In ancient China, there were many excellent health preservation methods and concepts that were highly regarded by the ancients, which modern people might also consider adopting.
Nine Health Preservation Methods of the Ancients 1. Meridian Health Preservation
1. Meridian Health Preservation
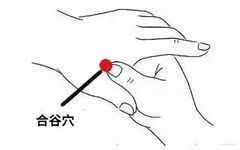
The Huangdi Neijing states that meridians have the power to determine life and death, address various diseases, and regulate deficiency and excess. Ancient health preservation scholars believed that unblocking the meridians is an important measure for health maintenance, and the simplest methods are to frequently stimulate, massage, or perform acupuncture on three key points: Hegu (LI4), Neiguan (PC6), and Zusanli (ST36).
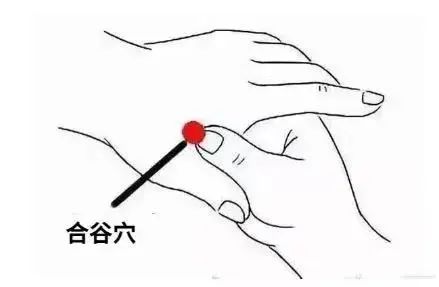
Hegu (LI4) can prevent and treat diseases related to the face and the five sense organs.
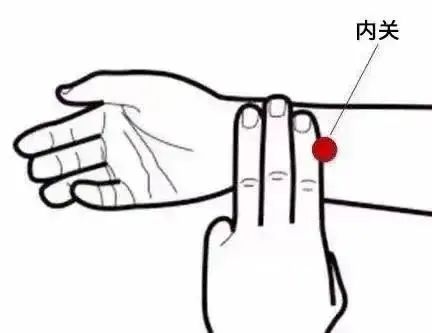
Neiguan (PC6) helps prevent and treat heart diseases.
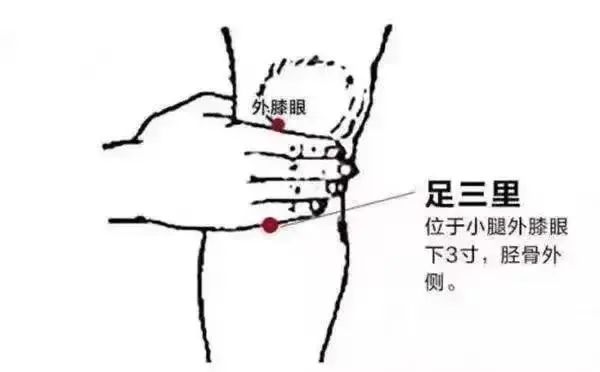
Zusanli (ST36) is most effective in preventing diseases of the internal organs, especially the digestive system.
 2. Dietary Health Preservation
2. Dietary Health Preservation
The ancients believed that a reasonable diet can nourish the essence and qi, correct the yin-yang imbalance of the organs, prevent diseases, and prolong life.
Therefore, diet should pay attention to “broad eating,” which means using “five grains for nourishment, five fruits for assistance, five livestock for benefit, and five vegetables for sustenance,” while also emphasizing the harmony of the five flavors; otherwise, nutritional imbalance, physical constitution bias, and dysfunction of the internal organs can lead to illness.
 3. Seasonal Health Preservation
3. Seasonal Health Preservation
There are different climatic changes in the four seasons, and all things on earth have their own rules of growth, maturation, harvest, and storage, which also applies to the human body. Therefore, the ancients proposed seasonal health preservation methods from aspects of clothing, food, housing, and behavior. The operation of the five internal organs, yin-yang, and qi-blood must adapt to the four seasons and should not go against them.
Adjusting one’s lifestyle according to the seasons helps maintain health and prevent diseases; otherwise, going against the spring can harm the liver, against summer can harm the heart, against autumn can harm the lungs, and against winter can harm the kidneys.

 4. Detoxification Health Preservation
4. Detoxification Health Preservation
The ancients believed that erratic emotions could lead to imbalances in yin-yang and qi-blood within the body. Excessive fatigue can damage the spleen qi, and improper diet can generate dampness, heat, and phlegm. Offending the six excesses and external pathogens can lead to a multitude of diseases. These pathogenic factors are viewed as “toxins” by the body, hence the concept of “detoxification” to preserve true qi.
By regulating diet, taking medications, and other measures to reduce accumulated toxins in the body, one can avoid diseases, prevent premature aging, and thus prolong life.
 5. Tranquility and Spirit Health Preservation
5. Tranquility and Spirit Health Preservation
Tranquility and spirit hold an important position in traditional health preservation. The ancients believed that the spirit governs life activities; maintaining a calm and peaceful mind can nourish the original qi, keep the five organs in harmony, and help prevent diseases, enhance health, and prolong life. Conversely, anger harms the liver, joy harms the heart, worry harms the lungs, and fear harms the kidneys, leading to various physical and mental ailments.
 6. Self-Cultivation Health Preservation
6. Self-Cultivation Health Preservation
The ancients believed that anyone pursuing health and longevity should start with self-cultivation. One should eliminate various distracting thoughts, speak kindly, and do good deeds.
The ancient physician Meng Shen said: “If one can preserve the body and nurture the spirit, one must often speak good words and not part from them”; “With good words, one should also act kindly.” Sun Simiao stated: “With a sincere heart and correct intentions, one can eliminate worries through proper reasoning.” Cultivating good character and frequently doing beneficial things for others can broaden one’s mind and bring joy.

 7. Qi Regulation Health Preservation
7. Qi Regulation Health Preservation
The ancients believed that the body’s original qi has the functions of transformation, promotion, and solidification of blood, warming and nourishing all tissues, resisting pathogens, and enhancing organ function. Nutritional imbalances, improper work-rest balance, emotional disturbances, and attacks from pathogens can lead to symptoms of qi deficiency, stagnation, and reversal, resulting in pathological changes in the body.
Qi regulation health preservation methods advocate a series of measures such as careful daily routines, adapting to the four seasons, avoiding overwork, preventing excessive leisure, adjusting diet, harmonizing the five flavors, regulating emotions, minimizing speech, practicing breathing techniques, and engaging in guided exercises to nourish original qi and prevent diseases while prolonging life.
 8. Nourishing Health Preservation
8. Nourishing Health Preservation
Traditional medicine highly values the use of nourishing herbs to regulate yin and yang, benefit the internal organs, and nourish essence and blood. Proper nourishment can strengthen the body, prevent diseases, and eliminate illnesses. However, nourishment must be based on differentiation of syndromes, be moderate, and consider seasonal appropriateness. For instance, if taking lung-nourishing herbs, autumn is more suitable; if taking warming herbs, winter is more appropriate.
 9. Essence Preservation Health Preservation
9. Essence Preservation Health Preservation
The ancients believed that essence and blood are the essence of the body’s nutrients and the material basis of life. The five internal organs can maintain their normal functions only with the nourishment of essence and blood. If sexual desire is excessive, leading to excessive loss of essence and blood, it can cause physical weakness, numerous diseases, and reduced lifespan. Preserving yin essence can delay aging.
Disclaimer: Some articles on this site are reprints, and the copyright belongs to the original author; reprinting is for the purpose of conveying information and sharing. If there are errors in source attribution or infringement of your legal rights, please contact the author with proof of ownership, and we will promptly correct or delete it. Thank you.Note: The above content is for reference only and may not be suitable for all populations. It is recommended to adjust under the guidance of a physician.