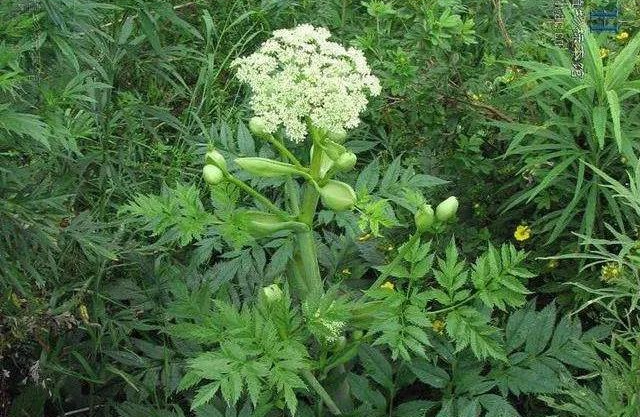
Angelica sinensis (Olive.) Diels, also known as Dong Quai or Chinese Angelica, is the dried root of the plant belonging to the Apiaceae family. It is renowned for its saying “Nine out of ten return to Dong Quai” and is honored as the “King of Herbs.” It is now listed among the food-medicine homologous items, possessing antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-depressant properties. Angelica sinensis is primarily distributed in the southeastern regions of Gansu, Yunnan, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Hubei provinces in China.

 Component Analysis【Nutritional Components】
Component Analysis【Nutritional Components】
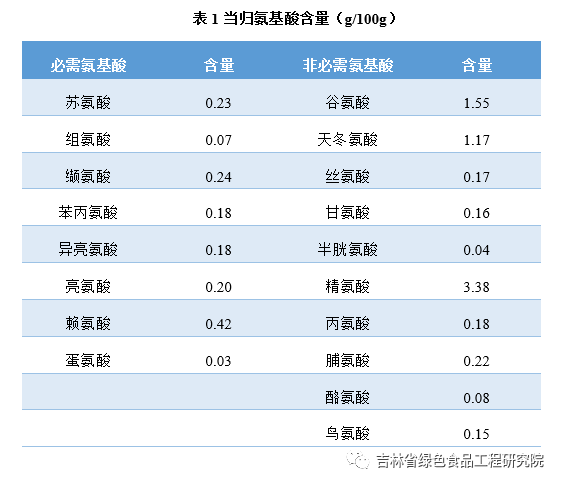
Angelica sinensis contains various nutritional components, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals, as well as 18 amino acids, among which are 8 essential amino acids. The specific content is shown in Table 1.
【Efficacy Components】
Angelica sinensis contains volatile oils (ligustilide, with a content of 46.75%), polysaccharides (composed of glucose, arabinose, xylose, rhamnose, galactose, etc.), flavonoids (luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoside and luteolin-7-O-rutinoside), and organic acids (ferulic acid, vanillic acid, succinic acid, niacin, anethole, nonanedioic acid, etc.).

 Functional Effects
Functional Effects
【Protection of Hematopoietic System】
Research has found that the polysaccharides in Angelica sinensis can induce bone marrow macrophages and monocytes in the hematopoietic microenvironment, promoting the synthesis and secretion of hematopoietic regulatory factors, thereby facilitating the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic-related cells such as granulocyte-monocyte progenitor cells and myeloid multipotent progenitor cells, thus playing a protective role in the hematopoietic system.
【Anti-tumor】
The polysaccharides in Angelica sinensis can directly or indirectly kill tumor cells by enhancing the body’s specific immune function and humoral immune function, thus exerting anti-tumor effects.
【Anti-depressant】
Research results indicate that Angelica sinensis can significantly increase the number of crossings and upright times in CUMS (chronic unpredictable mild stress) model rats, while significantly reducing the immobility time in forced swimming tests, thereby partially reversing the behavioral abnormalities caused by CUMS stress, thus exhibiting anti-depressant effects.
【Antioxidant】
The polysaccharides in Angelica sinensis can significantly enhance the activity of SOD (superoxide dismutase), CAT (catalase), and GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase) in D-galactose-induced aging model mice, while reducing the levels of LPO (lipid peroxidase) in plasma, brain homogenate, and liver homogenate, thus exhibiting antioxidant effects.
【Blood Sugar Reduction】
Research has found that the flavonoids in Angelica sinensis can accurately target CCL2 (chemokine), IL-1β (interleukin-1β), and other targets, regulating multiple signaling pathways related to diabetes and Nod-like receptors, thus achieving blood sugar reduction.
Additionally, Angelica sinensis also possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, cough relief, blood tonifying and activating blood circulation, menstrual regulation and pain relief, and intestinal lubrication and constipation relief effects.

References
[1]Cao Yandong. Analysis of the Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Effects of Angelica Sinensis[J]. World Latest Medical Information Abstracts, 2019,19(2):93-95.
[2]Yan Hui, Zhang Xiaobo, Zhu Shoudong, et al. Research on the Production Area Division of Angelica Sinensis[J]. China Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2016,41(17):3139-3147.
[3]Dai Xingde, Wang Fang. Determination of Amino Acid Content in Angelica Sinensis from Different Regions[J]. Health Vocational Education, 2012,30(7):118-119.
[4]Wang Shengxin, Shen Xiao, Meng Yingjiao, et al. Analysis of Volatile Oil Components in Various Medicinal Parts of Angelica Sinensis by HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. China Hospital Pharmacy Journal, 2019,39(5):433-438.
[5]Gong Wenxia. Study on the Anti-depressant Effects and Mechanisms of Angelica Sinensis and Its Active Components[D]. Shanxi University, 2019.
[6]Cao Xingwei, Gong Wei, Hu Tao, et al. Clinical Study on the Treatment of Postoperative Anemia with Iron Sucrose Injection Combined with Angelica Sinensis Blood-Tonifying Decoction[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine, 2016,12(8):117-118.
[7]Xing Lipeng. Preparation, Structural Identification, and In Vitro Anti-tumor Activity Study of Three Uniform Molecular Weight Polysaccharides from Angelica Sinensis[D]. Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[8]Liu Lihua. Study on the Antioxidant Effects of Polysaccharides from Angelica Sinensis[J]. Contemporary Medical Forum, 2014,12(3):284-285.
[9]Wang Dandan, Guo Lina, Pei Yuan, et al. Network Pharmacology Study on the Mechanism of Astragalus and Angelica Sinensis in Treating Diabetic Nephropathy[J]. New Chinese Medicine and Clinical Pharmacology, 2020,5(31):566-575.
Contributed by/Li Shuai
Reviewed by/Wang Ying
Typeset by/Jiang Shanshan

 Jilin Province Green Food Engineering Research Institutehttp://www.jl-greenfood.com
Jilin Province Green Food Engineering Research Institutehttp://www.jl-greenfood.com


WeChat ID: GreenFood-JL Official Website QR Code
Wholeheartedly serving the people!


