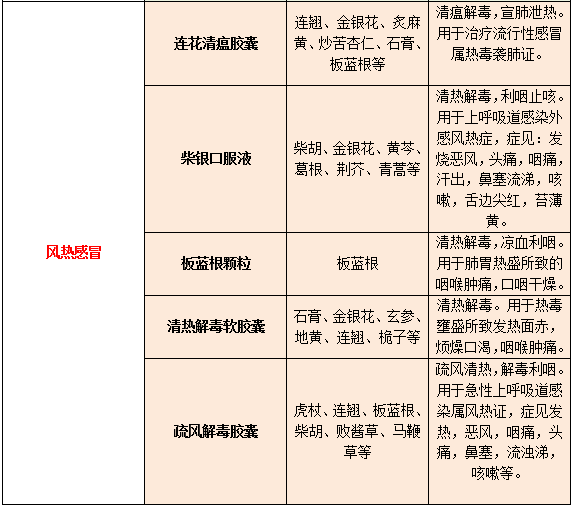
END
Previous Recommendations
1. Zhang Wenhong: The day the global pandemic ends is the day danger arrives in our country
2. Suggestions: Please abolish the titles of Associate Chief Physician and Chief Physician!
3. An 8-year-old boy visited the doctor 323 times and underwent 13 surgeries; there is a condition called: “Mom thinks you are sick”!
4. 9 medical staff were “poisoned” by colleagues!
5. 30 frequently asked questions about COVID-19 vaccination; everything you want to know is here


