
Different populations have varying constitutions due to differences in region, environment, and lifestyle. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), constitution refers to the relatively stable inherent characteristics of a person, which are formed based on innate endowment (inherited from parents) and acquired factors throughout life, encompassing physical structure, physiological functions, and psychological states. According to the constitution standards established by Master Wang Qi, TCM recognizes eight types of biased constitutions in addition to the balanced constitution.

1. Balanced Constitution
The balanced constitution is the most stable and healthiest type! It usually arises from outstanding innate endowment and proper care in later life. The balanced constitution is characterized by a moderate physique, a radiant complexion, abundant energy, and strong organ function. Approximately 32.75% of the population falls into this category, which is about one-third. Males are more prevalent than females, and the proportion of individuals with a balanced constitution decreases with age.
Characteristics of the Balanced Constitution:
Overall Characteristics: Harmony of Yin, Yang, Qi, and Blood, with a moderate physique, radiant complexion, and abundant energy as primary features.
Physical Characteristics: Well-proportioned and robust physique.
Common Manifestations: Radiant complexion and skin, thick and shiny hair, bright eyes, clear nasal passages, moist lips, not easily fatigued, energetic, tolerant of cold and heat, good sleep, good appetite, normal bowel movements, pale red tongue, thin white coating, and a relaxed and strong pulse.
Psychological Characteristics: Gentle and cheerful temperament.
Tendency to Illness: Rarely suffers from diseases.
Adaptability to External Environment: Strong adaptability to natural and social environments.
Health Tips:
For individuals with a balanced constitution, there are generally no special dietary restrictions. However, it is advisable to avoid consuming excessively cold or hot foods for extended periods.
In winter, those with a balanced constitution may choose to avoid or limit the consumption of nourishing tonics to prevent excessive supplementation, which can lead to symptoms of “internal heat” such as acne and constipation.

2. Yang Deficiency Constitution
Yang deficiency refers to a pathological condition characterized by weakened Yang Qi. Yang Qi is responsible for warming the body and supporting organ functions. When Yang is deficient, bodily functions decline, leading to symptoms of coldness. Common types include stomach Yang deficiency, spleen Yang deficiency, and kidney Yang deficiency. The main symptoms of Yang deficiency include cold intolerance, pale complexion, loose stools, clear and frequent urination, and a weak and deep pulse.
Manifestations of Yang Deficiency Constitution:
Heart Yang Deficiency: Accompanied by palpitations, chest discomfort, insomnia with vivid dreams, and anxiety.
Liver Yang Deficiency: Accompanied by dizziness, discomfort in the flanks, chest pain, and depression.
Spleen Yang Deficiency: Accompanied by poor appetite, nausea, belching, and loose stools.
Kidney Yang Deficiency: Accompanied by lower back and knee weakness, frequent urination, impotence, and decreased sexual function.
Lung Yang Deficiency: Coughing, shortness of breath, weak voice, and phlegm resembling white foam.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Lamb, pepper, lychee, fennel, shrimp, longan, etc.
Foods to Avoid: Mainly raw, cold, bitter, and greasy foods such as pears, watermelon, bananas, persimmons, cucumbers, bitter melon, mung beans, soft-shelled turtle, crab meat, green tea, and iced beverages.

3. Yin Deficiency Constitution
This constitution is similar to the damp-heat constitution, characterized by a deficiency of Yin and blood, leading to symptoms of heat such as frequent thirst, dry throat, insomnia, dizziness, irritability, dry and dull skin, weight loss, night sweats, hot palms and soles, yellow urine, hard stools, and frequent constipation, with a red tongue and little moisture.
Manifestations of Yin Deficiency Constitution:
Overall Characteristics: Deficiency of Yin fluids, with dry mouth and throat, hot palms and soles as primary symptoms.
Physical Characteristics: Generally slender physique.
Common Manifestations: Hot palms and soles, dry mouth and throat, slightly dry nose, preference for cold drinks, dry stools, red tongue with little moisture, and thin rapid pulse.
Psychological Characteristics: Impulsive, extroverted, and active personality.
Tendency to Illness: Prone to conditions such as fatigue, nocturnal emissions, and insomnia; susceptible to heat-related illnesses.
Adaptability to External Environment: Tolerates cold but not heat; sensitive to heat and dryness.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Duck, pork, pig skin, milk, soft-shelled turtle, pears, mulberries, white fungus, clams, etc.
Foods to Avoid: Mainly warming and drying foods such as dog meat, garlic, leeks, pepper, chili, and various fried foods. It is best to avoid smoking and alcohol.
4. Qi Deficiency Constitution
Qi deficiency refers to a lack of energy, resulting in fatigue and low vitality. Even slight exertion can lead to tiredness, and the body’s immune function and resistance to disease are relatively low. In simple terms, it is a series of pathological changes caused by a deficiency of vital energy.
Manifestations of Qi Deficiency Constitution:
Physical characteristics: Slender or slightly overweight, fatigue, pale complexion, low voice, spontaneous sweating, especially during activity, palpitations, poor appetite, pale tongue with white coating, and weak pulse are the basic features. If ill, symptoms may worsen, or be accompanied by shortness of breath, reluctance to speak, weak cough, poor appetite, abdominal distension, loose stools, prolapse, or fatigue.
Overall Characteristics: Deficiency of vital energy, with fatigue, shortness of breath, and spontaneous sweating as primary symptoms.
Physical Characteristics: Soft and weak muscles.
Common Manifestations: Usually low voice, shortness of breath, easy fatigue, and spontaneous sweating, with pale red tongue and weak pulse.
Psychological Characteristics: Introverted personality, not fond of risk.
Tendency to Illness: Prone to colds, organ prolapse, etc.; slow recovery after illness.
Adaptability to External Environment: Sensitive to wind, cold, heat, and dampness.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Glutinous rice, millet, red dates, longan, lotus seeds, chicken, beef, crucian carp, eel, shrimp, etc.
Foods to Avoid: Mint, pepper, garlic, perilla, raw radish, oranges, tea, and alcohol.

5. Blood Stasis Constitution
Blood stasis constitution refers to a systemic condition where blood circulation is not smooth, leading to a tendency for blood stasis. In cold weather or emotional distress, blood stasis can easily occur, resulting in dark or painful areas, dryness, itching, and lumps in affected areas, which also affects their function.
Typical blood stasis constitution often presents with a slender physique. “Without blood stasis, new blood cannot be generated”; poor microcirculation directly affects nutrient delivery, and even with adequate intake, nutrients may not reach their intended destinations. Additionally, prolonged stasis can impact appetite.
Individuals with blood stasis constitution often have dry skin, which can lead to itching. TCM believes this is due to wind; “to treat wind, one must first treat blood; when blood flows, wind will dissipate.” Itching is a manifestation of poor blood circulation in the skin.
Those with blood stasis constitution often do not have a clear and bright complexion, which can be a significant concern for women. They are prone to dark spots, dull complexion, dark lips, and “red threads in the eyes” (fine red veins in the eyes). Hair loss is common and difficult to treat, and they may also experience acne characterized by dark spots that are hard to fade.
Manifestations of Blood Stasis Constitution:
Overall Characteristics: Poor blood circulation, with dark complexion and purple tongue.
Physical Characteristics: Can be either thin or overweight.
Common Manifestations: Dark complexion, easy bruising, dark lips, purple or dark spots on the tongue, purple or thickened sublingual veins, and a choppy pulse.
Psychological Characteristics: Prone to irritability and forgetfulness.
Tendency to Illness: Prone to conditions such as masses, pain syndromes, and blood disorders.
Adaptability to External Environment: Sensitive to cold.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Hawthorn, red dates, oranges, red wine, cilantro, carrots, black fungus, lotus root, corn, ginger, chicken, beef, etc.
Foods to Avoid: Fava beans, sweet potatoes, chestnuts, persimmons, peanuts, dried plums, bitter melon, etc. Additionally, control salt intake.

6. Damp-Heat Constitution
In TCM, we often hear doctors mention “damp-heat.” So, what is damp-heat, what are its manifestations, and what issues should be noted? To understand damp-heat, one must first understand what dampness and heat are.
Dampness refers to water dampness, which can be external (due to humid weather, rain exposure, or damp living conditions) or internal (a pathological product often related to digestive function). TCM believes that the spleen has the function of “transporting and transforming water and dampness”; if the body is weak, digestion is poor, or if one overeats oily or sweet foods, the spleen cannot function properly, leading to “internal dampness”. Additionally, those with spleen deficiency are more susceptible to external dampness, which can also lead to internal dampness due to obstruction of the spleen and stomach, making the two interrelated.
Heat refers to a condition of excess heat. In damp-heat, heat coexists with dampness, either due to hot and humid weather in summer and autumn, prolonged dampness leading to heat, or due to “Yang-heat constitution” causing dampness to transform into heat. Thus, dampness and heat often coexist.
Manifestations of Damp-Heat Constitution:
Characteristics and Manifestations: Oily skin on the face and nose, prone to acne and boils, often experiencing bitter taste, bad breath, or unusual mouth odor, frequent sticky stools, burning sensation during urination, yellow urine, and women often have yellow discharge, while men may have a moist and sweaty scrotum.
Personality: Individuals with damp-heat constitution tend to be irritable and quick-tempered.
Body Type: Individuals with damp-heat constitution may be overweight or thin.
Common Manifestations: Oily skin, frequent acne, dry mouth, bitter taste, red eyes, irritability, fatigue, short and dark urine, dry or sticky stools, and increased discharge in women. Symptoms may worsen during illness.
Psychological Characteristics: Prone to irritability and anger; adaptability: poor tolerance to damp and hot environments.
Common Skin Conditions: Acne, eczema, psoriasis, sweat blisters, damp eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and rosacea.
Tendency to Illness: Individuals with damp-heat constitution are prone to conditions such as boils, jaundice, and febrile diseases.
Adaptability: Individuals with damp-heat constitution have difficulty adapting to humid environments or high temperatures, especially during late summer and early autumn when damp-heat conditions prevail.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Foods that clear damp-heat, such as Job’s tears, lotus seeds, bitter melon, red beans, mung beans, crucian carp, winter melon, loofah, cabbage, lotus root, water spinach, etc.
Foods to Avoid: Spicy foods, garlic, scallions, leeks, honey, alcohol, beef, dog meat, and venison.

7. Phlegm-Damp Constitution
Phlegm-damp constitution is a relatively common type of constitution. When the body’s organs, Yin and Yang are imbalanced, and the circulation of Qi, blood, and body fluids is disrupted, phlegm-damp can easily form, leading to this constitution, often seen in overweight individuals or those who have recently gained weight. Individuals with this constitution often present with a stout physique, soft and full abdomen, oily skin, excessive sweating, chest tightness, phlegm, dull yellow complexion, slightly puffy eyelids, easy fatigue, often with a large tongue and white greasy or sweet coating, feeling heavy and uncomfortable, preferring fatty and sweet foods, with normal or loose stools and little or cloudy urine. Their personality tends to be gentle and cautious, often enduring discomfort. This constitution is prone to diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, asthma, gout, coronary heart disease, metabolic syndrome, and cerebrovascular diseases.
Manifestations of Phlegm-Damp Constitution:
Overall Characteristics: Accumulation of phlegm-damp, with a stout physique, full abdomen, and greasy tongue.
Physical Characteristics: Stout physique, soft and full abdomen.
Common Manifestations: Oily skin, excessive sweating, chest tightness, phlegm, greasy or sweet mouth, preference for fatty and sweet foods, greasy tongue, and slippery pulse.
Psychological Characteristics: Gentle and cautious personality, often enduring discomfort.
Tendency to Illness: Prone to thirst, stroke, and chest obstruction.
Adaptability to External Environment: Poor adaptability to rainy seasons and humid environments.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Foods that strengthen the spleen, benefit Qi, promote water metabolism, and resolve phlegm, such as corn, Job’s tears, kelp, winter melon, seaweed, black fungus, asparagus, lentils, red beans, and crucian carp.
Foods to Avoid: Sweet, greasy, and sour foods such as pomegranate, grapefruit, sugar, and soft-shelled turtle.

8. Qi Stagnation Constitution
Qi is the fundamental energy and driving force of life activities. The maintenance of life activities relies on Qi. Qi in the body is closely related to innate endowment, external environment, and the physiological functions of the kidneys, spleen, stomach, and lungs. Therefore, various physiological activities in the body are essentially manifestations of Qi movement. When Qi cannot be expressed and accumulates internally, it leads to “Qi stagnation.” TCM believes that Qi stagnation is often caused by emotional distress and unhappiness. Prolonged Qi stagnation can lead to poor blood circulation, severely affecting health.
Manifestations of Qi Stagnation Constitution:
1. Depressed demeanor, emotional weakness, unhappiness;
2. Sentimental, irritable, and restless;
3. Frequently sighing for no reason, easily feeling anxious and having insomnia;
4. Easily startled and fearful in stressful situations;
5. Pale red tongue, thin white coating, and tenderness or pain in the flanks or chest;
6. Adaptability to External Environment: Poor adaptability to emotional influences; not accustomed to rainy weather.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Oranges, leeks, fennel, white radish, mint, milk, and jujubes.
Foods to Avoid: Pomegranate, dried plum, persimmon, cheese, coffee, and strong tea.
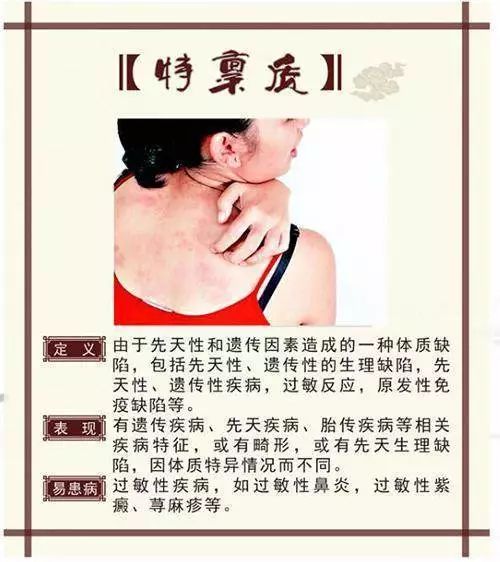
9. Special Constitution
Special constitution, also known as special physiological defects or allergies, refers to a unique condition of constitution caused by genetic and innate factors, primarily including allergic constitution, hereditary disease constitution, and fetal transmission constitution.
Manifestations of Special Constitution:
Individuals with special constitution may frequently experience nasal congestion, sneezing, and runny nose even without a cold, are prone to asthma, and may have allergies to medications, foods, odors, pollen, and seasonal changes. Some individuals may develop urticaria, with skin showing purple-red spots or bruises due to allergies, resembling what Western medicine describes as allergic constitution.
Overall Characteristics: Abnormal innate characteristics, primarily characterized by physiological defects and allergic reactions.
Physical Characteristics: Individuals with allergic constitution typically do not have specific features; those with abnormal innate characteristics may have deformities or physiological defects.
Common Manifestations: Individuals with allergic constitution often experience asthma, hives, throat itching, nasal congestion, and sneezing; those with hereditary diseases may exhibit vertical inheritance, congenital, or familial traits; those with fetal transmission diseases may show characteristics influenced by maternal factors on fetal growth and development.
Adaptability to External Environment: Poor adaptability to seasonal allergies, prone to chronic diseases.
Individuals with special constitution account for 4.91% of the population, primarily due to genetic factors; their distribution, physique, and personality are generally unremarkable; they are characterized by poor adaptability and a tendency to suffer from drug allergies, pollen allergies, asthma, etc. It is recommended to maintain a light and balanced diet and avoid allergens as much as possible.
Health Tips:
Foods to Eat: Yam, sweet potatoes, chestnuts, red dates, peanuts, black sesame, and black rice.
Foods to Avoid: Bitter melon, water chestnuts, kelp, seaweed, Chinese toon, shrimp, crab, carp, chili, coffee, and lettuce.
More Articles:
Actively participate and showcase the charm of TCM while growing in progress.
Winter diseases treated in summer: Guanyun County Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital is currently conducting Sanfu paste treatments.
“Treating upper diseases by addressing lower ones, one disease, one unique remedy” (illustrated).

Guanyun County Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital
m.sdgxzyyy.com
Long press the QR code to follow us.

