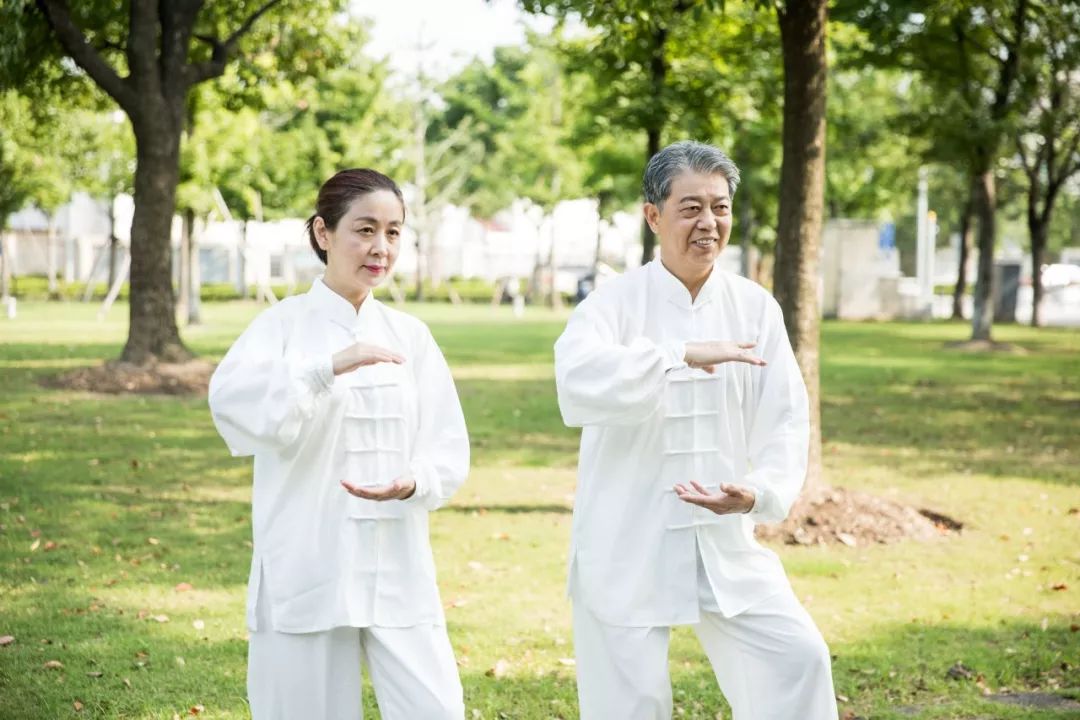

In recent years, with the improvement of people’s living standards and the significant enrichment of material life, health has become an increasingly important topic for humanity. People are trying to maximize their health levels and quality of life.Health preservation, recognized as a necessary path to strengthen the body and prolong life, has naturally become a trend and fashion.The author believes that health preservation is about our dietary habits and daily routines, with the core concept being a rational lifestyle attitude.
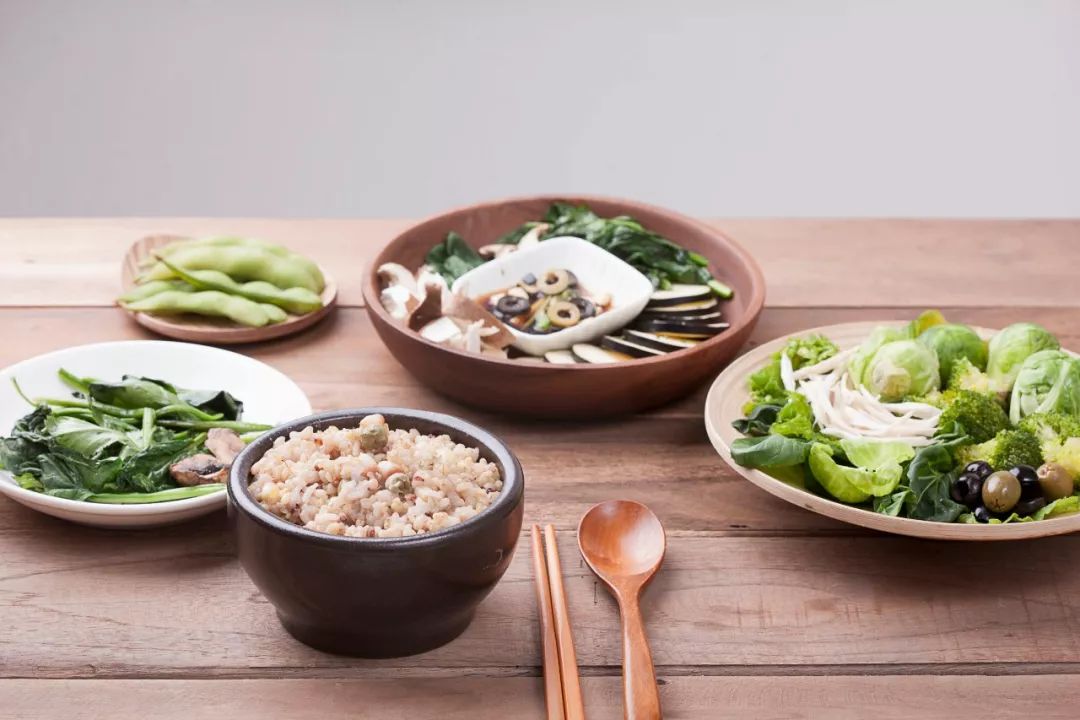


1. Dietary Moderation
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) theory holds that the human body has both congenital essence (xiān tiān zhī jīng) and acquired essence (hòu tiān zhī jīng); only when both are abundant can the body maintain a healthy state. Congenital essence is inherited from the mother and has relative stability; acquired essence consists of nutrients absorbed through digestion. Proper nourishment and appropriate dietary practices can enhance acquired essence and, to some extent, nourish congenital essence, thus maintaining the balance of yin and yang, resulting in a strong body free from diseases. Many illnesses often enter through the mouth, so to maintain a healthy life, one must pay attention to diet. Dietary moderation includes four meanings: cleanliness, timing, quality, and quantity. “Cleanliness” means ensuring the cleanliness and safety of food, selecting safe food sources, and using appropriate washing and cooking methods. “Timing” refers to having regular meal times; this not only ensures adequate nutritional supply and energy but also establishes a routine for digestive fluid secretion, ensuring proper digestion and absorption of food. “Quality” pertains to the variety of food; for healthy individuals, a balanced diet is essential, with attention to the intake of different nutrients while avoiding unhealthy foods. For patients with chronic diseases, individualized dietary plans should be developed to promote recovery and avoid foods that may worsen their conditions. “Quantity” addresses the amount of food intake; it is important to ensure appropriate portions, as overeating can burden the gastrointestinal system, leading to poor digestion and absorption, and causing excess substances to accumulate in the body, resulting in metabolic syndrome. Conversely, extreme dieting for weight loss is also inadvisable.


2. Balance of Work and Rest
The balance of work and rest simply means combining labor with leisure. The functions of human organs are like springs; excessive fatigue beyond the body’s self-regulation and compensation capacity can lead to a decline in organ function and, over time, result in disease. In daily life, people should maintain a regular schedule. TCM emphasizes that “man is in harmony with heaven and earth” and “heaven and man correspond”; humans and nature must follow the same “way” to thrive. From a modern medical perspective, the body’s functions and metabolism have their own rhythms; hormone secretion and functional repair must occur at specific times.


3. Moderate Exercise
Moderate exercise is one of the important measures to keep the body’s functions active and maintain health stability. Many people feel invigorated after exercising, and even sleep quality can improve. Western medical theory suggests that exercise can enhance the immune system, improve cardiopulmonary function, promote the activity of internal organs, and also help relax the mind. TCM theory posits that humans are a unity of yin and yang, with yin and yang generating and restraining each other, maintaining the body’s balance and stability; “when yin is balanced and yang is secreted, the spirit is treated; when yin and yang are separated, the spirit is lost”; harmony and balance of yin and yang are prerequisites for health. “Movement generates yang”; exercise is considered one of the methods to nourish yang. In modern society, the work style is monotonous, the pace is fast, and stress is high, leaving little time for exercise. This lifestyle leads to a deficiency of yang energy, decreased resistance, and insufficient organ function, making it particularly important to maintain moderate exercise.
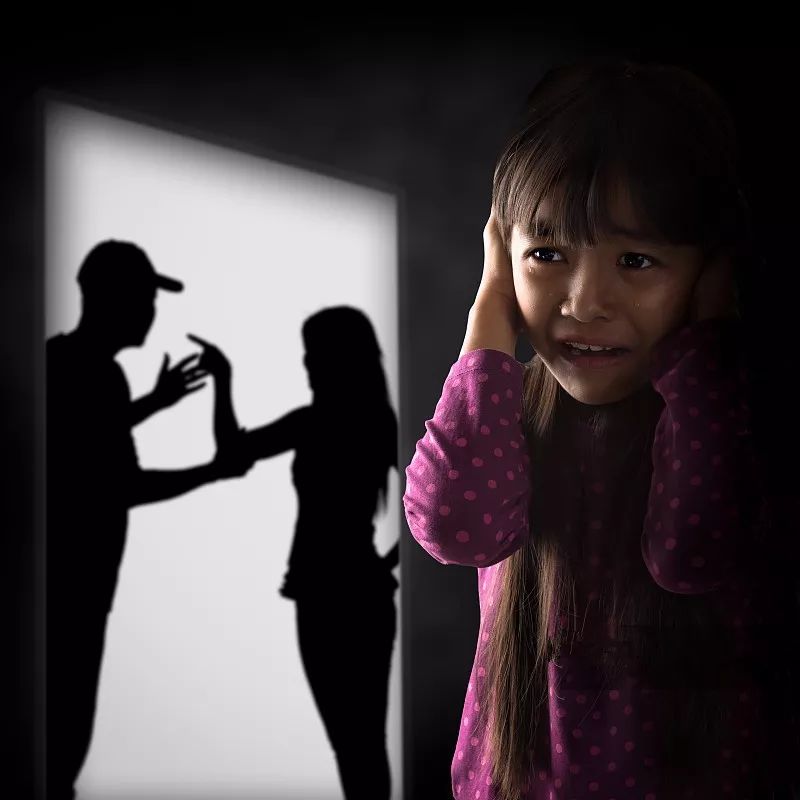


4. Emotional Regulation
People have long recognized the pathogenic effects of excessive emotions. TCM theory elaborates on the pathological changes caused by excessive emotions in the theory of the seven emotions (qī qíng zhì bìng). The “Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Medicine)” states: “Anger causes qi to rise, joy causes qi to relax, sadness causes qi to dissipate, fear causes qi to descend, cold causes qi to contract, heat causes qi to leak, shock causes qi to become chaotic, labor causes qi to be consumed, and thinking causes qi to be exhausted.” Excessive emotions can disrupt the qi mechanisms of the internal organs, leading to pathological changes and various diseases. In daily life, examples abound where emotional changes from arguments or work stress lead to physical discomfort, and extreme cases of stroke or fainting due to intense anger are not uncommon.There is a saying in China: “A smile can take ten years off your life”; many believe that only negative emotions (such as anger, sadness, fear, shock, etc.) can cause diseases, while positive emotions like joy should be beneficial to health. However, this is not entirely true. The “Huangdi Neijing” also states: “Joy harmonizes qi and allows the spirit to flow, thus qi becomes relaxed.” This means that when a person is in a good mood, the qi of the defensive and nutritive systems flows smoothly, but excessive joy can scatter the heart qi. The “Neijing” also mentions that “joy harms the heart.” Thus, it can be seen that even “joy,” if uncontrolled, can lead to disease; the story of Fan Jin passing the imperial examination and becoming mad with joy is a tragic example.Health preservation is not an esoteric TCM theory; it is not a one-time effort and cannot be achieved overnight; health preservation is about the little things in life and requires persistent effort every day. It is a lifelong habit, and health preservation is a rational lifestyle attitude.Share this article 
 ·
·
 Sharing takes just a second
Sharing takes just a second

