

Auricular acupuncture is a treatment technique that uses specific needles or pellet-like substances to stimulate corresponding acupuncture points on the auricle to diagnose and treat diseases. This technique is based on the theory in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that there is a certain connection between the auricle and various parts of the human body, as well as the principle that observing the shape and color of the ear can assist in diagnosing diseases. By stimulating auricular acupuncture points, this technique can prevent and treat diseases. Its treatment range is broad and is commonly used in clinical practice for various painful conditions and certain functional disorders.
1. Commonly Used Needles and BasicOperating Methods
(1) Commonly Used Needles
The commonly used needles include15mmshort handle filiform needles, pin-shaped press needles, and pellets such as Wang Bu Liu Xing (Vaccaria seed) and Lai Fu Zi (Radish seed).
(2) Point Selection Methods(See point distribution in Figure1 and Figure2)
1.Select points based on the location of the disease: for example, select the stomach point for stomach pain, the lung point for lung diseases, and the shoulder point for shoulder pain.
2.Select points based on TCM theory: for example, for skin diseases, select the lung point, based on the theory that “the lung governs the skin”; for tinnitus, select the kidney point, as “the kidney opens to the ear”; for migraines, select the gallbladder point, as the gallbladder meridian runs “up to the head”; for red and swollen eyes, select the liver point, as “the liver opens to the eyes”.
3.Select points based on modern medical theory: for example, for menstrual irregularities, select the endocrine point; for insomnia, select the Shenmen (Spirit Gate) point; for arrhythmia, select the heart point; for hypertension, select the antihypertensive groove.
4.Select points based on clinical experience: for example, for red and swollen eyes, use the ear apex point.
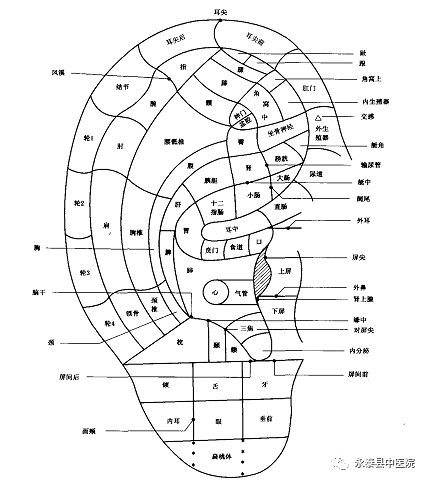
Figure1 Standard Auricular Acupuncture Point Location Diagram (Front)
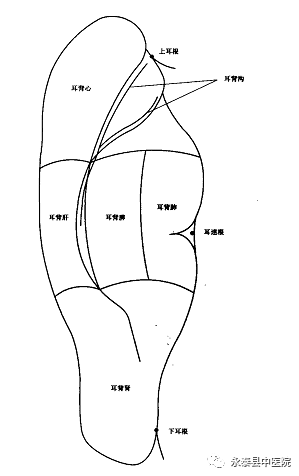
Figure2 Standard Auricular Acupuncture Point Location Diagram (Back)
(3) Needling Technique
After determining the acupuncture point or finding the reaction point on the auricular acupuncture point, routine disinfection is performed. Depending on the need, use a15mmshort handle filiform needle or a specific pin-shaped press needle. During needling, hold the auricle with the left hand and insert the needle with the right hand, ensuring the needle penetrates the cartilage but does not pierce through to the opposite skin. Retain the needle for15 to30 minutes. After removing the needle, apply pressure with a disinfected cotton ball to the needle hole to prevent bleeding. If necessary, apply ethanol or iodine to prevent infection. For press needles, cover with adhesive tape and retain for1 to2 days. If using the auricular pellet method, one hand holds the auricle while the other hand uses tweezers to place the auricular pellet patch on the acupuncture point and gently press and rub it, instructing the patient to press and rub at regular intervals based on their condition. It is advisable to leave it in place for2 to4 days.
2. Auricular Acupuncture Techniques for Common Diseases
(1) Head Wind (Primary Headache)
This condition is characterized by pain in the head and can be caused by various external and internal factors leading to dysfunction of the meridians in the head, imbalance of Qi and blood, obstruction of the meridians, or insufficient nourishment to the brain. This technique is suitable for the acute phase of primary headaches.
[Treatment Principle] Unblock the meridians, regulate Qi, and relieve pain.
[Operating Method] Use press needles buried in the brain, forehead, occiput, gallbladder, and Shenmen ear area points. Treat once or twice a week, retaining the needles for 1 to 2 days, with a treatment course of 2 weeks.
(2) Dysmenorrhea (Primary Dysmenorrhea)
Dysmenorrhea refers to pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen during or before and after menstruation, affecting normal life or work. It is often caused by emotional disturbances, Qi stagnation, and blood stasis; or by external cold and dampness invading the uterus, leading to poor circulation of Qi and blood; or by deficiency of liver and kidney, resulting in insufficient nourishment to the uterus.
[Treatment Principle] Regulate the Chong and Ren meridians, invigorate blood, and relieve pain.
[Operating Method] Use short handle filiform needles or pin-shaped press needles to needle the uterus, kidney, perineum, and ovary ear area points. Retain the short handle filiform needles for 30 minutes, and the press needles for 1 to 2 days. Treat twice a week, with a treatment course of 1 month.
(3) Insomnia (Primary Insomnia)
Insomnia is characterized by the inability to obtain normal sleep, difficulty falling asleep, restless sleep with frequent awakenings, or early waking, and in severe cases, inability to sleep through the night. This condition is often due to emotional disturbances or overthinking, leading to internal injury of the heart and spleen, and insufficient nourishment to the heart spirit; or due to disharmony between the heart and kidney, with excessive heart fire; or due to food stagnation, leading to disharmony in the stomach and restlessness during sleep.
[Treatment Principle] Nourish the heart, calm the spirit, and promote sleep.
[Operating Method] Use press needles buried in the subcutaneous layer, heart, kidney, liver, Shenmen, and back heart ear area points. Treat twice a week, retaining the needles for 1 to 2 days, with a treatment course of 1 month.
(4) Constipation (Functional Constipation)
This condition refers to difficulty in passing stools, with dry and hard feces, and often requiring laxatives, suppositories, or enemas to facilitate bowel movements. It is often caused by dysfunction of the large intestine, closely related to the spleen, stomach, and kidneys, and can be classified into deficiency and excess types.
[Treatment Principle] Moisten the intestines and promote bowel movements.
[Operating Method] Use press needles buried in the lower rectum, large intestine, and brain ear area points. Treat twice a week, retaining the needles for 1 to 2 days, with a treatment course of 2 weeks.
3. Contraindications
1.Pregnant women with a history of habitual miscarriage.
2.Individuals who are elderly, weak, severely anemic, or excessively fatigued.
3.Individuals with skin lesions or infections in the auricular area.
4. Precautions
1.Auricular acupuncture for pain-related diseases and functional disorders is usually used as an auxiliary technique and should be combined with other specialized treatment methods based on the clinical condition to prevent delays in treatment.
2.Strict disinfection is required to prevent infection. Needling is prohibited in areas of frostbite or inflammation on the auricle. If redness or swelling occurs at the needle site, apply 2% iodine solution or take anti-inflammatory medication promptly.
3.Auricular acupuncture may also cause needle fainting; precautions should be taken.
4.For patients with sprains or limb movement disorders, after needling, it is advisable to encourage appropriate movement of the affected area once the auricle becomes congested and warm, or to massage the affected area or apply moxibustion to enhance efficacy.

Previous Articles:
[Traditional Chinese Medicine Techniques 01] Acupuncture Techniques – Filiform Needles
[Traditional Chinese Medicine Techniques 02] Acupuncture Techniques – Scalp Acupuncture

