Click the blue text to follow us
Gui Gen Qigong (Part 1)
Gui Gen Qigong consists of both dynamic and static practices, which need to be practiced simultaneously and in coordination.
Due to the extensive content of Gui Gen Qigong, it is divided into two parts for introduction. The first part introduces the beginning and ending postures, as well as the first three movements of the dynamic practice, while the second part covers the last three movements, the concluding posture, and the static practice.
1. Dynamic Practice of Gui Gen Qigong
The dynamic practice includes six main movements and a concluding posture. Additionally, this set of techniques includes the beginning and ending postures (used before starting the dynamic practice or after completing each section) and the transitional movements (known as “Cheng Jie Shi”). For ease of reading, we will first introduce the beginning and ending postures, followed by the dynamic techniques.
Beginning and Ending Postures
Key Points of Operation
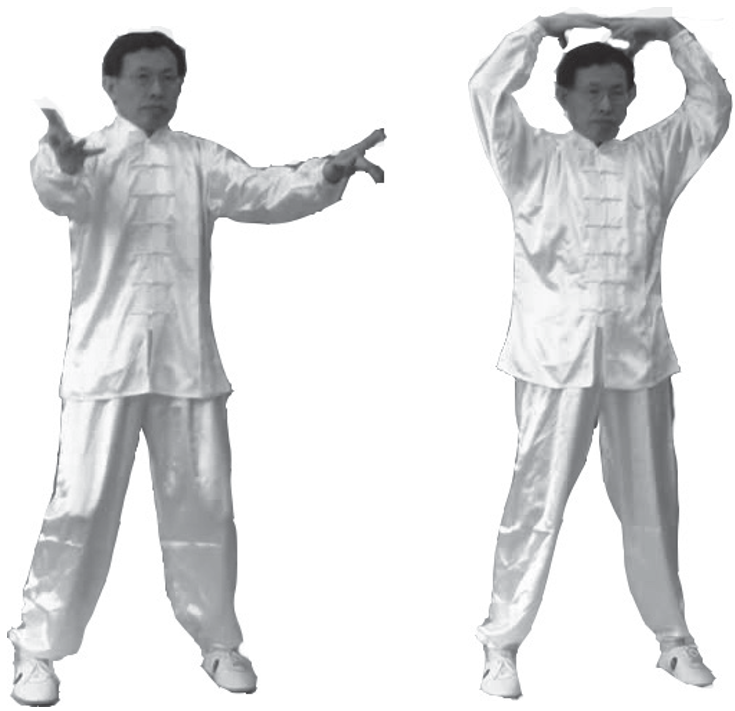
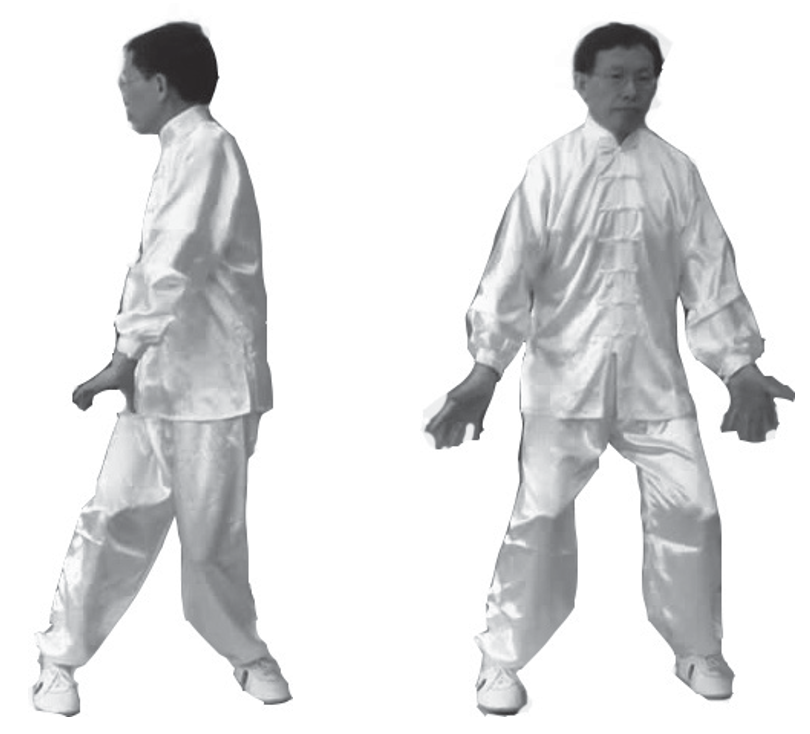
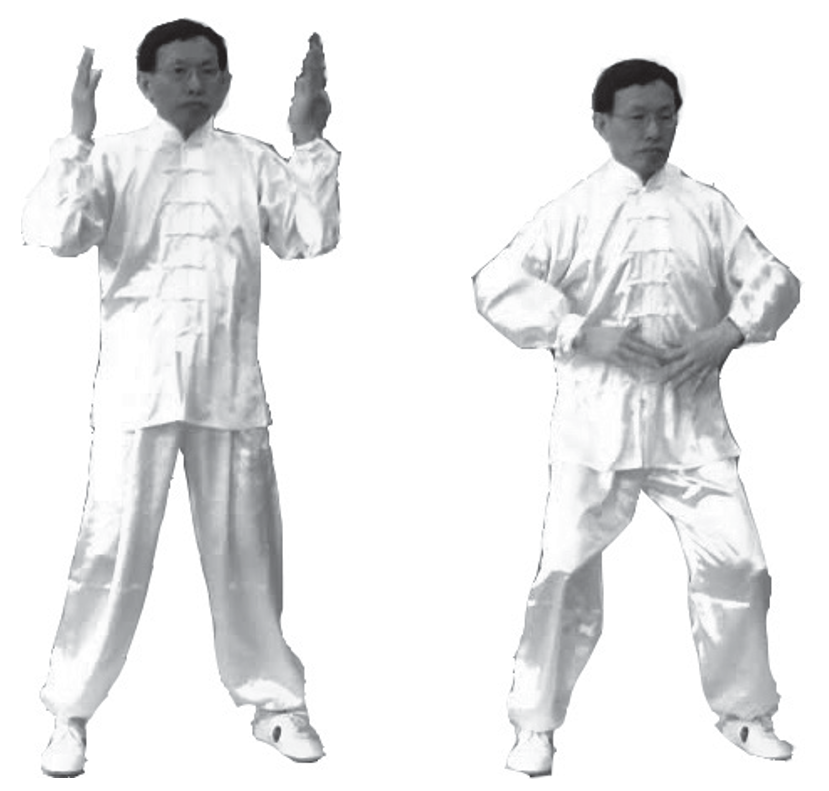
1. Beginning Posture: Stand naturally with feet shoulder-width apart. Knees slightly bent or straight. Arms hang naturally at the sides, palms facing backward. Eyes look straight ahead, without focusing on anything; ears are relaxed; lips are lightly closed, and the tongue touches the upper palate. Breathe naturally with abdominal breathing, relax the whole body. Clear your mind, and focus your intention on the Dantian. Stand still for 1 to 3 minutes (see image below).

2. Transitional Movement (Cheng Jie Shi): Also known as the starting and concluding movements. Transition from the beginning posture, turning the palms forward, visualize both hands lifting the earth’s energy upwards, as if holding a heavy ball, merging with the sky (left image). Then turn the palms downward, guiding the cosmic energy down through the crown, penetrating the skin and bones, nourishing the internal organs, and dispersing the turbid energy within the body, which is then absorbed into the earth (right image).

This movement is used at the beginning or end of each dynamic practice section and for transitions between movements. Its functions include activating the Qi mechanism, guiding Qi throughout the body, and absorbing the pure while expelling the turbid. When used as a concluding movement, guide the Qi down to the lower Dantian, pausing briefly with your intention, and then continue.
Functions and Uses
1. The beginning posture serves as a preparatory position before starting the dynamic practice and as a process of calming the mind and gathering Qi for one to two minutes after completing the dynamic practice; another function of the beginning posture is to be used after each movement or pair of movements, which is relatively brief.
2. The transitional movement is used at the beginning and end of each section. It may also be used during transitions between movements.
First Movement: Heaven, Earth, and Humanity
Key Points of Operation
1. Starting Movement: Same as the “Beginning Posture”.
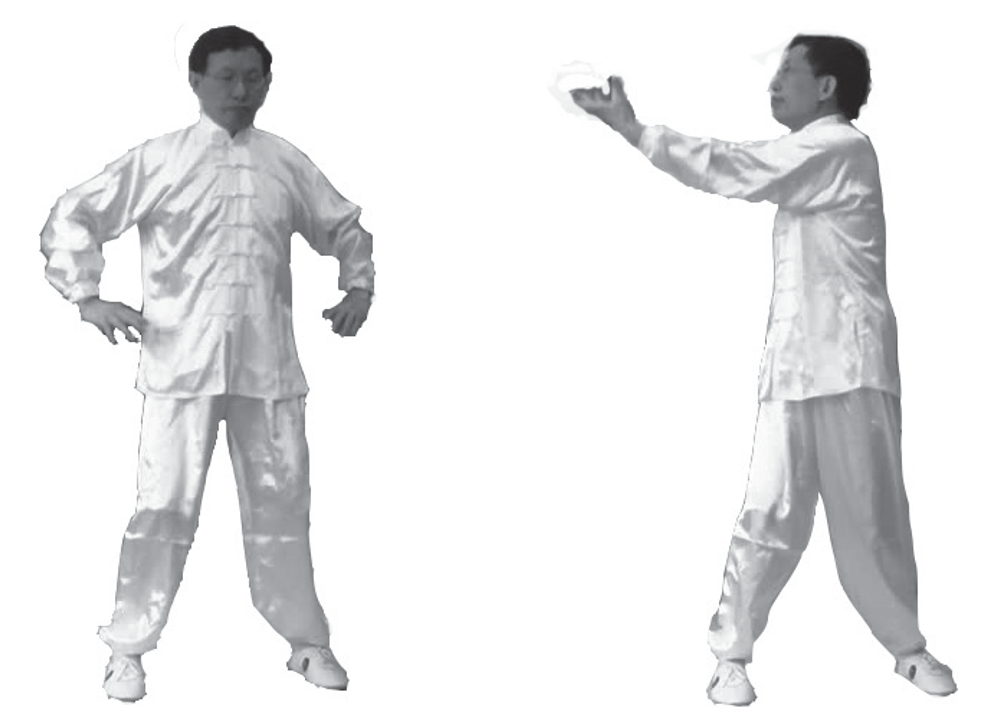
2. Pressing the Floating Ball: Spread your fingers, with the tiger mouth facing inward, gently lift from the sides of the body to the outer sides of the hips, then gently press down as if pressing a floating ball (left image).
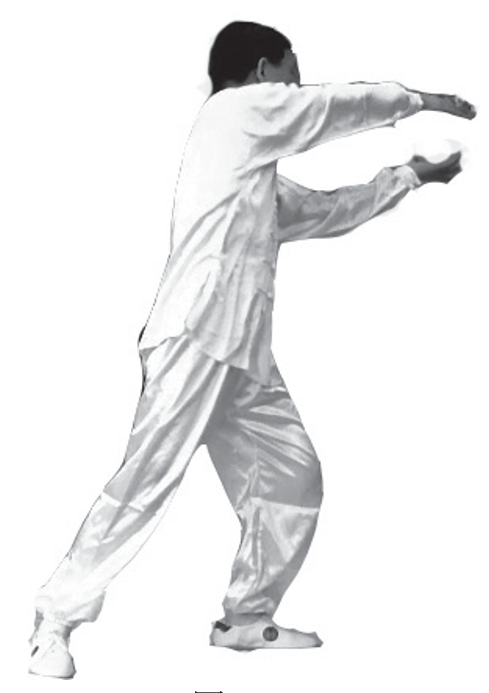
3. Fishing for the Moon at the Bottom of the Sea (Left): First, use the left hand to lift from the lower left to the upper right, turning the body to the right front, while the right hand presses the floating ball at the outer side of the right hip (right image).

4. Bathing in Vital Energy (Left): The left hand guides Qi down the midline of the body, visualizing the pure energy penetrating the skin, bones, and nourishing the internal organs. The turbid energy is directed into the depths of the earth. At the same time, the body turns to the left, with both arms moving in accordance, the left hand moving to the right rear and the right hand to the left front (left image).

5. Sunlight on the Heel and Toe (Left): Both hands in a ball-pressing position, the left hand presses down on the right heel. The right hand presses down on the left toe, lifting and then pressing (left image).
6. Right Turn and Guiding Qi: The right hand is flat, turning the body to the right side, guiding Qi from left to right with the right hand, while the left hand relaxes and presses the floating ball at the outer side of the left hip (right image).
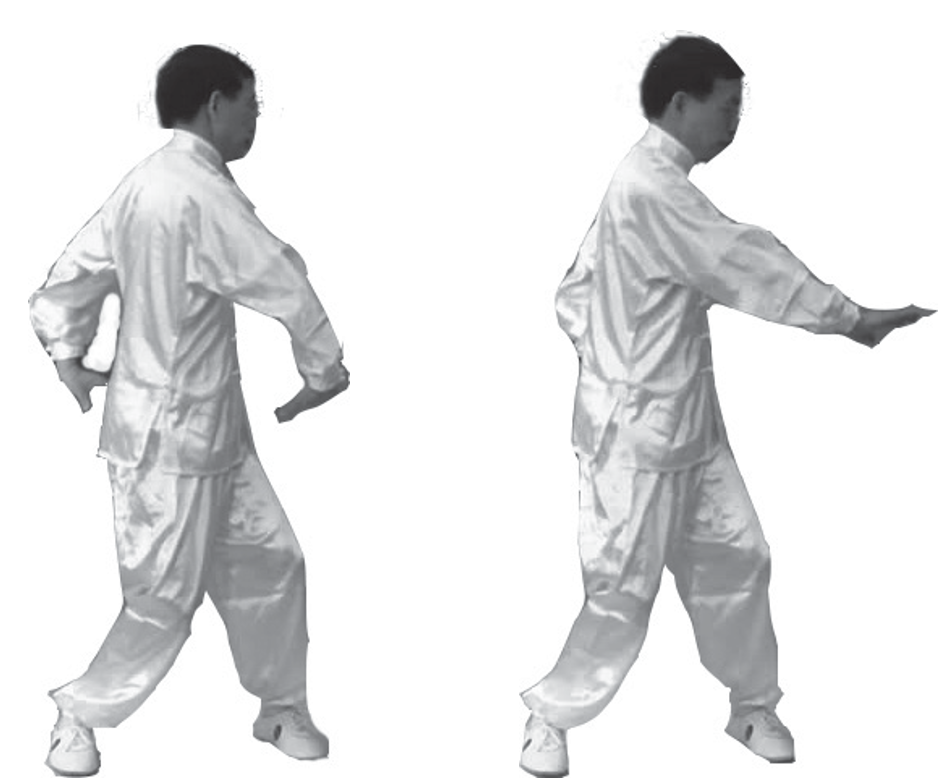
7. Fishing for the Moon at the Bottom of the Sea (Right): The right side movement is the same as the left side, but in the opposite direction. The left hand presses the floating ball at the outer side of the left hip (left image).
8. Bathing in Vital Energy (Right): The right hand guides Qi down the midline of the body, visualizing the pure energy penetrating the skin, bones, and nourishing the internal organs. The turbid energy is directed into the depths of the earth. At the same time, the body turns to the right side (right image).
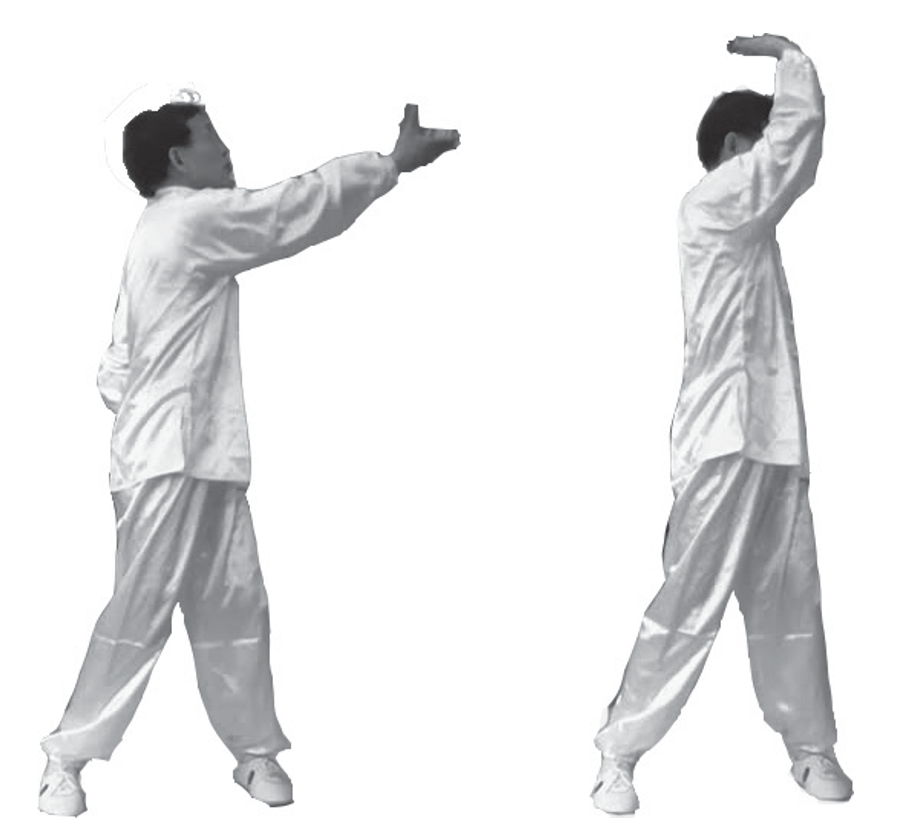

9. Sunlight on the Heel and Toe (Right): The right side movement is the same as the left side, but with the left and right switched, the right hand presses down on the left heel. The left hand presses down on the right toe, lifting and then pressing (left image).
10. Body Rotation and Bathing: Both palms slightly raised, while both arms turn to face forward. Perform the “Transitional Movement” (right image).
11. Fishing for the Moon at the Bottom of the Sea (Right): Start from the right side to perform Fishing for the Moon at the Bottom of the Sea. Repeat the actions from 3 to 10, but in the opposite direction. Starting from the left and right counts as one complete practice, and the entire movement is repeated three times.
12. “Transitional Movement” or Concluding Movement.
Overview of Functions
The main function of this section can be summarized as “Moving the palms left and right to connect the six harmonies,” with functions to regulate Yin and Yang, guide Qi downwards, and absorb the pure while expelling the turbid.
Second Movement: Spleen and Stomach Function
Key Points of Operation
1. “Starting Movement” or connecting to the previous concluding movement.
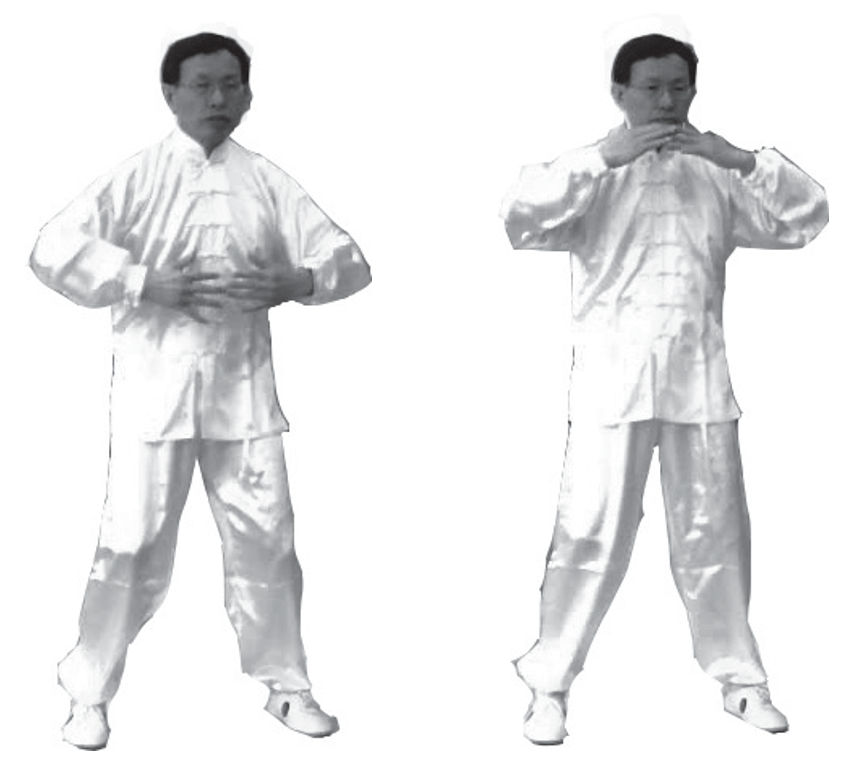
2. Qi Filling the Zhongwan: Both hands expand outward and upward, holding Qi to fill the Zhongwan point or stomach area, penetrating the stomach and pancreas, and through the back (penetrating the abdomen to the back). Repeat the opening and closing three times. The knees move in accordance with the arms (left image).
3. Descending Qi and Harmonizing the Stomach: Both hands descend outward and then come together at the Chengjiang point. Starting from the Chengjiang point, guide Qi down through the Chengjiang, Shanzhong, Jiuwei, Zhongwan, or through the chin, esophagus, and stomach, continuing downwards, visualizing the turbid Qi in the stomach going deep into the earth. Repeat this three times. The knees move in accordance with the palms (right image).

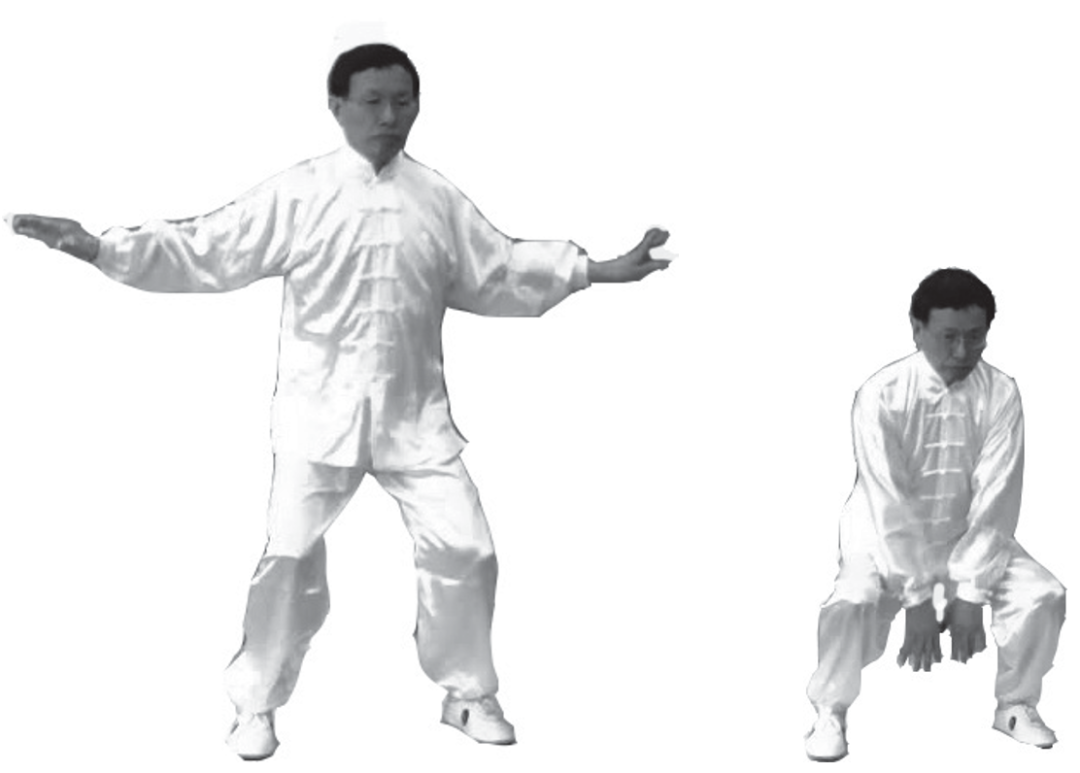
4. Caressing Qi and Connecting to the Earth: Both arms open outward, elbows slightly bent, floating up from the sides of the body, then squatting down, both hands pressing down lightly as if pressing a floating ball, repeating this three times, gradually lowering the body. The knees move in accordance with the arms. On the third time, bring both hands together between the legs, palms facing backward and outward (left image).
5. Rising Qi and Moving the Spleen: The descending Qi rebounds upwards, lifting both hands along the Spleen Meridian (inner thigh) upwards, while the knees slowly straighten, bringing the hands to the lower abdomen near the pubic bone (right image).

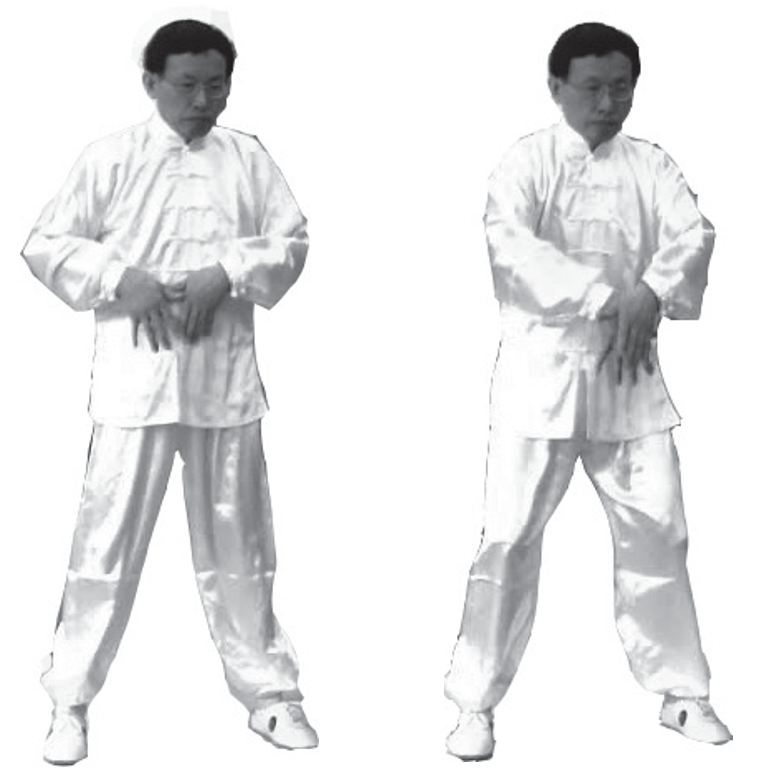
6. Qi Solidifying the Lower Yuan: Guide Qi along the lower abdomen (Dantian) in a clockwise and counterclockwise direction for three circles, while the knees move in accordance with the palms (left image).
7. Qi Opening and Closing: Both palms overlap in the same direction, palms facing the lower Dantian (lower abdomen), with the left hand on the outside and the right hand on the inside, about a fist’s distance apart. Then, guide Qi into the lower abdomen three times, penetrating the lower Dantian and through the waist and sacrum. At the same time, the knees move in accordance with the palms (right image).

8. Qi Moistening the Flower Pool: Both hands open flat, moving up the front of the abdomen to the upper chest, turning the palms inward and outward, opening and closing three times at the Jaw and Great Welcome points (salivary glands, base of the tongue, etc.) The knees move in accordance with the palms (left image).
9. Moistening the Lower Dantian: Both palms move down the midline, and if there is more saliva, it can be swallowed in portions, visualizing the precious liquid entering the lower Dantian, pausing briefly with your intention. Continue guiding the turbid Qi down into the depths of the earth (right image).

10. Connect to the “Transitional Movement”.
11. Repeat the actions from 2 to 9 three times.
12. “Transitional Movement” or “Concluding Movement”.
Overview of Functions
The main function of this section can be summarized as “Spleen Earth transforming food and water,” with functions to descend Qi and harmonize the stomach, and to transform the Spleen Earth, suitable for gastrointestinal diseases and various diseases related to deficiency and fatigue of the lower Yuan.
Third Movement: Lung and Large Intestine Function
Key Points of Operation
1. “Starting Movement” or connecting to the previous concluding movement.
2. Left Side Ball Lifting: Turn the body to the left side, while the left foot turns to the left side, forming a left bow stance, with both arms covering and lifting (right arm on top, left arm underneath), forming a left side ball-holding position (left image).

3. Qi Moving to the Lungs and Intestines: The left hand is in a Yin palm position, extending outward, while the right hand moves along the outer side of the left arm’s Yang Meridian up to the left shoulder. The left foot returns, and the body turns to face forward; the left hand becomes a Yang palm, bending the elbow to gather Qi to the center of the chest, while the right hand’s palm faces inward, continuing from the left shoulder, left chest, left abdomen, to the center of the lower abdomen, turning the body to face forward (left and right images) (can be coordinated with inhalation).
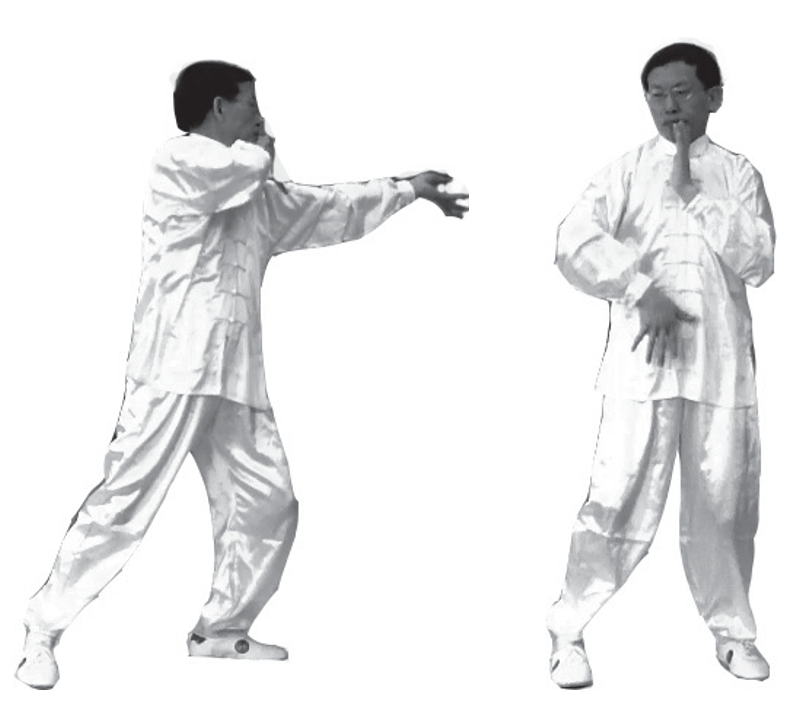

4. Expelling Turbid and Clearing the Lungs: Turn the body to the right side, with the right foot turned outward, forming a right bow stance. The right hand’s palm moves along the right lower abdomen, right chest to the front of the right shoulder, extending the right arm outward, while the left palm moves along the right shoulder and inner side of the right arm’s Yin Meridian outward, with the body slightly turning to the right, and the right hand retracting slightly (can be coordinated with exhalation).
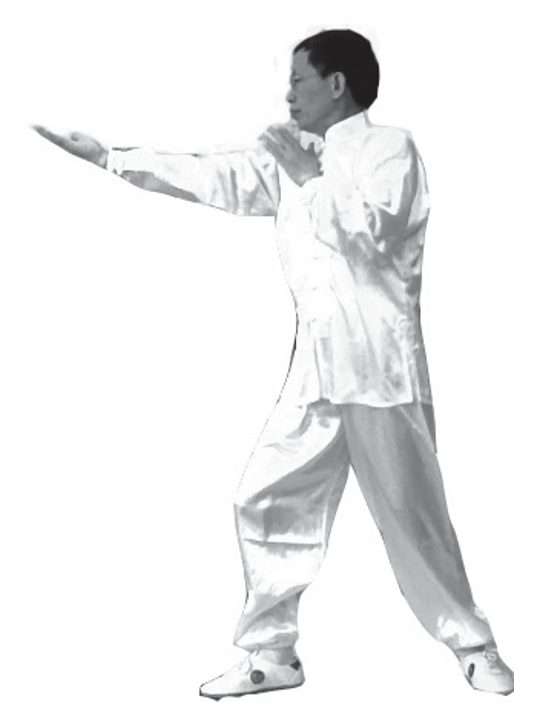

6. Yin Palm, right arm extended, while the left hand moves along the outer side of the right arm’s Yang Meridian up to the right shoulder. The right foot returns, and the body turns to face forward; the right hand becomes a Yang palm, bending the elbow to gather Qi to the center of the chest, while the left hand’s palm faces inward, continuing from the right shoulder, right chest, right abdomen, to the center of the lower abdomen, turning the body to face forward (left and right images) (can be coordinated with inhalation).
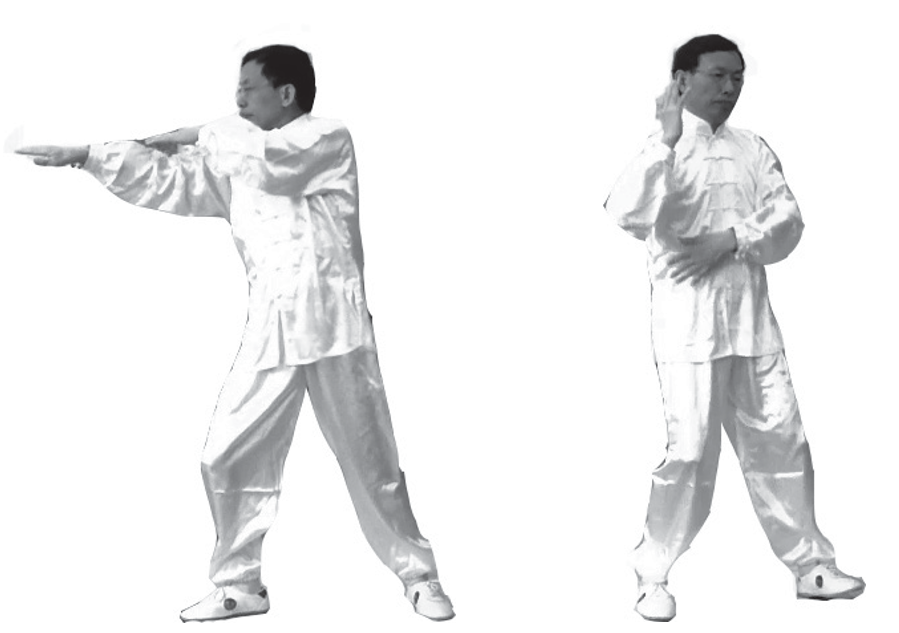

7. Continue turning the body to the left side, with the left foot turned outward, forming a left bow stance. The left hand’s palm moves along the left lower abdomen, left chest to the front of the left shoulder, extending the left arm outward, while the right palm moves along the inner side of the left arm’s Yin Meridian outward, continuing to turn the body to the left, with the left hand retracting slightly (left image) (can be coordinated with exhalation).
8. When both hands are opposite each other, both elbows begin to push outward while the left foot returns to its original position, turning the body to face forward (right image) (can be coordinated with inhalation).
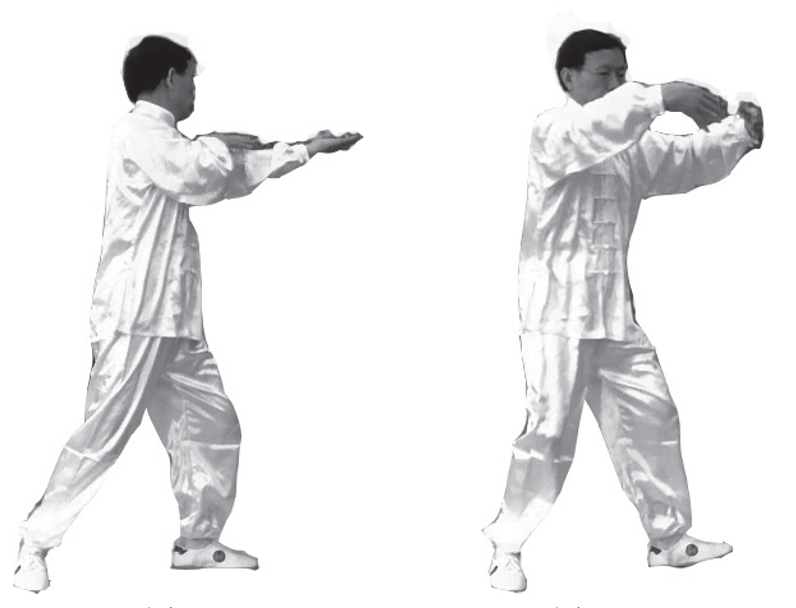

9. Qi Regulating the Lungs: Both palms or both Laogong points face the lungs, guiding Qi into the lungs, reaching the back, opening and closing three times, while the knees move in accordance with the arms (left image) (can be coordinated with breathing).
10. Qi Penetrating the Yingxiang: At the end of the third opening and closing, turn the palms downward, inward, and outward, with fingers pointing up, both Laogong points facing the Yingxiang points on both sides, guiding Qi three times, penetrating the face and jaw, while the knees move in accordance with the palms (right image) (can be coordinated with breathing).
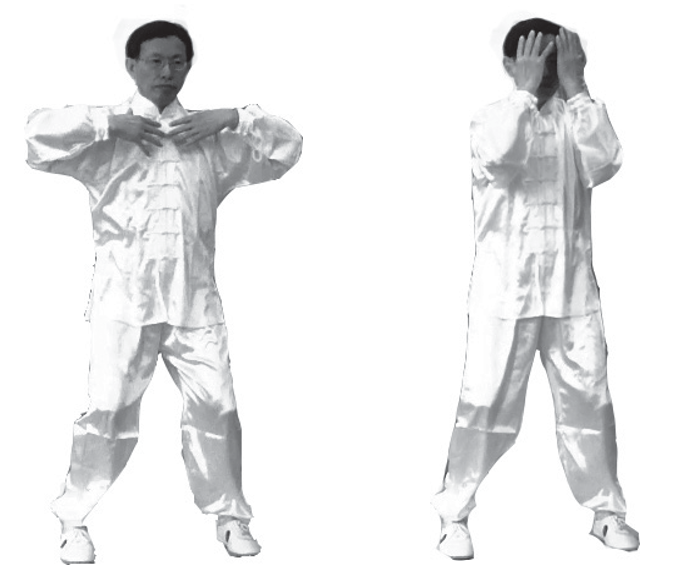

10. Qi Sinking to the Lower Dantian: Turn the palms downward, guiding Qi along the front of the body down to the lower Dantian, pausing briefly with your intention (image below).

Overview of Functions
The main function of this section can be summarized as “Lung Metal expelling turbid and receiving pure Qi,” with functions to expel turbid and receive pure, open the chest and regulate Qi, suitable for respiratory system, chest diseases, and large intestine diseases.
Editor | Meng Bofei
Reviewed by | Yang Ling

Kuaishou Account
1484394819

Douyin Account
CAMQigong

Bilibili Account
516340612

