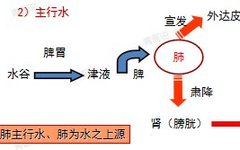
The Six Fu Organs and the Extraordinary Fu Organs
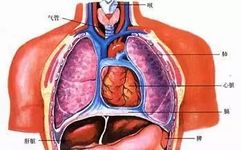
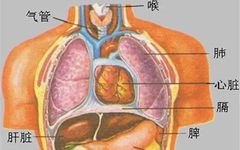
The Six Fu Organs and the Extraordinary Fu Organs The Six Fu organs refer to the six organs: the gallbladder (Dan), stomach (Wei), large intestine (Da Chang), small intestine (Xiao Chang), bladder (Pang Guang), and the San Jiao (Triple Burner). In ancient times, “Fu” was synonymous with “Fu” (storehouse), meaning a hollow place for storing … Read more