
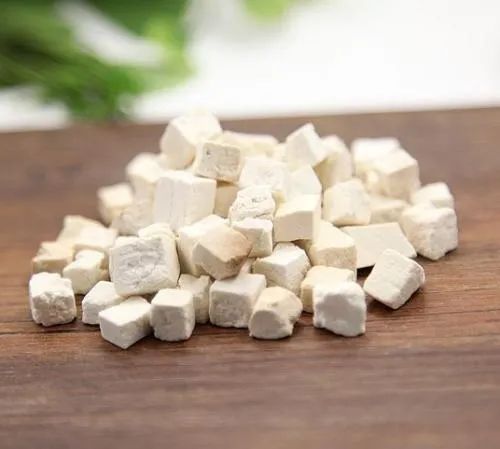
Poria (Fu Ling), also known as Yuling and Songshu, has a sweet taste and neutral nature. It is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that provides excellent health benefits for the human body and can assist in the treatment of various diseases. Poria can be used in medicinal preparations and can also be consumed in medicinal dishes, helping to alleviate lower back pain and insomnia. Let’s explore the effects and functions of Poria, as well as its contraindications and side effects!

01
Effects and Functions of Poria
1. Promotes Hematopoiesis
Poria is rich in polysaccharides, various vitamins, and trace elements such as selenium. When these components are absorbed by the body, they can effectively enhance the immune function of blood cells and body fluids, thereby improving the hematopoietic capacity of the bone marrow. Studies have shown that Poria can effectively increase the white blood cell count in patients with leukopenia and is beneficial for stabilizing red blood cell levels in the body.
2. Promotes Digestion and Detoxification
Poria contains a high amount of dietary fiber, which can help stimulate gastrointestinal peristalsis, promote digestion, and accelerate the excretion of metabolic waste and toxins, thus detoxifying and cleansing the intestines. Additionally, some medicinal components in Poria can effectively assist in treating gastrointestinal diseases caused by inflammation, providing excellent health benefits for the digestive system.
3. Tonifies Qi and Strengthens the Spleen
As people’s living standards continue to improve, their dietary requirements have become increasingly refined. However, due to the pressures of modern life, many individuals experience symptoms of spleen and stomach discomfort, often feeling helpless in the face of delicious food or enduring pain. TCM believes that Poria has the effect of strengthening the spleen and nourishing the stomach, making it useful for treating spleen deficiency and diarrhea. It is particularly effective for diarrhea and leukorrhea caused by spleen deficiency and dysfunction. It is often used in combination with Dang Shen (Codonopsis), Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes), and Shan Yao (Chinese Yam).

02
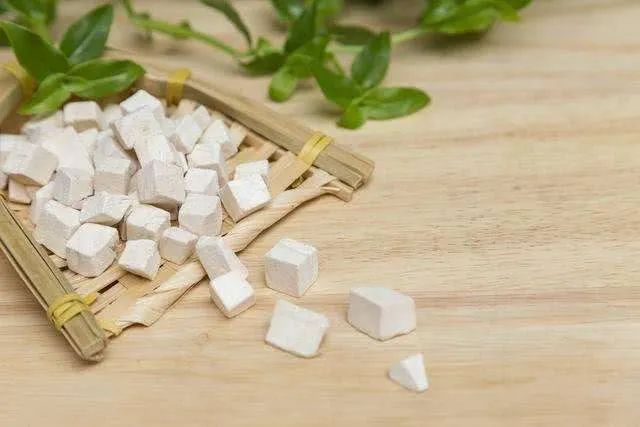
Contraindications and Side Effects of Poria
For most people, Poria is safe to consume, especially for those experiencing internal dampness, edema, low urine output, dizziness, palpitations, poor appetite, loose stools, anxiety, insomnia, and vivid dreams. However, it is not suitable for individuals with kidney deficiency and frequent urination, cold and slippery essence, qi deficiency with sinking, or those with dry mouth due to fluid damage.
When consuming Poria, it is important to avoid excessive amounts. Overconsumption can lead to adverse effects, as Poria has diuretic properties. Excessive intake may result in increased urination, which can harm the body’s foundation and severely deplete vital energy. Additionally, for patients with kidney deficiency, consuming Poria may exacerbate symptoms, potentially leading to conditions such as nocturnal emissions, so attention should be paid to dosage and special populations.
Individuals with diabetes should also avoid Poria, as they need to control their starch intake, limiting it to no more than 250 grams of staple food per day. Poria has a high starch content, making it unsuitable for diabetics.
While taking Poria, it is advisable to avoid substances like rice vinegar and strong tea, and to monitor the dosage. Otherwise, it may not only affect the efficacy of the medicine but also lead to allergic reactions such as abdominal pain, skin redness and swelling, and bronchial asthma attacks, which can seriously jeopardize health.
Reprinted from Kaixin Yangdao



TCM Acupuncture and Massage Department: Xie Yibing

★ Associate Professor
★ Associate Chief Physician
Profile
Graduated from Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 1990, with over 30 years of clinical experience.
Pain Specialty * Introduction to Unique Techniques
TCM Pain Specialty
Rapid Pain Relief Technique
“Rapid Pain Relief Technique” is a unique quick treatment method by Dr. Xie, which can rapidly alleviate various acute and chronic pains and quickly restore limited limb functions. Most indications can be effectively treated on-site.
“Rapid Pain Relief Technique” comprehensively utilizes the advantages of TCM massage, bone setting, acupuncture, joint mobilization, floating needle therapy, and guiding techniques, providing integrated treatment based on the condition. It is suitable for various acute and chronic soft tissue injuries, pain caused by degenerative changes, neuralgia, arthritis, spinal diseases, and related visceral dysfunction, as well as some internal and external gynecological and pediatric conditions.
The Rapid Pain Relief Technique is characterized by its “quick effect, minimal pain, and safety.”

Main Treatment Scope of the Rapid Pain Relief Technique(Red text indicates better treatment effects)
Head and Facial Pain:Vasculoneurogenic headache, dizziness,,temporomandibular joint pain,trigeminal neuralgia, tinnitus, toothache,facial nerve inflammation (facial paralysis);
Neck and Shoulder Pain:Cervical spondylosis, stiff neck,fat pad (hump);
Chest and Back Pain:Muscle strain pain, thoracic joint dysfunction,chest wall sprain, intercostal neuralgia,postherpetic neuralgia;
Lumbar and Sacral Pain:Acute lumbar sprain, lumbar disc herniation, lumbar muscle strain, third lumbar transverse process syndrome,spinal curvature, ankylosing spondylitis, lumbar spinal stenosis,lumbar synovial entrapment, sacroiliac arthritis,sacroiliac joint dislocation, coccygodynia;
Upper Limb Pain:Shoulder periarthritis,post-stroke shoulder pain, biceps tendonitis,rotator cuff injury,subacromial bursitis, tennis elbow,student’s elbow,carpal tunnel syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, radial styloid tenosynovitis, trigger finger;
Lower Limb Pain:Piriformis syndrome, sciatica,avascular necrosis of the femoral head,knee arthritis, infrapatellar fat pad inflammation, knee ligament injuries, acute and chronic ankle sprains,plantar fasciitis,gouty arthritis;
Miscellaneous Internal, External, and Gynecological Conditions:Rheumatic and rheumatoid joint and muscle pain,dysmenorrhea, menstrual irregularities, uterine cold infertility, lobular hyperplasia of the breast,chronic gastritis,chronic abdominal pain and bloating,biliary colic, ureteral stone pain,enuresis,chronic pelvic pain, cancer pain,localized skin allergies,acne, cough.


[Disclaimer] The images and text are sourced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!
Warm Reminder: This platform shares health-related images and information for reference, learning, and communication purposes only, and should not be used as a basis for medical diagnosis. Please consult a physician for guidance if needed.

