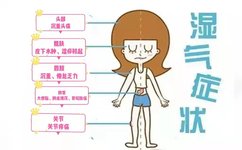
Understanding Coix Seed: A Minute Overview of Its Benefits in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Coix seed (Yìyǐrén) is a common medicinal material and also a frequently used ingredient in our daily diet. It comes from a plant called coix (Yìmǐ), and the mature seeds of this plant are dried and hulled to become what we commonly refer to as coix seed. The main production areas in China include Fujian, … Read more