Ginseng (Rén Shēn) is a precious traditional Chinese medicine with a long history and worldwide fame. Consuming 3 grams of ginseng daily can strengthen the body. However, do you know the effects and functions of ginseng and the best ways to consume it?
Ginseng, a medicinal herb, is the dried root of the plant Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. Cultivated ginseng is referred to as “garden ginseng” (园参, yuán shēn), while wild ginseng is called “mountain ginseng” (山参, shān shēn). It is typically harvested in the autumn, cleaned, and then dried. Garden ginseng is sun-dried or air-dried, known as “raw sun-dried ginseng” (生晒参, shēng shài shēn); mountain ginseng is sun-dried, referred to as “raw sun-dried mountain ginseng” (生晒山参, shēng shài shān shēn); when blanched in water and dried with sugar, it is called “sugar ginseng” (白糖参, bái táng shēn); and when steamed and then dried, it is known as “red ginseng” (红参, hóng shēn). Ginseng grows in dense forests on mountain slopes and is distributed across several provinces in Northeast China, with significant cultivation in Liaoning and Jilin. In recent years, it has also been planted in Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, and Hubei. Ginseng is known for its ability to tonify qi, stabilize the pulse, strengthen the spleen and lungs, generate fluids, and calm the spirit. It is used for symptoms such as fatigue, cold limbs, weak pulse, spleen deficiency with poor appetite, lung deficiency with cough and wheezing, fluid depletion with thirst, internal heat with diabetes, prolonged illness with weakness, palpitations, insomnia, impotence, and heart failure.
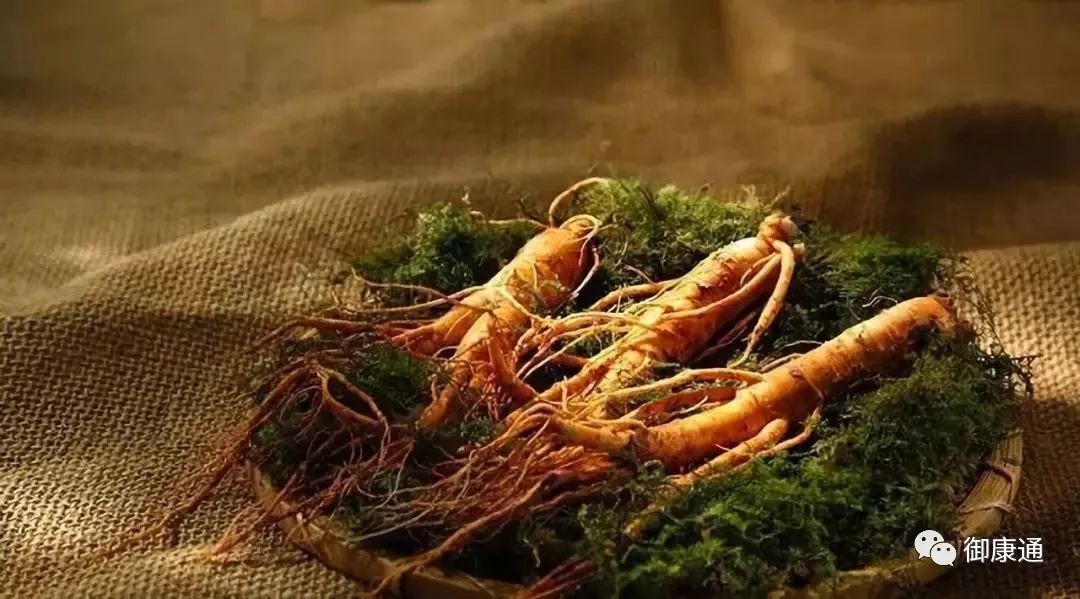

Herb Name:Ginseng
Pinyin:Rén Shēn
Alias:棒锤 (bàng chuí), 山参 (shān shēn), 园参 (yuán shēn), 参叶 (shēn yè)
Source:This product is the dried root of the plant Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. Cultivated ginseng is referred to as “garden ginseng” (园参, yuán shēn), while wild ginseng is called “mountain ginseng” (山参, shān shēn). It is typically harvested in the autumn, cleaned, and then dried. Garden ginseng is sun-dried or air-dried, known as “raw sun-dried ginseng” (生晒参, shēng shài shēn); mountain ginseng is sun-dried, referred to as “raw sun-dried mountain ginseng” (生晒山参, shēng shài shān shēn); when blanched in water and dried with sugar, it is called “sugar ginseng” (白糖参, bái táng shēn); and when steamed and then dried, it is known as “red ginseng” (红参, hóng shēn).
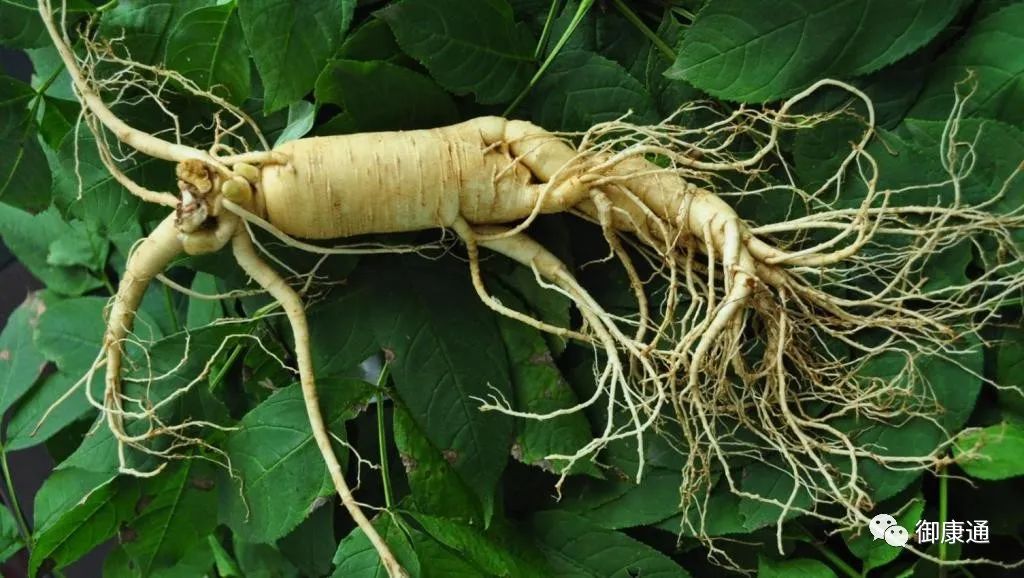

Characteristics:Raw sun-dried ginseng: The main root is spindle-shaped or cylindrical, measuring 3-15 cm in length and 1-2 cm in diameter. The surface is grayish-yellow, with shallow, intermittent coarse transverse wrinkles and obvious longitudinal folds. The lower part has 2-3 lateral roots and numerous long fibrous roots, often with small, inconspicuous warty protrusions. The rhizome (bulb) is 1-4 cm long and 0.3-1.5 cm in diameter, often twisted and curved, with adventitious roots and sparse, pit-like stem scars (bulb scars). The texture is relatively hard, with a pale yellow-white cross-section, showing a powdery appearance, and the growth rings are brownish-yellow. The bark has yellow-brown dotted resin ducts and radial fissures. It has a distinctive aroma and a slightly bitter, sweet taste.
Raw sun-dried mountain ginseng:The main root and rhizome are of equal length or shorter, shaped like a human character, diamond, or cylindrical, measuring 2-10 cm in length. The surface is grayish-yellow with longitudinal wrinkles, and the upper end has tightly packed, deeply sunken circular transverse wrinkles. The lateral roots are mostly 2, with long, clear fibrous roots and obvious warty protrusions, commonly referred to as “pearl bumps.” The rhizome is slender, with dense stem scars at the top, and the adventitious roots are thicker, resembling jujube pits.
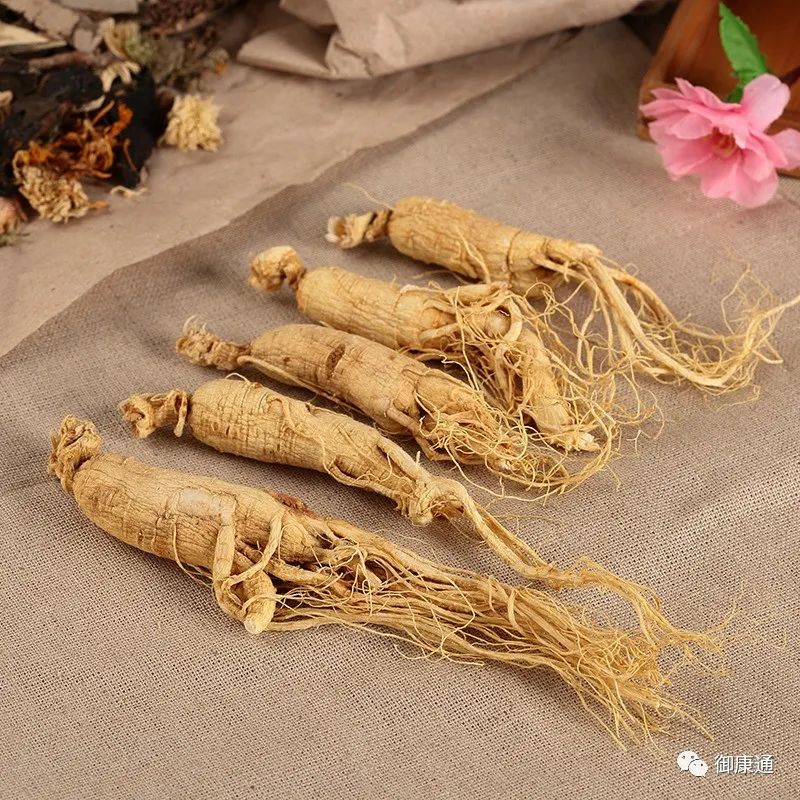

Chemical Components:Contains ginsenoside, ginsenoside (also known as ginseng saponin), ginseng acid, vitamins, inorganic salts, mucilage, sucrose, glucose, fructose, maltose, choline, etc.
Taste and Properties:Sweet, slightly bitter, neutral.
Meridians Entered:Enters the spleen, lungs, and heart meridians.
Storage:Store in a cool, dry place, sealed to prevent pests.
Contraindications:Should not be used with Li Lu (藜芦, lí lú) or Wu Ling Zhi (五灵脂, wǔ líng zhī). Contraindicated in cases of excess syndrome or heat syndrome.
The Effects and Functions of Ginseng
1. Regulating the Central Nervous System: Ginseng can regulate the central nervous system, improving the balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain; it enhances both mental and physical work capacity, increases work efficiency, and has anti-fatigue effects.
2. Enhancing Brain Function: Ginseng can help improve learning and memory abilities due to its components that support cognitive function.
3. Improving Heart Function: Ginseng can increase myocardial contractility, slow the heart rate, and enhance cardiac output and coronary blood flow, providing protection against myocardial ischemia and arrhythmias. It has a significant effect on heart function, cardiovascular health, and blood flow. Ginseng exhibits notable anti-hypoxia effects, and its preparations can effectively counteract sinus bradycardia. Ginsenosides can accelerate lipid metabolism and significantly lower high cholesterol levels. Low doses of ginseng can mildly raise blood pressure in anesthetized animals, while high doses can lower it. Different ginseng preparations enhance the function of isolated frog hearts and the hearts of rabbits, cats, and dogs, improving myocardial weakness during ventricular fibrillation.
4. Blood Sugar Lowering Effects: Ginseng contains ginsenosides and ginseng polysaccharides. Notably, ginsenoside Rb2 has a significant blood sugar-lowering effect, and ginseng polysaccharides (or glycopeptides) are another class of blood sugar-lowering components in ginseng.
5. Enhancing Immune Function: Ginseng contains active components that can regulate and enhance the immune function of the body, benefiting those with weakened immunity.
How to Consume Ginseng for Best Results
There are many ways to consume ginseng. Besides the common method of brewing it as tea, it can also be sliced and chewed, or ground into powder. If using fresh ginseng, it can be juiced. The specific methods of consuming ginseng are as follows:
First, Brew as Tea
This is the most common way to consume ginseng. Slice the ginseng and place an appropriate amount in a cup, add boiling water, cover, and let it steep for half an hour before drinking as tea. The ginseng slices can be steeped multiple times until the flavor diminishes. This method is very simple and can be done in any setting. It is recommended for the general population to consume regularly to improve physical health.
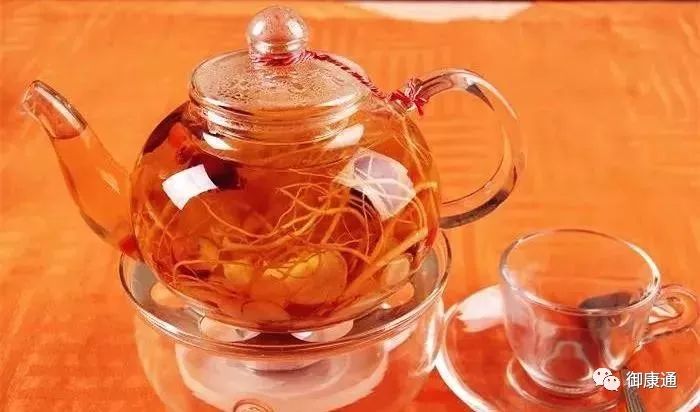

Second, Chewable Slices
We can also choose to slice ginseng thinly and consume it. Take one or two slices and place them in the mouth, allowing them to dissolve before chewing and swallowing. This method is more convenient than brewing and can be done in almost any situation, making it suitable for those who are weak or recovering from serious illness and need to replenish their strength.

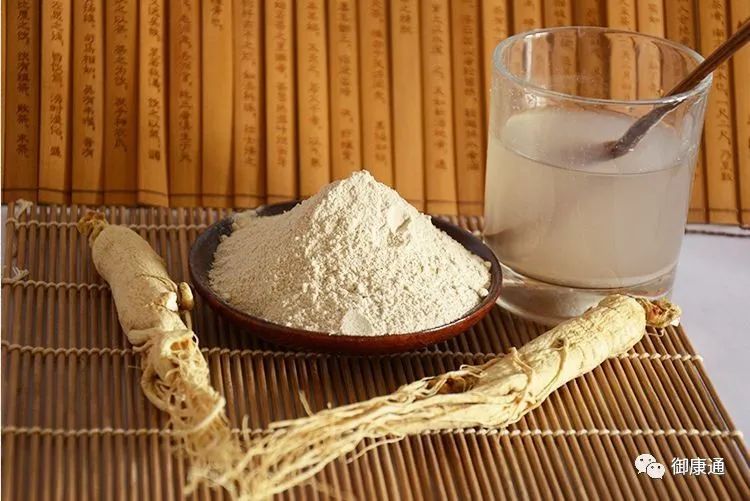
Third, Ground into Powder
We can also dry ginseng and grind it into powder, then take it with boiling water, consuming 3 grams three times a day. Alternatively, the prepared ginseng powder can be placed in empty capsules, taking two capsules daily, also three times a day. This method is suitable for more expensive health supplements, allowing for better utilization of the effective components without waste.

Fourth, Ginseng Juice
Slice fresh ginseng and place it in a container, soaking it in clean water for twenty minutes before adding more clean water, just enough to cover the ginseng. Cover and simmer for one hour before consuming the liquid. This method produces a highly concentrated ginseng juice, which is more effective for nourishing the body and acts quickly, suitable for patients recovering from serious illness who need urgent replenishment. Additionally, ginseng can also be boiled in a pot, which is another good method of consumption.

 Ginseng Recipes
Ginseng Recipes
First: Eight Treasure Ginseng Soup
Ingredients: Ginseng, lotus seeds, apples, snow pears, pineapples, peaches, loofah, green silk, red silk, rock candy, water starch, etc.

Method: Place ginseng in a bowl with clean water and rock candy, steam in a steamer for four hours; clean the lotus seeds and place them in a bowl with water and rock candy, steam until soft. Peel and core the other ingredients and cut them into small pieces. When the water in the pot boils, add the ginseng juice and all the prepared ingredients, finally thicken with rock candy and water starch, and serve.
Second: Steamed Ginseng Chicken
Ingredients: Ginseng, hen, yam slices, shiitake mushrooms, salt, monosodium glutamate, green onion, ginger, ham, chicken broth.

Method: Clean the hen after slaughtering, blanch it in boiling water, and rinse with cold water. Slice the yam, shiitake mushrooms, ham, green onion, and ginger for later use. Soak the ginseng in boiling water, then add clean water and steam for half an hour. Place the hen in a pot, add the other prepared ingredients and seasonings, and add enough chicken broth to cover the hen, then steam in a steamer until the meat is tender.

 Click “Read the Original” for further progress together.
Click “Read the Original” for further progress together.

