As the saying goes, “Many diseases are caused by phlegm,” and “phlegm” is a very undesirable substance, closely related to many diseases.
Many modern individuals have a phlegm-damp constitution, but it is important to note that the concept of “phlegm” in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) differs from the phlegm we commonly expect to cough up.
In TCM, “phlegm” refers to the excessive accumulation of body fluids that have not been expelled, leading to phlegm-damp.
One can understand it as a tangible phlegm versus an intangible “phlegm.”

It is like everyone has a small pond inside their body; those without dampness have fresh water flowing in and waste flowing out daily;
however, those with heavy dampness retain waste inside, leading to phlegm-damp over time, and their bodies become increasingly overweight.
Phlegm-damp encompasses a wide range, typically categorized into phlegm-damp, cold phlegm, and phlegm-heat.
Phlegm-Damp
Are your stools soft and unformed? Does your hair and facial skin easily secrete oil?
If your tongue coating is thick and greasy, and you have excessive saliva, this indicates phlegm-damp.
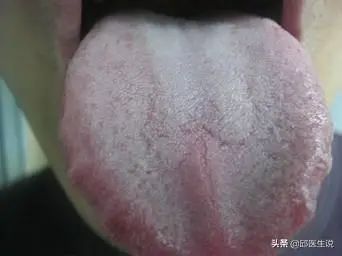
Common symptoms associated with phlegm-damp include:
(1) Coughing with phlegm, with a lot of phlegm.
(2) Headaches, a heavy body feeling, and frequent drowsiness.
(3) Lack of thirst and little desire to drink.
(4) Excessive sweating, with sticky sweat.
(5) Oily secretion from the face, skin, and hair.
(6) Decreased appetite, with a feeling of bloating in the chest and abdomen.
(7) Frequent urination, clear urine, and stools that are soft and unformed, easily sticking to the toilet.

Dietary habits such as consuming greasy foods and sweet treats, along with spleen deficiency and poor transformation, are all causes of phlegm-damp.
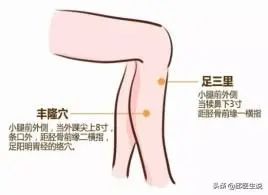
Regularly massaging the Fenglong (Stomach 40) point can help regulate the spleen and stomach, effectively eliminating dampness and phlegm.
It is advisable to maintain a light diet, consuming foods that strengthen the spleen, eliminate dampness, and resolve phlegm, such as white radish, water chestnut, seaweed, onion, ginkgo, lentils, red beans, and cabbage.
Recommended Recipe: Red Bean Carp Soup
Ingredients: Live carp, 50g red beans, 30g poria (Fu Ling), 10g dried tangerine peel (Chen Pi), 6g grass fruit, cooking wine, ginger, scallions, pepper, and a little salt.
Preparation Method: Clean thoroughly, boil together, and it is ready to eat once cooked.
For tea, you can choose the original flavor of Poria and Job’s Tears Tea.

Cold Damp
Do you experience cold pain in the abdomen? Is your complexion pale and do you easily feel cold?
If your tongue coating is white and greasy, this indicates cold phlegm, which is characterized by phlegm-damp along with signs of yang deficiency and coldness.
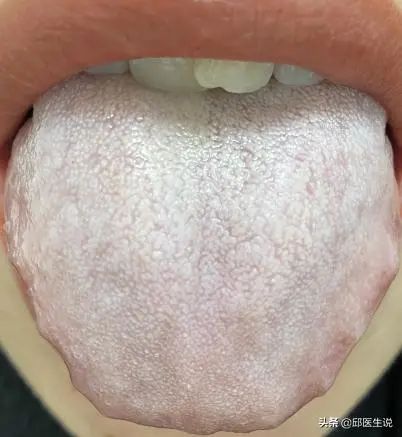
Common symptoms associated with cold damp include:
(1) Always feeling fatigued and lacking strength.
(2) Poor sleep quality, drooling during sleep.
(3) Sensitivity to cold, cold hands and feet, pale complexion.
(4) Dizziness and headaches, feeling heavy as if carrying a lead ball.
(5) Decreased appetite, with vague abdominal pain or cold pain, more pronounced when fasting.
(6) Stools that are soft and unformed or constipation.

Long-term exposure to cold, a cold constitution, and a preference for raw, cold, and sweet foods can all lead to cold phlegm.
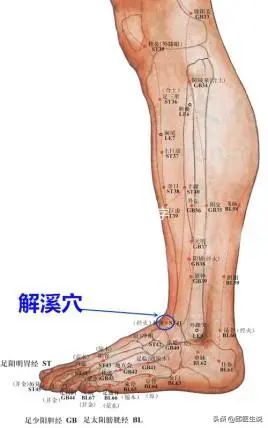
You can perform moxibustion on the Jiexi (Stomach 41) point, which is located on the stomach meridian and is effective in expelling phlegm-damp from the body, while moxa is a “pure yang substance” that can also dispel cold.
It is advisable to avoid consuming cold drinks, cold dishes, and icy porridge as they can damage the spleen qi; fatty meats and desserts that are high in fat and sugar are also hard to digest and can obstruct the spleen’s transformation function.
You can eat warming foods that strengthen the spleen, such as loofah, glutinous rice, red beans, fox nuts, yam, coix seed, and white lentils.
Recommended Recipe: Chestnut Stewed Chicken
Ingredients: 150g chestnuts, 1 hen (about 1500g), 3 slices of ginger, scallions, fine salt, and cooking wine to taste.
Preparation Method: You can do it yourself; no need for me to teach you.
For cold damp, you can also drink the original flavor of Poria and Job’s Tears Tea, adding ginger to steep together.

Damp Heat
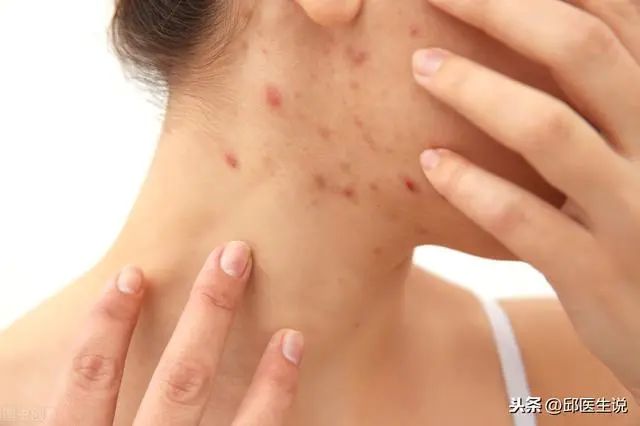
Do you have bad breath? Is your urine yellow and do you have acne on your face?
If your tongue coating is greasy with yellow patches, this is often due to phlegm-damp transforming into heat.
Common symptoms associated with damp heat include:
(1) Dizziness and a heavy feeling in the head.
(2) Insomnia with vivid dreams and difficulty falling asleep.
(3) Bitter taste in the mouth and bad breath.
(4) Yellow complexion and acne.
(5) Yellow urine, or frequent urination, urgency, and dry stools or a feeling of incomplete bowel movements.
(6) In women, abnormal vaginal discharge that is yellow and has a fishy odor.
Spicy and greasy foods, exposure to damp heat, and emotional distress can all contribute to phlegm-damp and heat accumulation.
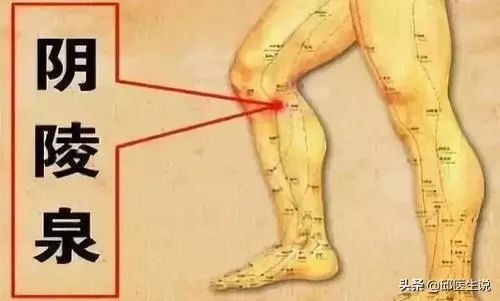
For those with a phlegm-heat constitution, massaging the Yinlingquan (Spleen 9) point can help clear damp heat and strengthen the spleen and kidneys.

It is advisable to maintain a light diet, consuming more celery, lotus root, lotus seeds, poria, mung beans, cabbage, and purslane.
Recommended Recipe: Dried Tangerine Peel and Job’s Tears Winter Melon Soup
Ingredients: 150g winter melon, 10g dried tangerine peel, 30g Job’s tears, 1 piece of ginger, and 50g lotus seeds.
Preparation Method: Boil together as usual.
For tea, you can choose the clear
I am Dr. Qiu Chaoping,
sharing good methods for health and wellness with you, along with good things and good stories.
Thank you for your likes and attention!

