Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) culture is a treasure of Chinese culture, with a long history and wide influence. From ancient times to the present, it has accumulated the wisdom and experience of countless physicians, forming its unique therapies and transmission methods, making outstanding contributions to the prosperity of the Chinese nation and human health.
1
What is Traditional Chinese Medicine?
In simple terms, TCM is traditional medicine from China, but the “Chinese” does not only refer to China, nor is it solely to distinguish it from Western medicine. “Chinese” embodies the doctrine of the mean, neutrality, and balance. TCM seeks harmony and follows the natural flow.
 TCM is based on the theories of Yin-Yang and the Five Elements, viewing the human body as a unity of Qi (vital energy), form, and spirit. It emphasizes that maintaining a balance of Yin and Yang is essential to prevent diseases.TCM employs the four diagnostic methods of “observation, listening, inquiry, and palpation” to determine the disease name, summarize the symptom patterns, and treat according to the principle of syndrome differentiation.Treatment methods include “sweating, vomiting, purging, digesting, warming, clearing, tonifying, and harmonizing.”Therapeutic modalities include Chinese herbs, acupuncture, tui na (Chinese therapeutic massage), cupping, qigong, and dietary therapy, aiming to achieve harmony of Yin and Yang for recovery.
TCM is based on the theories of Yin-Yang and the Five Elements, viewing the human body as a unity of Qi (vital energy), form, and spirit. It emphasizes that maintaining a balance of Yin and Yang is essential to prevent diseases.TCM employs the four diagnostic methods of “observation, listening, inquiry, and palpation” to determine the disease name, summarize the symptom patterns, and treat according to the principle of syndrome differentiation.Treatment methods include “sweating, vomiting, purging, digesting, warming, clearing, tonifying, and harmonizing.”Therapeutic modalities include Chinese herbs, acupuncture, tui na (Chinese therapeutic massage), cupping, qigong, and dietary therapy, aiming to achieve harmony of Yin and Yang for recovery.
2
The History of TCM
The history of TCM can be traced back thousands of years to ancient China, originating from the development of ancient Chinese culture and philosophy.

The earliest medical literature can be traced back to oracle bone inscriptions from the Shang Dynasty, which recorded diseases and treatment methods.
The Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon) is one of the classics of TCM, documenting the theories and practical experiences of ancient medicine.
During the Tang, Song, Ming, and Qing dynasties, TCM experienced a period of prosperity, with many important medical classics and schools emerging.
3
Basic Theories of TCM
The basic theories of TCM include the theories of Yin-Yang, the Five Elements, Qi and Blood, and the theory of organs and meridians.
The Yin-Yang theory states that everything in the universe has two opposing aspects, and maintaining a balance of Yin and Yang is essential for health.
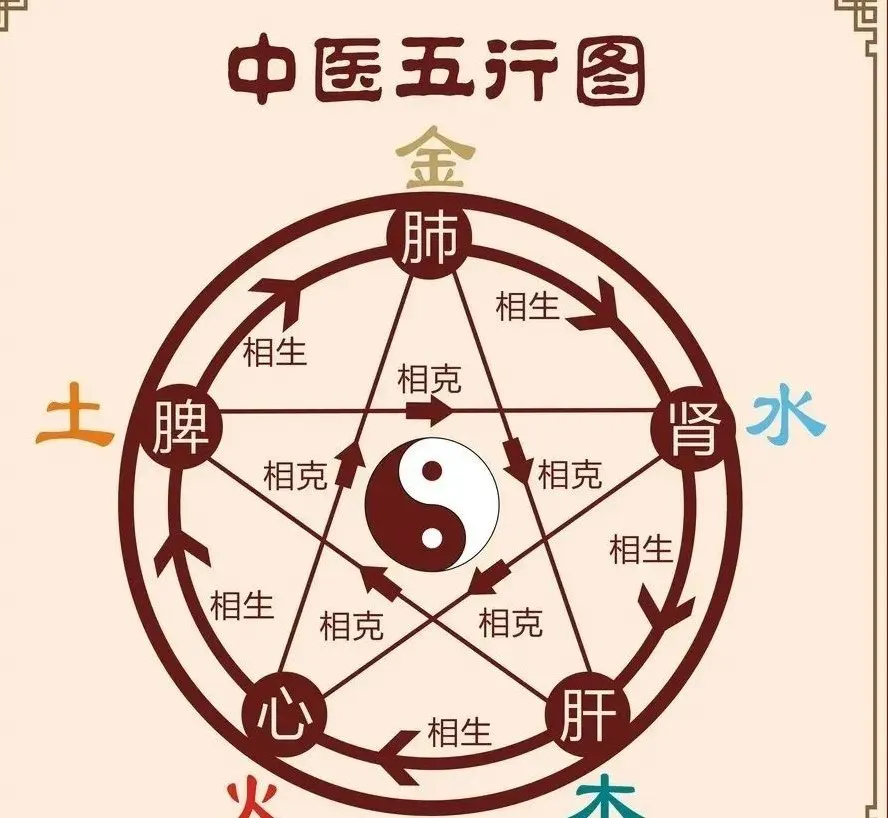 The Five Elements theory posits that all things in nature, including the human body, can be categorized into five elements (Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, Water), which influence health through their interrelationships.The Qi and Blood theory emphasizes the importance of the circulation and balance of Qi and Blood for health.The organ and meridian theory posits that the internal organs of the body are interconnected through meridians, and maintaining the function of the organs is essential for health.
The Five Elements theory posits that all things in nature, including the human body, can be categorized into five elements (Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, Water), which influence health through their interrelationships.The Qi and Blood theory emphasizes the importance of the circulation and balance of Qi and Blood for health.The organ and meridian theory posits that the internal organs of the body are interconnected through meridians, and maintaining the function of the organs is essential for health.
4
Common Chinese Herbs and Their Applications
Below are some common Chinese herbs, their effects and applications, along with a brief introduction to their materials, formulas, and pharmacological actions:
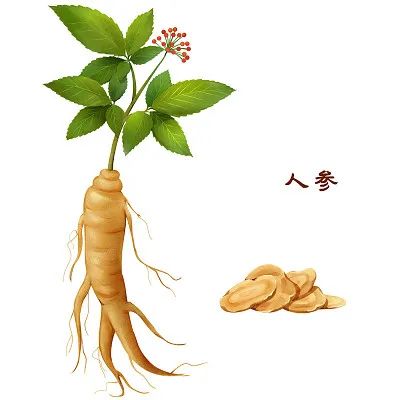
Ren Shen (Ginseng)
|
1 |
Effects and Applications: Tonifies Qi and nourishes Blood, enhances immunity, boosts energy, and combats fatigue. |
|
2 |
Related Formulas: Ginseng Chicken Soup, Ginseng Slices, Ginseng Pills, etc. |
|
3 |
Pharmacological Actions: Ginseng contains various active components, such as ginsenosides, which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-regulating effects. |

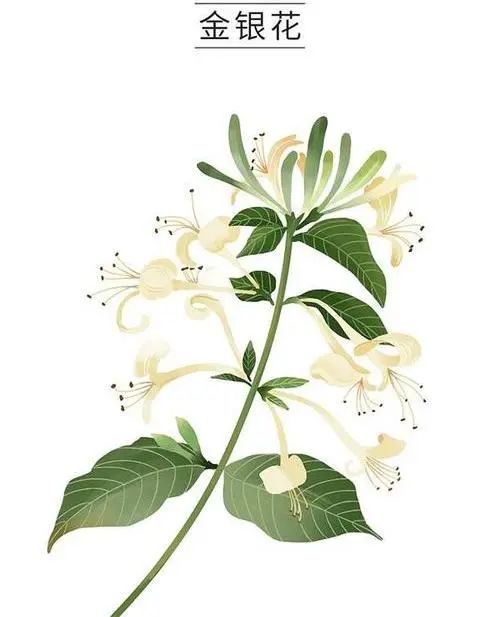
Jin Yin Hua (Honeysuckle)
|
1 |
Effects and Applications: Clears heat and detoxifies, disperses wind, used for colds, fevers, and pharyngitis. |
|
2 |
Related Formulas: Heat-clearing detoxifying oral liquid, Honeysuckle tea, Honeysuckle granules, etc. |
|
3 |
Pharmacological Actions: The active components in Honeysuckle have certain inhibitory effects on viruses, as well as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. |

The above are just brief introductions to the effects and applications of some common Chinese herbs. There are many types of Chinese herbs, each with its unique effects and application scope.When using Chinese herbs, one should follow the advice of a physician and pay attention to the dosage and side effects.

5
Health Preservation Methods in TCM
Health preservation methods in TCM emphasize the overall balance and self-regulation of individuals, including dietary therapy, massage, qigong, and various other methods. Here are some common TCM health preservation methods:
1. Dietary Therapy
According to TCM theory, a reasonable diet can help maintain the balance of Yin and Yang and the functions of the organs. However, it should be tailored to individuals, based on personal constitution, seasons, and needs to choose appropriate foods.
2. Massage
TCM massage utilizes manual techniques to stimulate the body’s acupoints and meridians, helping to relieve muscle fatigue, promote blood circulation, and relax the body and mind.Examples include tui na massage and meridian massage.
3. Qigong
Qigong adjusts breathing and movement to regulate the circulation of Qi and Blood and energy balance, which can improve the body’s immune function, enhance mental state, and increase physical strength.Common qigong practices include Tai Chi and health-preserving exercises.
4. Chinese Herbal Health Preservation
Chinese herbs play an important role in health preservation. Based on individual constitution characteristics and specific situations, practical TCM health preservation formulas and healthy recipes can be provided by professional physicians to promote health.


6
Therapies in TCM
The unique diagnostic and therapeutic methods in TCM are diverse, reflecting the holistic view and the principle of syndrome differentiation in TCM, while also embodying profound cultural connotations and unique therapeutic effects.
01
Acupuncture Therapy
① Definition: Acupuncture is an ancient health care therapy in China that directly stimulates the body’s acupoints using fine needles.
② Effects: Acupuncture can enhance bodily functions, unblock meridians, harmonize Yin and Yang, and support the body in preventing and treating diseases.
③ Characteristics: Acupuncture therapy diagnoses the cause of disease according to TCM diagnostic methods, identifies the key issues of the disease, differentiates the nature of the disease, and then formulates corresponding acupoint prescriptions for treatment.

02
Moxibustion Therapy
① Definition: Moxibustion involves burning moxa or other herbs on the body’s acupoints to warm and stimulate them, using the heat of the moxa and the medicinal properties to treat diseases.
② Effects:Moxibustion has effects such as unblocking meridians, promoting Qi and Blood circulation, dispelling dampness and cold, reducing swelling, and rescuing Yang.
③ Classification: Includes various types such as moxa stick moxibustion, moxa cone moxibustion, herbal roll moxibustion, and warm needle moxibustion.

03
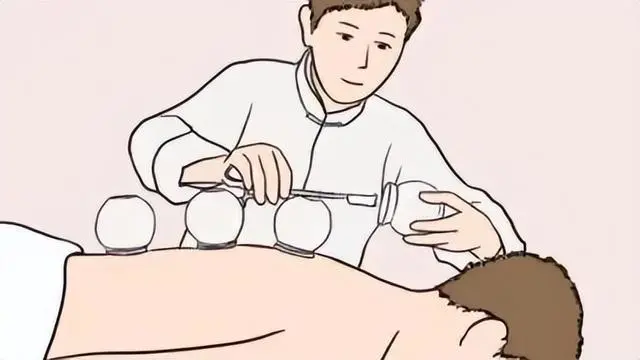
Cupping Therapy
① Definition: Cupping therapy uses cups as tools, creating a vacuum inside the cups through fire or suction, which are then applied to the skin over painful areas to treat diseases.
② Effects: Cupping promotes Qi and Blood circulation, dispels stagnation, warms the meridians, and relaxes the muscles.
③ Indications: Used for treating wind-cold-damp obstruction, dysmenorrhea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, etc.
04
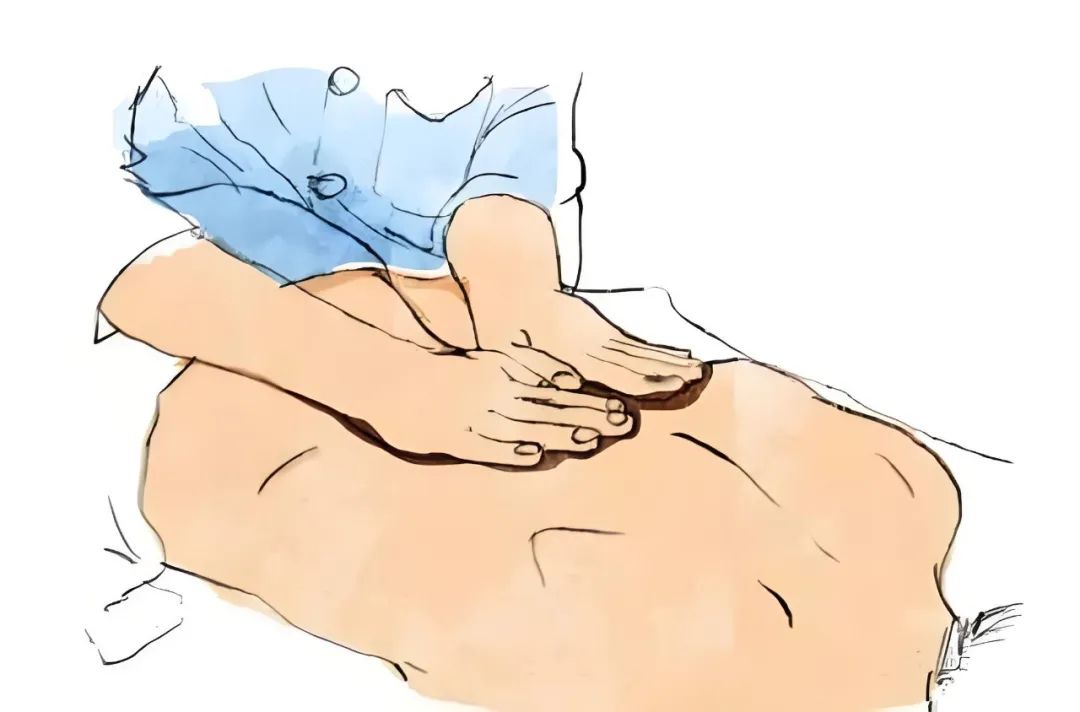
Tui Na Therapy
① Definition: Tui na is a natural and physical therapy in TCM, where practitioners use their hands on the patient’s body, employing various techniques such as pushing, grasping, pressing, rubbing, pinching, tapping, etc.
② Effects: Tui na therapy can unblock meridians, promote Qi and Blood circulation, relieve pain, dispel pathogens, and harmonize Yin and Yang.
05
Gua Sha Therapy
① Definition: Gua sha enhances the body’s defense mechanisms by stimulating nerve endings, accelerating blood flow, enhancing circulation, and speeding up metabolism.
② Effects: Gua sha promotes Qi and Blood circulation, induces sweating, relaxes muscles, and regulates the spleen and stomach.
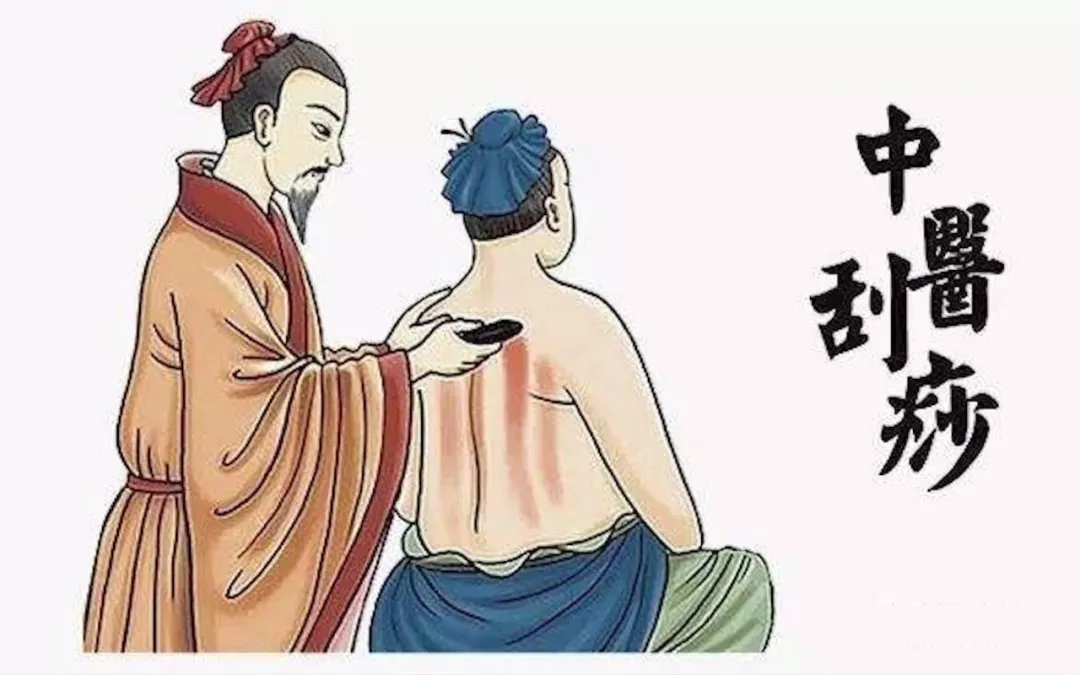
06
Chinese Herbal Steaming Therapy
① Definition: Chinese herbal steaming therapy is guided by the basic theories of TCM, using steam generated from boiling herbs to directly act on the steaming area.
② Effects: This therapy can dilate local blood vessels, promote blood circulation, warm the meridians, detoxify, sterilize, clean wounds, and reduce swelling and pain.
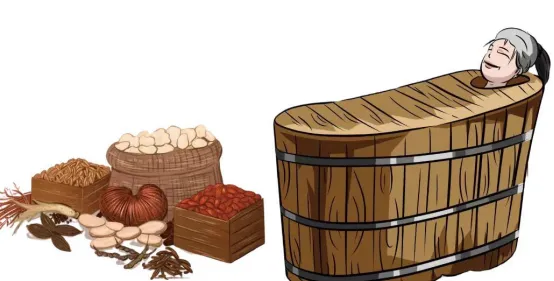
07
Special Moxibustion Therapy
① Definition: Special moxibustion is an innovative treatment method that combines the characteristics of traditional moxibustion.
② Effects: Special moxibustion has effects such as benefiting the kidneys, warming Yang, strengthening bones, dispelling stagnation, and alleviating pain.
08
Acupoint Application Therapy
① Definition: Acupoint application is a non-invasive and painless acupoint therapy that utilizes the principles of meridian acupoints to conduct and communicate Qi and Blood.
② Effects: Acupoint application can coordinate Yin and Yang, adjust deficiency and excess, and resist diseases.
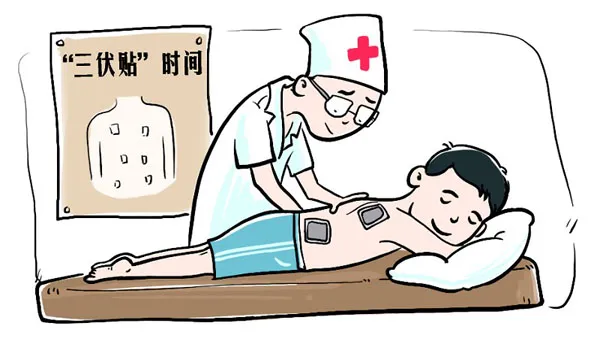
These methods not only reflect the unique charm of TCM but also demonstrate significant therapeutic effects in clinical practice, making important contributions to safeguarding public health.