

Honghua (Safflower) is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine. It is referred to as “Honglanhua” in the Han Book and “Honghua” in the Kaibao Materia Medica.
Aliases: Nanhonghua, Caohonghua, Honglanhua, Honghuamao.
Source: The dried flower of the annual or biennial herb Carthamus tinctorius (Asteraceae), mostly cultivated.
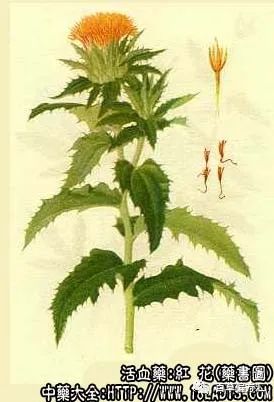
Plant morphology: The stem is cylindrical with fine shallow grooves, reaching heights of 30 to 90 cm, with a woody base and many branches at the top. The leaves are alternate, nearly sessile and slightly clasping the stem, ovate or ovate-lanceolate, slightly thick, with a sharp apex and serrated or spiny margins. The capitulum is terminal, with an ovate or hemispherical involucre, bracts arranged in whorls, with 2 to 3 outer rows leaf-like and spiny, and inner rows membranous without spines. The flowers are tubular, with the upper part red-yellow and the base gradually narrowing to yellow, clustered on the receptacle, with 5 stamens and 1 pistil, the stigma bifid and also yellow. The achene is ovate, white, with 4 prominent ribs and no pappus.
Production area: Mainly produced in Henan, now cultivated nationwide, with large-scale planting in Xinjiang.
Identification: The flowers are wrinkled, curved, and scattered, red-yellow, and fine like hair, hence the local name “Honghuamao”. A single flower is about 2 cm long, with a linear yellow or orange base, the upper flower crown tubular, about 0.8 cm long and 1.5 mm in diameter, with 5 lobes at the tip, red or orange, with yellow stamens and stigma, slightly fragrant, with a mildly sweet and bitter taste. The best quality has a long flower crown and bright red color.
Main components: Contains honghua glycoside, also known as red pigment; also contains safflower yellow pigment.
Efficacy and functions: Invigorates blood and regulates menstruation. According to preliminary animal experiments, its effects include:
1. Uterine stimulation: Its decoction and tincture can cause tonic or rhythmic contractions of the uterus, more pronounced in pregnant uteri, with rapid and lasting effects.
2. Blood pressure reduction: It has a blood pressure-lowering effect and can maintain it for a long time.
3. Vasodilation: The water extract of safflower has a certain effect on dilating coronary arteries.
Preparation: Used raw.
Properties: Pungent, warm.
Meridians entered: Heart, Liver.
Functions: Invigorates blood, regulates menstruation.
Indications: Menstrual irregularities, postpartum abdominal pain, masses, traumatic bruising, and painful swellings.
Clinical applications: 1. Treats blood stasis menstrual pain and amenorrhea, utilizing its stimulating effect on the uterus to invigorate blood and regulate menstruation. The indications, usage, and dosage are similar to Taoren (Peach Kernel). For postpartum lochia retention, blood stasis, and lower abdominal distension and pain, safflower can also be used, often combined with Danggui (Angelica Sinensis), Niuxi (Achyranthes), Rougui (Cinnamon), in formulas like Zhechong Decoction.
2. Treats coronary heart disease and angina. Ancients recognized that safflower combined with Chuanxiong (Ligusticum) and Danggui can treat “chest and abdominal blood stasis pain”. Modern practice uses 15g of safflower combined with 15g of Chuanxiong, decocted daily (or in tablet form), as a basic formula for treating angina due to qi stagnation and blood stasis, with certain efficacy, possibly related to the vasodilatory effects of Chuanxiong and safflower on coronary arteries. Reports indicate a relatively high recent effective rate for treating angina, but the overall efficacy remains unsatisfactory. It can also be combined with Ginkgo biloba to create Yinchuan Hongshuxue tablets, which also show good efficacy for angina.
3. Treats traumatic injuries, with stronger efficacy than Taoren. For contusions and sprains with subcutaneous bruising and swelling, safflower oil or safflower wine (prepared by soaking in alcohol or decocting with rice wine) can be applied externally; for internal injuries with blood stasis, it can be combined with Su Mu (Sappan Wood), Danggui, Chishaoyao (Red Peony), to help alleviate pain, in formulas like Die Da Huoxue Decoction.
4. Used for nourishing qi and blood, in small doses, it can be added to warming tonics. For postpartum blood collapse, dizziness, blurred vision, cold qi, or even lockjaw (trismus), it is advisable to use Bazhen Decoction or Zhi Gancao Decoction, adding 0.9 to 1.5g of safflower for better results.
5. Safflower is used in ophthalmology, mainly for clearing heat and reducing inflammation, combined with Shengdi (Rehmannia), Chishaoyao, Lianqiao (Forsythia) to treat red and swollen eyes (including acute conjunctivitis, styes, etc.), in formulas like Honghua San.
Usage precautions: 1. Pregnant women should avoid use, as it can stimulate uterine contractions; those with excessive menstruation or bleeding tendencies should not use it; 2. Large doses of safflower invigorate blood and break stasis, while small doses nourish blood and harmonize it; 3. Both safflower and Taoren can dispel stasis, but Taoren is more widely used in blood conditions; for heat syndrome with blood stasis, Taoren is more commonly used; for heart and abdominal stasis pain, safflower is more effective.
Dosage: Generally 3 to 9g, slightly larger doses of 12 to 15g, and for nourishing blood, 0.9 to 15g.
Example prescriptions: 1. Zhechong Decoction: 9g safflower, 9g Taoren (crushed), 9g Chishaoyao, 9g Guizhi (Cinnamon), 4.5g Chuanxiong, 6g Danpi (Moutan), 6g Yanhusuo, decocted with equal parts of wine and water.
2. Coronary Heart Tablets (Beijing Coronary Heart Disease Prevention and Treatment Cooperative Group): (Each 12 tablets contain 15g of Chuanxiong and safflower), taken three times daily, 4 tablets each time, with warm water.
3. Die Da Huoxue Decoction: 6g safflower, 6g Taoren (crushed), 6g Su Mu, 9g Guizhi, 9g Chishaoyao, 6g Zhike, 1.5g Muxiang, 9.5g Ruxiang, 4.5g Moyi, decocted for oral administration.
4. Honghua San: 4.5g safflower, 6g Lianqiao, 4g Danggui, 9g Shengdi, 6g Zicao, 9g Chishaoyao, 4.5g Dahuang, 3g Gancao, decocted for oral administration.
Note: Safflower leaves and bracts can have spiny or non-spiny varieties.
More exciting recommendations:
Chinese Herbs: The Efficacy and Functions of Danpi
Chinese Herbs: The Efficacy and Functions of Huashi
【Disclaimer】: Articles reproduced from other platforms or media will be credited to the source and author, but no express or implied guarantee is made regarding the accuracy, reliability, or completeness of the content, and it is for reference only. If there is any infringement, please contact this platform and provide relevant proof, and this platform will correct the source and author or delete the article based on the copyright owner’s opinion, and will not bear any other responsibility.
The above contentis sourced from the internet,for reference only,infringement will be deleted!
Follow the doctor’s advice! Do not self-medicate! Be the first to collect and share with friends,the more people see it, the more health benefits!
Be the first to collect and share with friends,the more people see it, the more health benefits!

