
Shortness of breath, low voice, lack of energy, poor appetite, fatigue, and susceptibility to colds are common symptoms of Qi Deficiency (Qi Xu). This condition falls within the realm of sub-health in modern medicine. Individuals with Qi deficiency often have lower immunity and resistance to diseases compared to healthy individuals. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Qi is categorized into six types: Yuan Qi (Original Qi), Zong Qi (Ancestral Qi), Ying Qi (Nutritive Qi), Wei Qi (Defensive Qi), Zang-Fu Qi (Organ Qi), and Jing Luo Qi (Meridian Qi). It has four functions: promoting, consolidating, warming, and defending. Therefore, the so-called Qi deficiency syndrome refers to the insufficiency of at least one of the six types of Qi, leading to a failure in at least one of the four functions. How should individuals with Qi deficiency adjust their lifestyle to correct this condition and restore health?

1. Diet
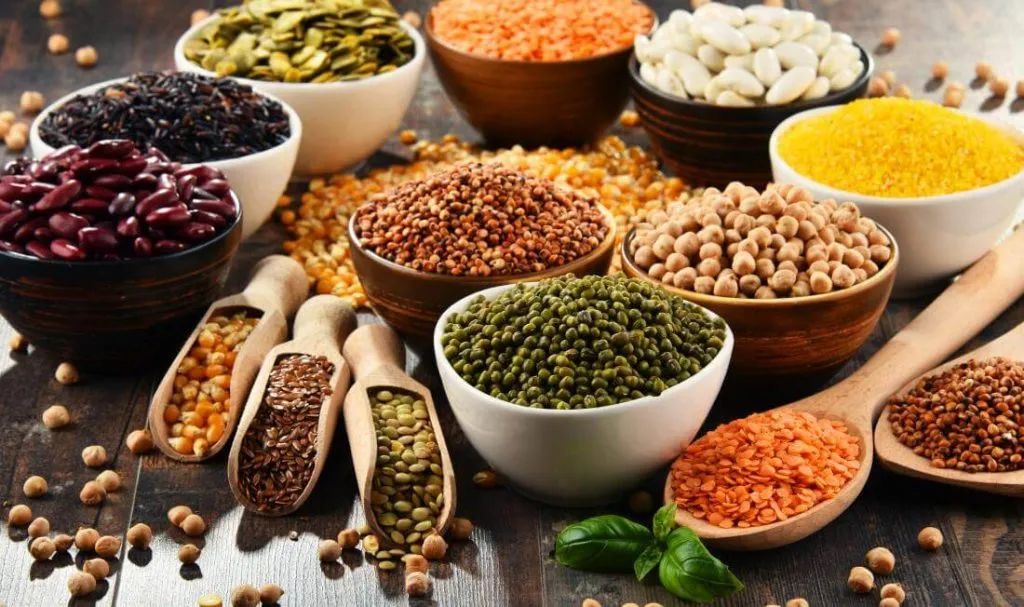


Individuals with Qi deficiency should consume more Qi-tonifying foods, such as Ling Zhi (Reishi Mushroom), glutinous rice, japonica rice, millet, barley, yellow millet, Shan Yao (Chinese Yam), potatoes, Da Zao (Jujube), honey, carrots, Xiang Gu (Shiitake Mushroom), Huang Dou (Yellow Soybean), Bai Bian Dou (White Lentil), tofu, chicken, rabbit, quail, beef, dog meat, Qing Yu (Green Fish), Lian Yu (Pangasius), and Huang Yu (Yellow Croaker). It is advisable to avoid excessive consumption of Qi-dispersing, laxative foods, such as chili and bitter melon.

2. Daily Routine


Individuals with Qi deficiency often have weak lung and spleen functions, with insufficient Wei Qi, making them susceptible to external pathogens. Therefore, they should pay attention to warmth, avoid excessive labor or vigorous exercise that causes sweating and exposure to wind. Daily routines should be regular, with appropriate rest during the summer afternoons, ensuring adequate sleep to strengthen the body. Avoid overworking and blind dieting to prevent damage to the righteous Qi.

3. Exercise


Due to insufficient Qi, individuals with Qi deficiency are more prone to fatigue and shortness of breath during exercise. Therefore, they should avoid high-intensity workouts and excessive sweating, and refrain from strenuous activities and prolonged breath-holding to prevent bodily harm. Instead, they should choose gentler forms of exercise, such as walking, jogging, Tai Chi, Wu Qin Xi (Five Animal Frolics), and Qigong. Notably, traditional exercises like Tai Chi, Wu Qin Xi, and Qigong emphasize the coordination of intention, breathing, and body movement to strengthen the body externally, harmonize the organs internally, and promote the smooth flow of meridians, providing comprehensive and balanced exercise for all body parts.

4. Emotional Well-being


Individuals with Qi deficiency often exhibit introverted, timid, emotionally unstable, and sensitive personality traits, often accompanied by weakened lung and spleen functions. Excessive worry can harm the spleen, while prolonged sadness can damage the lungs. Therefore, individuals with Qi deficiency should avoid excessive worry and sadness, and prevent emotional stagnation. They should learn to shift their focus, cultivate hobbies, and engage in activities like music, chess, calligraphy, and painting. It is also beneficial to make more friends and develop an outgoing personality to ensure emotional expression is smooth and moderate.

5. TCM Health Maintenance
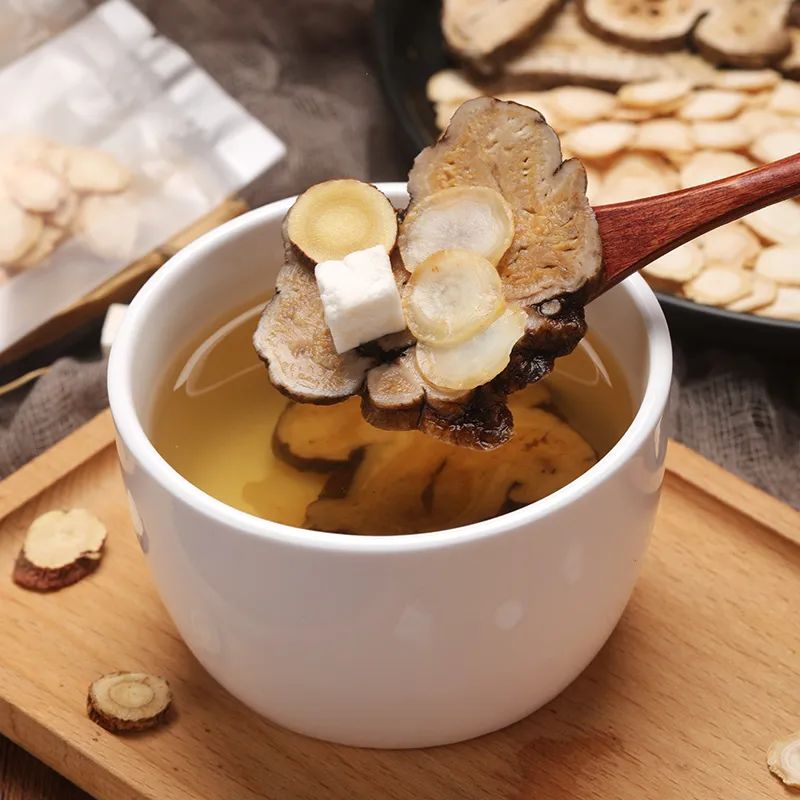


TCM health maintenance includes herbal teas, medicinal meals, foot baths, moxibustion, and acupressure. Individuals with Qi deficiency can use Si Jun Zi Tang (Four Gentlemen Decoction) as a tea substitute, which consists of Ren Shen (Ginseng), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), Fu Ling (Poria), and Zhi Gan Cao (Honey-fried Licorice), known for its spleen-strengthening and Qi-tonifying effects. Alternatively, they can prepare medicinal porridge using Ren Shen, Fu Ling, Sheng Jiang (Fresh Ginger), and japonica rice. Foot baths can be made with herbs like Sheng Huang Qi (Astragalus), Ai Ye (Mugwort), Bai Zhu, and Fang Feng (Siler). In daily life, regular acupressure or moxibustion on points such as Guanyuan (CV4), Qihai (CV6), and Zusanli (ST36) can be beneficial for health maintenance.

// Subscription Account //
Fujian Provincial Second Hospital Health Management Center

// Service Account //
Fujian Provincial Second Hospital Health Management
Preventive Medicine Center

