The phlegm-damp constitution refers to a physical state characterized by the accumulation of phlegm and dampness in the body, leading to a tendency towards obesity and other manifestations such as heaviness and turbidity.This constitution is a normal physiological state, not pathological nor entirely healthy, placing individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution in a sub-healthy state between disease and health.The formation of phlegm-damp constitution is related to factors such as invasion by external pathogens, congenital endowment, irregular diet, and emotional disturbances. If early intervention is applied to the phlegm-damp constitution, it can effectively reduce the incidence of related diseases; if not adjusted in time, it may easily lead to conditions such as diabetes, stroke, dizziness, cough and asthma, gout, hypertension, and coronary heart disease.Characteristics of Phlegm-Damp ConstitutionIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have reduced metabolic capacity, leading to the accumulation of “phlegm” and “dampness” in the body, resulting in internal “garbage accumulation” and external manifestations such as obesity, sticky sweating, and snoring during sleep.There are five main characteristics of phlegm-damp constitution:1Body ShapeIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution typically exhibit abdominal obesity, characterized by soft and loose fat in the abdomen. This is due to the accumulation of “garbage” in the body, which manifests as oily skin on the face and obesity in body shape. Many individuals with this constitution are abdominally obese, with a significant amount of soft and loose fat in the abdomen.
If early intervention is applied to the phlegm-damp constitution, it can effectively reduce the incidence of related diseases; if not adjusted in time, it may easily lead to conditions such as diabetes, stroke, dizziness, cough and asthma, gout, hypertension, and coronary heart disease.Characteristics of Phlegm-Damp ConstitutionIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have reduced metabolic capacity, leading to the accumulation of “phlegm” and “dampness” in the body, resulting in internal “garbage accumulation” and external manifestations such as obesity, sticky sweating, and snoring during sleep.There are five main characteristics of phlegm-damp constitution:1Body ShapeIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution typically exhibit abdominal obesity, characterized by soft and loose fat in the abdomen. This is due to the accumulation of “garbage” in the body, which manifests as oily skin on the face and obesity in body shape. Many individuals with this constitution are abdominally obese, with a significant amount of soft and loose fat in the abdomen. Due to the high levels of phlegm and dampness in the body, individuals with this constitution may feel uncomfortable and find it difficult to adapt during external damp and rainy weather (such as the plum rain season in the south).2DietIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have a good appetite and enjoy eating, especially preferring fatty, sweet, and oily foods. These foods turn into greasy fats that accumulate in the body, and the body cannot clear the “garbage” quickly enough, leading to further accumulation.3SleepIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are prone to loud snoring during sleep, which can be described as “thunderous”. Particularly, those weighing over 90 kg may experience breathing difficulties during sleep, known medically as “obstructive sleep apnea syndrome”, which can be fatal for many.
Due to the high levels of phlegm and dampness in the body, individuals with this constitution may feel uncomfortable and find it difficult to adapt during external damp and rainy weather (such as the plum rain season in the south).2DietIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have a good appetite and enjoy eating, especially preferring fatty, sweet, and oily foods. These foods turn into greasy fats that accumulate in the body, and the body cannot clear the “garbage” quickly enough, leading to further accumulation.3SleepIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are prone to loud snoring during sleep, which can be described as “thunderous”. Particularly, those weighing over 90 kg may experience breathing difficulties during sleep, known medically as “obstructive sleep apnea syndrome”, which can be fatal for many.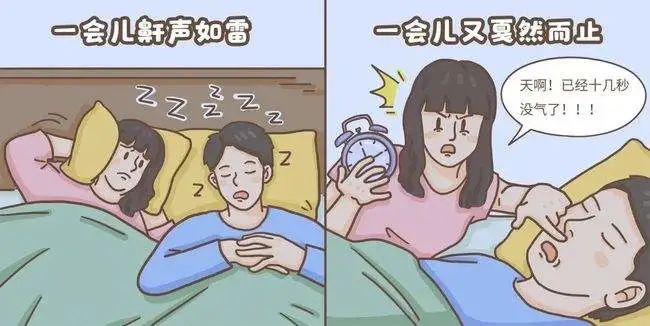 Additionally, individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution often have poor spleen and stomach function, leading to drowsiness after meals. It can be said that they tend to feel sleepy and love to sleep, but once asleep, they snore and experience sleep apnea, which is quite concerning.4Psychological StateIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution generally have a mild temperament, are not hasty in their actions, and are relatively stable in their dealings with others, exhibiting a good temper. A phrase that vividly summarizes their personality traits is “steady as Mount Tai”.5ExcretionIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution tend to sweat in a sticky manner, and their stools are often loose and unformed. Some may also experience constipation due to the obstruction of gastrointestinal motility by phlegm and dampness.How to Adjust Phlegm-Damp ConstitutionFor those with a phlegm-damp constitution, the main adjustment method is to transform phlegm and eliminate dampness, while also strengthening the spleen and assisting in transportation.
Additionally, individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution often have poor spleen and stomach function, leading to drowsiness after meals. It can be said that they tend to feel sleepy and love to sleep, but once asleep, they snore and experience sleep apnea, which is quite concerning.4Psychological StateIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution generally have a mild temperament, are not hasty in their actions, and are relatively stable in their dealings with others, exhibiting a good temper. A phrase that vividly summarizes their personality traits is “steady as Mount Tai”.5ExcretionIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution tend to sweat in a sticky manner, and their stools are often loose and unformed. Some may also experience constipation due to the obstruction of gastrointestinal motility by phlegm and dampness.How to Adjust Phlegm-Damp ConstitutionFor those with a phlegm-damp constitution, the main adjustment method is to transform phlegm and eliminate dampness, while also strengthening the spleen and assisting in transportation.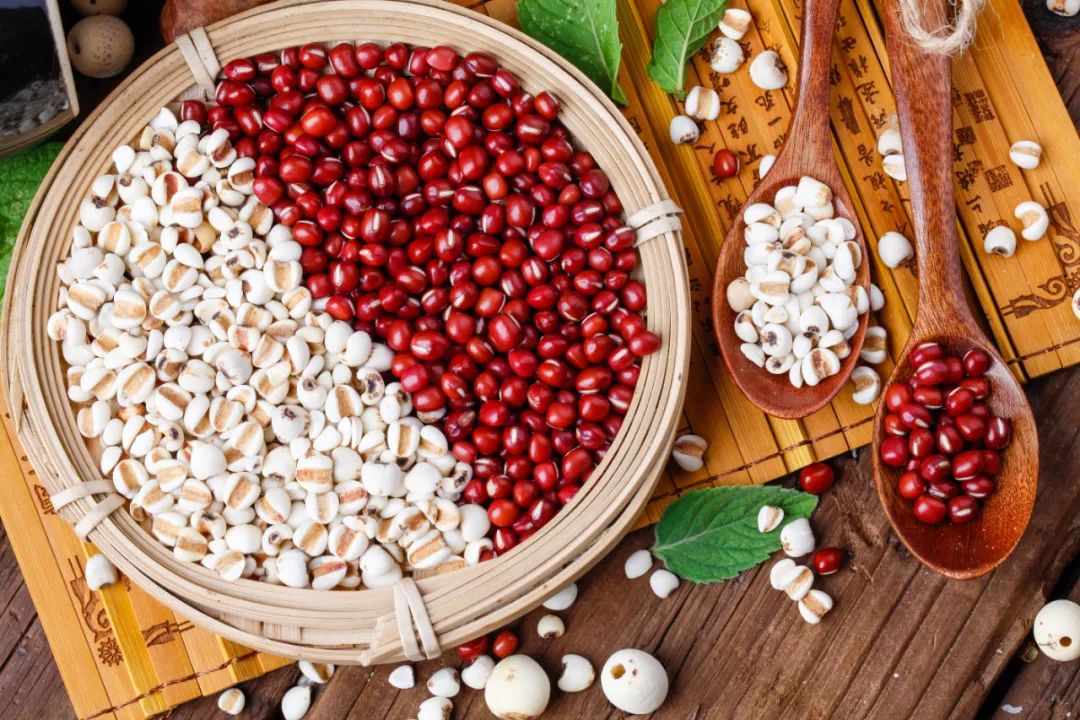 1Dietary AdjustmentsIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should choose foods that strengthen the spleen and assist in transportation, and eliminate dampness and transform phlegm. They should avoid fatty, sweet, oily, and sticky foods. Meals should not be too full; eating until 70% full is recommended, and binge eating and eating too quickly should be avoided.Recommended aquatic products include carp, crucian carp, bass, kelp, jellyfish, and clams. Grains and legumes such as lentils, coix seeds, red adzuki beans, and yam are also beneficial, as well as fruits and vegetables like winter melon, lotus leaves, white radish, ginger, shepherd’s purse, and nori.Coix Seed: Cool in nature, sweet and bland in taste, entering the spleen, lung, and kidney meridians, it has the effects of promoting urination, strengthening the spleen, dispelling dampness, and clearing heat and pus. Due to its mild action and slight cooling nature that does not harm the stomach, it is suitable for daily consumption by those with a phlegm-damp constitution.Carp: Sweet in taste, neutral in nature, entering the spleen and kidney meridians, it has the effects of tonifying the spleen and stomach, promoting urination, and reducing swelling. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states: “Carp is particularly effective for promoting urination, thus alleviating swelling, jaundice, beriberi, cough, and damp-heat diseases, cooking it helps to clear water retention and promote urination.” It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution.Lentils: Sweet in taste, neutral in nature, entering the spleen and stomach meridians, it has the effects of strengthening the spleen and stomach, dispelling summer heat, and transforming dampness. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states: “Hard-shelled white lentils are full, white with a slight yellow hue, with a fragrant smell, and their nature is warm and neutral, suitable for the spleen.” It enters the Taiyin qi division, unblocking the three burners, and can transform clarity and descend turbidity, thus specifically treating diseases of the middle palace, dispelling summer heat and dampness, and detoxifying. The soft-shelled and black varieties are slightly cool but can also be consumed to regulate the spleen and stomach.” It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who experience abdominal distension.
1Dietary AdjustmentsIndividuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should choose foods that strengthen the spleen and assist in transportation, and eliminate dampness and transform phlegm. They should avoid fatty, sweet, oily, and sticky foods. Meals should not be too full; eating until 70% full is recommended, and binge eating and eating too quickly should be avoided.Recommended aquatic products include carp, crucian carp, bass, kelp, jellyfish, and clams. Grains and legumes such as lentils, coix seeds, red adzuki beans, and yam are also beneficial, as well as fruits and vegetables like winter melon, lotus leaves, white radish, ginger, shepherd’s purse, and nori.Coix Seed: Cool in nature, sweet and bland in taste, entering the spleen, lung, and kidney meridians, it has the effects of promoting urination, strengthening the spleen, dispelling dampness, and clearing heat and pus. Due to its mild action and slight cooling nature that does not harm the stomach, it is suitable for daily consumption by those with a phlegm-damp constitution.Carp: Sweet in taste, neutral in nature, entering the spleen and kidney meridians, it has the effects of tonifying the spleen and stomach, promoting urination, and reducing swelling. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states: “Carp is particularly effective for promoting urination, thus alleviating swelling, jaundice, beriberi, cough, and damp-heat diseases, cooking it helps to clear water retention and promote urination.” It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution.Lentils: Sweet in taste, neutral in nature, entering the spleen and stomach meridians, it has the effects of strengthening the spleen and stomach, dispelling summer heat, and transforming dampness. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states: “Hard-shelled white lentils are full, white with a slight yellow hue, with a fragrant smell, and their nature is warm and neutral, suitable for the spleen.” It enters the Taiyin qi division, unblocking the three burners, and can transform clarity and descend turbidity, thus specifically treating diseases of the middle palace, dispelling summer heat and dampness, and detoxifying. The soft-shelled and black varieties are slightly cool but can also be consumed to regulate the spleen and stomach.” It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who experience abdominal distension. Red Adzuki Bean: Neutral in nature, sweet and sour in taste, entering the heart and liver meridians, it has the effects of promoting urination, reducing swelling, and detoxifying. Modern research has shown that red adzuki beans contain saponins, which have laxative, diuretic, and swelling-reducing effects, and can detoxify and relieve intoxication. They are suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution and those prone to edema.White Radish: Cool in nature, sweet in taste, entering the lung and stomach meridians, it has the effects of promoting digestion, transforming accumulation, clearing heat and phlegm, and regulating qi. Modern studies have found that regular consumption can lower blood lipids and blood pressure, aiding in weight loss. It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who are obese and have excessive phlegm.Winter Melon: Sweet and bland in taste, cool in nature, entering the lung, large intestine, and bladder meridians, it functions to promote urination, reduce swelling, transform phlegm, and lower lipids. The “Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica” states that “long-term consumption can lighten the body and resist aging.”
Red Adzuki Bean: Neutral in nature, sweet and sour in taste, entering the heart and liver meridians, it has the effects of promoting urination, reducing swelling, and detoxifying. Modern research has shown that red adzuki beans contain saponins, which have laxative, diuretic, and swelling-reducing effects, and can detoxify and relieve intoxication. They are suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution and those prone to edema.White Radish: Cool in nature, sweet in taste, entering the lung and stomach meridians, it has the effects of promoting digestion, transforming accumulation, clearing heat and phlegm, and regulating qi. Modern studies have found that regular consumption can lower blood lipids and blood pressure, aiding in weight loss. It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who are obese and have excessive phlegm.Winter Melon: Sweet and bland in taste, cool in nature, entering the lung, large intestine, and bladder meridians, it functions to promote urination, reduce swelling, transform phlegm, and lower lipids. The “Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica” states that “long-term consumption can lighten the body and resist aging.”
In the Tang Dynasty, dietary therapy expert Meng Shen believed that winter melon can “benefit qi and resist aging” and pointed out that “to achieve a slim and healthy body, one should consume it regularly; if one desires to gain weight, then one should avoid it.” This indicates that winter melon not only has anti-aging effects but also aids in weight loss. It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who experience eyelid swelling and obesity.

Nori: Sweet and salty in taste, cold in nature, entering the lung meridian, it has the effects of transforming phlegm, softening hardness, clearing heat, and promoting urination. It is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution and those without disease to strengthen the body.Lotus Leaf: Bitter and astringent in taste, neutral in nature, entering the heart, liver, and spleen meridians, it has the effects of clearing heat, eliminating dampness, and uplifting clear yang. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” records that lotus leaf “uplifts yang qi and reduces fat and weight.” Because it can eliminate dampness, uplift clarity, and reduce lipids, it is suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution who have a tendency towards high blood lipids.2Physical ExerciseExercise should be sustained. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution tend to be overweight and easily fatigued, so they should gradually increase their exercise based on their specific conditions and maintain a long-term exercise regimen. Physical fitness methods suitable for simple obesity are also suitable for those with a phlegm-damp constitution, such as walking, jogging, playing table tennis, badminton, tennis, swimming, practicing martial arts, and various forms of dance that suit them. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should enhance their metabolic processes and engage in prolonged aerobic exercise to gradually firm and tighten their loose flesh.Moderate-intensity, longer-duration full-body exercises are considered aerobic exercise.Generally, warm-up for about 15 minutes, then gradually increase the intensity, with an optimal exercise duration of 1 hour.Exercise should be done between 2:00 PM and 4:00 PM, when yang qi is at its peak, and the exercise environment should be warm and pleasant. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution typically have higher body weight, so they should pay attention to the rhythm of their exercise and gradually increase their training to ensure safety.For those with significantly high body weight and poor land-based exercise capacity, swimming is recommended. Swimming is an excellent full-body exercise and a great method for weight loss, and it is very effective for improving cardiovascular function.
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should enhance their metabolic processes and engage in prolonged aerobic exercise to gradually firm and tighten their loose flesh.Moderate-intensity, longer-duration full-body exercises are considered aerobic exercise.Generally, warm-up for about 15 minutes, then gradually increase the intensity, with an optimal exercise duration of 1 hour.Exercise should be done between 2:00 PM and 4:00 PM, when yang qi is at its peak, and the exercise environment should be warm and pleasant. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution typically have higher body weight, so they should pay attention to the rhythm of their exercise and gradually increase their training to ensure safety.For those with significantly high body weight and poor land-based exercise capacity, swimming is recommended. Swimming is an excellent full-body exercise and a great method for weight loss, and it is very effective for improving cardiovascular function. 3Mental RegulationMaintain a positive mindset, and uplifting music can invigorate. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have a mild temperament and are stable in their dealings, often good at enduring. However, due to the internal accumulation of phlegm-damp, which obstructs yang qi, they are prone to feelings of fatigue. Therefore, they should enhance their exercise, participate in social activities, and cultivate a wide range of interests and hobbies.They can also listen to some upbeat and invigorating music, such as Strauss’s waltz series, Bizet’s Carmen Overture, Radetzky March, and the Erhu piece “Horse Racing”.4Living AdjustmentsAvoid dampness in daily life. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are characterized by excessive dampness and should not stay in damp environments for long. During rainy seasons, they should be cautious to avoid dampness invasion, and in damp and cold weather, they should reduce outdoor activities to avoid getting cold and wet. Dampness is heavy and turbid, easily obstructing qi and harming yang qi.
3Mental RegulationMaintain a positive mindset, and uplifting music can invigorate. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution have a mild temperament and are stable in their dealings, often good at enduring. However, due to the internal accumulation of phlegm-damp, which obstructs yang qi, they are prone to feelings of fatigue. Therefore, they should enhance their exercise, participate in social activities, and cultivate a wide range of interests and hobbies.They can also listen to some upbeat and invigorating music, such as Strauss’s waltz series, Bizet’s Carmen Overture, Radetzky March, and the Erhu piece “Horse Racing”.4Living AdjustmentsAvoid dampness in daily life. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are characterized by excessive dampness and should not stay in damp environments for long. During rainy seasons, they should be cautious to avoid dampness invasion, and in damp and cold weather, they should reduce outdoor activities to avoid getting cold and wet. Dampness is heavy and turbid, easily obstructing qi and harming yang qi. Therefore, the living environment should be warm and dry, rather than cold and damp. Clothing should be breathable to disperse dampness, primarily made from natural fibers such as cotton, linen, and silk, which facilitate sweat evaporation and eliminate internal dampness. At the same time, attention should be paid to warmth. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should frequently take warm baths, to the extent that the skin turns slightly red and they sweat all over.Those with a phlegm-damp constitution tend to be sleepy, so they should appropriately reduce sleep time, avoid excessive comfort, and not be overly attached to the bed. At night, the pillow should not be too high to prevent worsening snoring; they should engage in more outdoor activities to activate bodily functions.Encourage individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution to participate in group travel, hiking, and other activities to increase outdoor exercise and promote yang qi and qi circulation. They should also regularly monitor their blood sugar, blood lipids, and blood pressure.5Acupuncture and MassageSelected Points: Fenglong (Stomach 40), Zusanli (Stomach 36).Fenglong is located at the midpoint of the line connecting the outer knee eye (Xiyan) and the outer ankle tip, 2 horizontal finger widths lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. The point can be accessed while sitting with the knee bent or lying supine.Zusanli is located 4 horizontal finger widths below the outer knee eye, one finger width lateral to the edge of the tibia. The point can be accessed while sitting with the knee bent.Effects: Fenglong is a point on the stomach meridian that connects with the spleen meridian, capable of regulating the spleen and stomach, and is a key point for transforming phlegm, with effects of eliminating dampness and phlegm. Zusanli is the lower he-sea point of the stomach, which has the effects of tonifying the spleen and stomach, and strengthening the spleen to transform phlegm.
Therefore, the living environment should be warm and dry, rather than cold and damp. Clothing should be breathable to disperse dampness, primarily made from natural fibers such as cotton, linen, and silk, which facilitate sweat evaporation and eliminate internal dampness. At the same time, attention should be paid to warmth. Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution should frequently take warm baths, to the extent that the skin turns slightly red and they sweat all over.Those with a phlegm-damp constitution tend to be sleepy, so they should appropriately reduce sleep time, avoid excessive comfort, and not be overly attached to the bed. At night, the pillow should not be too high to prevent worsening snoring; they should engage in more outdoor activities to activate bodily functions.Encourage individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution to participate in group travel, hiking, and other activities to increase outdoor exercise and promote yang qi and qi circulation. They should also regularly monitor their blood sugar, blood lipids, and blood pressure.5Acupuncture and MassageSelected Points: Fenglong (Stomach 40), Zusanli (Stomach 36).Fenglong is located at the midpoint of the line connecting the outer knee eye (Xiyan) and the outer ankle tip, 2 horizontal finger widths lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. The point can be accessed while sitting with the knee bent or lying supine.Zusanli is located 4 horizontal finger widths below the outer knee eye, one finger width lateral to the edge of the tibia. The point can be accessed while sitting with the knee bent.Effects: Fenglong is a point on the stomach meridian that connects with the spleen meridian, capable of regulating the spleen and stomach, and is a key point for transforming phlegm, with effects of eliminating dampness and phlegm. Zusanli is the lower he-sea point of the stomach, which has the effects of tonifying the spleen and stomach, and strengthening the spleen to transform phlegm.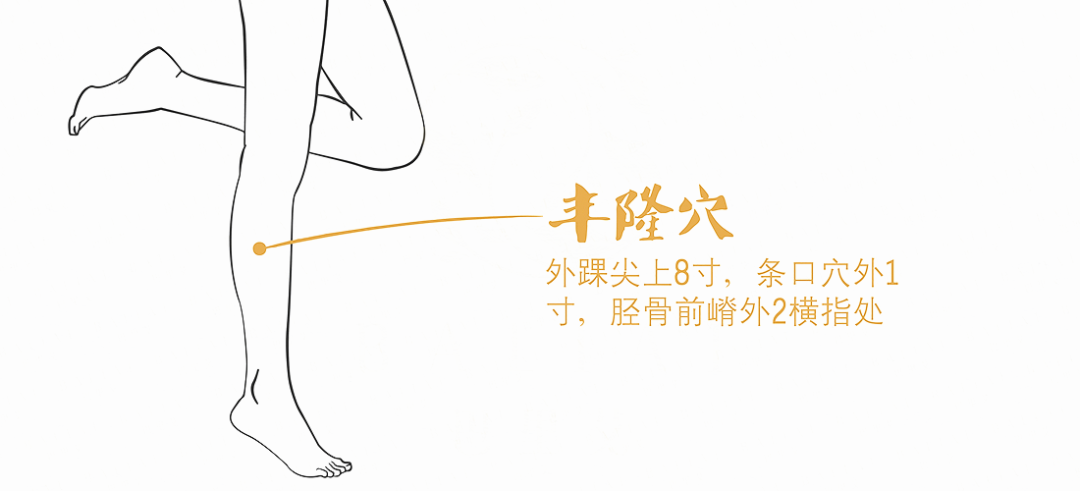 Procedure: Use gentle finger pressure, guasha, and moxibustion methods. Press each acupoint for 2-3 minutes, once or twice a day. Perform moxibustion on each point for 10 minutes, once a day.
Procedure: Use gentle finger pressure, guasha, and moxibustion methods. Press each acupoint for 2-3 minutes, once or twice a day. Perform moxibustion on each point for 10 minutes, once a day.

