In a warm and humid environment, the dampness in the human body can increase, making one feel drowsy, have a poor appetite, or even experience abdominal bloating. Those with pre-existing health conditions may also be affected by this dampness.
1. Where Does Dampness in the Body Come From?
From the External Environment
“Dampness” is easy to understand; when something is wet, it is considered “damp.” However, dampness can be in liquid or gaseous form. For example, during the humid days of spring, clothes do not dry because the humidity in the air is very high. Even a dry piece of clothing hung out will become damp. The internal environment of the body is similar. When the external environment is damp, the internal humidity naturally increases because our mouth and nose need to breathe, and our skin also “breathes.”

When external dampness enters the body, it can normally be regulated and metabolized, which relies on the spleen and stomach’s function. If the spleen and stomach cannot metabolize it, the dampness stagnates in the body, affecting the function of the five organs.
From Unreasonable Diet
Diet has a significant impact on the dampness within the body. Foods that easily generate dampness in the spleen and stomach include greasy and rich meats, hard-to-digest foods, sweets, and cold drinks. Since food enters through the mouth, its digestion and absorption are entrusted to the “spleen and stomach.” Eating too much of the aforementioned foods leads to insufficient spleen and stomach energy, making it unable to process dampness, which results in the accumulation of undigested food in the spleen and stomach, forming new dampness and further obstructing the spleen and stomach’s function.
2. Why is Dampness So Difficult to Eliminate?
Poor Spleen and Stomach Function
The water and dampness in the body are metabolized by the spleen and stomach. Therefore, individuals with poor spleen and stomach function naturally have more dampness than average. When encountering humid weather, the dampness in their bodies increases, putting more burden on the spleen and stomach. If combined with an unreasonable diet, the dampness worsens.
Using Incorrect Methods
If you ask someone from the south what to eat to dispel dampness, they can list many options, such as five-flower tea, adzuki bean and coix seed water, lotus leaf tea, etc. However, they often find that drinking these does not alleviate dampness and may even make them feel weaker. This could be due to using the wrong methods to dispel dampness.
3. How to Determine if There is Dampness in the Body?
Check the Stool
The most well-known sign is sticky stools that are difficult to flush away. Other signs include unformed stools, loose stools, a feeling of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement, or the urge to defecate without being able to do so, resulting in unformed stools.
Check the Tongue
A thick, white tongue coating generally indicates cold dampness, while a thick yellow coating indicates damp-heat. The thicker the coating, the heavier the dampness.
Check the State of Being
Waking up in the morning feeling drowsy, with a heavy head, as if the brain is in a fog; lacking energy, being taciturn, and feeling lethargic.

Check the Skin
Skin manifestations may include excessive oiliness, acne, itching, and rashes.
4. What Problems Can Heavy Dampness Cause?
As the saying goes, “It is easy to remove a thousand cold, but hard to eliminate dampness.” Dampness differs from other evils in the “six qi” such as wind, cold, and dryness in that it is sticky and turbid, easily combining with other evils to create complications. For example, dampness combined with wind can lead to colds and joint issues; dampness combined with cold can cause digestive problems, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain; dampness combined with heat can lead to damp-heat conditions, commonly seen as damp-heat diarrhea, sore throat, and restlessness. Moreover, these combinations are often not simple pairings; they can act simultaneously, such as wind-cold with dampness, wind-heat with dampness, and phlegm-damp conditions.
People are particularly concerned about dispelling dampness from the spleen and stomach because the spleen governs the transformation and transportation of water and dampness, making it most susceptible to dampness. Symptoms in the gastrointestinal tract are also the most apparent. Especially in southern regions, where the climate is humid and hot, the spleen and stomach are often affected by damp evils, leading to nine out of ten people having spleen deficiency. Spleen deficiency further reduces the ability to transform and transport water and dampness, creating a vicious cycle. The spleen is the source of postnatal vitality; when it is damaged by damp evils, it also affects the liver’s regulation, the lung’s dispersing function, and the kidney’s receiving function.
Recently, many people have experienced lingering “after-effects” after COVID-19 infection, such as cough, insomnia, and gastrointestinal issues that persist. On one hand, the viral evil itself harms the spleen, stomach, and lung qi, and on the other hand, improper medication can exacerbate these issues, making them difficult to resolve. Now, the humid weather of spring may worsen or prolong these symptoms.
5. Understand the Methods to Eliminate Dampness Before Trying!
When it comes to dispelling dampness, people can at least name a few dietary therapies, yet they still feel that dampness lingers. In fact, TCM methods for dispelling dampness have specific principles. Common methods include promoting diuresis, transforming dampness, overcoming dampness, and drying dampness. Although the wording differs slightly, the treatment plan varies for each individual’s constitution. Below are some simple approaches suitable for daily use:
Promote Water and Drain Dampness
Promoting water and draining dampness essentially means regulating the water pathways to expel dampness through urine and sweat, especially suitable for conditions like edema, urinary retention, and diarrhea caused by excessive internal dampness.
What is water disease? In TCM, water is referred to as “jinye” (津液), which is essential for nourishment, a component of blood, a metabolic substance, and one of the foundations for sustaining life activities. If the proportion of water in the body exceeds seventy percent and there is stagnation or overflow, it is considered a water disease.Wu Ling San (Five-Ingredient Powder) is commonly used for diarrhea, urinary tract infections, night sweats, chronic nephritis-related edema, ascites due to liver cirrhosis, cardiac edema, acute enteritis, urinary retention, and hydrocephalus.
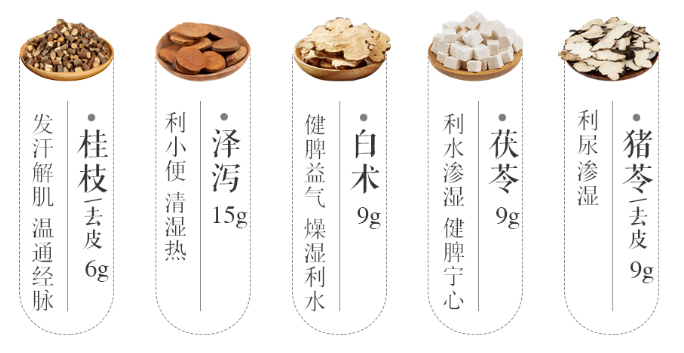
【Commonly Used Herbs】Poria (茯苓, Fuling), Alisma (泽泻, Zexie), Adzuki Bean (赤小豆, Chixiaodou), Plantago Seed (车前子, Cheqianzi), Coix Seed (薏苡仁, Yiyiren), Winter Melon Skin (冬瓜皮, Dongguapi), Corn Silk (玉米须, Yumi xu).
【Dietary Recommendation】Adzuki Bean and Carp Soup
Ingredients: 50g adzuki beans, 2g dried tangerine peel, 3 slices of ginger, 1 carp.
Method: Soak the adzuki beans for 30 minutes; clean the carp, remove the internal organs, and pan-fry both sides; place all ingredients in a pot, add an appropriate amount of water, and simmer for 1 hour, then season to taste.
Warm Yang and Transform Dampness
Warm yang and transform dampness can be likened to drying a damp towel in the sun. Everyone knows that clothes do not dry easily in winter due to low temperatures, which prevent the moisture from evaporating. The same applies to the human body; those who are both cold and damp find it difficult to expel dampness.
Such individuals should adopt the approach of warming yang and transforming dampness, represented by the formula: Zhen Wu Tang (真武汤): 9g white poria (白茯苓, Bai Fuling), 9g white peony (白芍, Bai Shao), 6g white atractylodes (白术, Bai Zhu), 9g ginger (生姜, Sheng Jiang), and 9g prepared aconite (炮附子, Pao Fuzi) (first decoct for 40 minutes).
Regular sun exposure and sweating can open the skin’s pores, allowing dampness to evaporate. Those with heavy cold dampness should focus on warming yang and transforming dampness.
【Commonly Used Herbs】Codonopsis (党参, Dangshen), Astragalus (黄芪, Huangqi), Euryale (芡实, Qianshi), Atractylodes (白术, Bai Zhu), Cuscuta (菟丝子, Tusizi), Dried Ginger (干姜, Ganjiang), Longan (桂圆, Guiyuan), Sichuan Pepper (花椒, Huajiao), etc.
【Dietary Recommendation】Ginseng and Goji Berry Porridge
Ingredients: 10g codonopsis, 10g longan, 10g euryale, 150g japonica rice.
Method: Slice the codonopsis and soak it with euryale for 15 minutes, then cook all ingredients with the japonica rice to make porridge.
Fragrant Transformation of Dampness
In traditional Chinese medicine, there is a category of herbs with unique fragrances. The distinctive aromatic scent can dispel turbid qi, and since dampness is inherently turbid, it can also transform dampness. Additionally, the aromatic scent can awaken the spleen, enhancing its ability to transform and transport, which further aids in dispelling dampness. Those who experience abdominal bloating, lack of appetite, a heavy body, and low energy can try the fragrant transformation of dampness method.
【Commonly Used Herbs】Agastache (藿香, Huoxiang), Eupatorium (佩兰, Peilan), Atractylodes (苍术, Cangzhu), Amomum (草果, Caoguo), Wood Fragrance (木香, Muxiang), Cardamom (豆蔻, Doukou), Sand Ginger (砂仁, Sharen), etc.
【Dietary Recommendation】Sand Ginger and Dried Tangerine Peel Carp Soup
Ingredients: 5g dried tangerine peel, 5g sand ginger, 10g cilantro, 3 slices of ginger, 1 carp.
Method: Crush the sand ginger and cut the cilantro into sections; clean the carp, remove the internal organs, and cook it with the dried tangerine peel and ginger in an appropriate amount of water for about 1 hour; add the sand ginger and cilantro, cook for another 5 minutes, then season and serve.
Clear Heat and Dispel Dampness
In TCM, dampness is considered a yin evil, while heat is a yang evil, and their natures are opposite. When combined, they can lead to a situation of damp-heat, requiring the addition of heat-clearing and detoxifying herbs to assist in dispelling dampness. Individuals exhibiting symptoms such as diarrhea, sticky stools, acne, dry mouth, and a yellow, thick tongue coating may benefit from this approach.
【Commonly Used Herbs】Lotus Leaf (荷叶, He Ye), Artemisia (茵陈, Yincheng), Mulberry Leaf (桑叶, Sang Ye), Honeysuckle (金银花, Jinyinhua), White Flower Snake Tongue Grass (白花蛇舌草, Baihuasheshecao), White Reed Root (白茅根, Baimaogen), Cotton Flower (木棉花, Mumianghua), Sophora Flower (槐花, Huaihua), etc.
【Dietary Recommendation】Mulberry and Chrysanthemum Drink
Ingredients: 5g mulberry leaves, 3 chrysanthemum flowers, steep in tea or boil in water to drink.

Strengthen the Spleen and Promote Dampness Transformation
Strengthening the spleen and promoting dampness transformation refers to enhancing the spleen and stomach’s ability to metabolize dampness. This is particularly important for individuals with inherently weak spleen and stomach function, as addressing spleen and stomach issues is essential for effectively resolving dampness caused by environmental and dietary factors.
【Commonly Used Herbs】Chinese Yam (山药, Shanyao), Lotus Seed (莲子, Lianzi), Hyacinth Bean (白扁豆, Bai Biandou), Jujube (大枣, Dazao), Five-Finger Peach (五指毛桃, Wuzhimaotao).
【Dietary Recommendation】Five-Finger Peach and Pork Rib Soup
Ingredients: 20g five-finger peach, 10g lotus seed, 10g dried yam, 2 slices of ginger, 200g pork ribs.
Method: Soak the five-finger peach, lotus seed, and dried yam for 15 minutes, blanch the pork ribs, then add all ingredients to a pot with an appropriate amount of water and simmer for about 1 hour, then season and serve.
As the saying goes, “It is easy to remove a thousand cold, but hard to eliminate dampness.” The removal of dampness is indeed not easy, especially for people in southern regions who are often in damp environments. Dispersing dampness has become a necessary aspect of daily health maintenance. Mastering certain methods for dispelling dampness can aid in daily health care, but when physical discomfort is evident, it is essential to seek medical help and not delay treatment for illness.
“External Dampness” and “Internal Dampness”
In fact, “dampness” is a concept in TCM etiology, referring to pathogenic factors that are heavy, turbid, sticky, and tend to descend, also known as damp evil. Damp evil can be categorized into “external dampness” and “internal dampness.”
“External Dampness”
Related to weather and environment, such as humid climates, exposure to rain, or long-term residence in damp environments, leading to external damp evils invading the body;
“Internal Dampness”
Refers to dampness generated within the body, often due to the spleen’s failure to transport, the lung’s failure to disperse, and the kidney’s failure to warm, leading to the accumulation of water and dampness in the body. The primary issue is the dysfunction of the spleen’s transport function, known as “spleen deficiency leading to dampness.”
Although external and internal dampness differ, they share common characteristics in clinical manifestations and often influence each other during the disease process. External dampness can harm the spleen, leading to internal dampness, while spleen dysfunction can lead to the accumulation of water and dampness, making the body more susceptible to external dampness. Moreover, damp evil often coexists with wind, cold, and heat evils, complicating treatment.
What Obvious Symptoms Indicate Heavy Dampness in the Body?
01“Heavy and Turbid” State
Feeling heavy-headed, with aching limbs and a tendency to feel drowsy;
02“Sticky” State
Sticky mouth, sweet taste, sticky skin, unsatisfactory bowel movements, difficult urination, teeth marks on the tongue, and a slippery tongue coating;
03“Dampness Obstructing the Spleen” State
Reduced appetite, fullness in the chest, abdominal bloating, and even symptoms like limb edema and skin eczema.
Additionally, humid weather can easily trigger the recurrence and exacerbation of chronic diseases such as rheumatism, joint pain, and muscle pain.
How to Effectively Dispel Dampness in Spring?
01Avoid “External Dampness”
Avoid living in excessively damp rooms, keep windows open on sunny days to ensure air circulation, and use dehumidifiers regularly during rainy weather. Keep bedding, sheets, and clothes dry and fresh, and regularly sun-dry them. Avoid getting wet in the rain, and pay special attention to warmth during cold spring weather. After bathing or washing hair, dry off promptly.
02Regulate “Internal Dampness”
TCM believes that the spleen prefers dryness and dislikes dampness; if the spleen is deficient, it is prone to generate dampness. Therefore, individuals with “internal dampness” should eliminate dietary habits that harm the spleen and stomach’s transport function, such as consuming raw, cold, sweet, and greasy foods, and excessive alcohol. In daily meals, one can choose TCM dietary therapies that have spleen-strengthening and damp-dispelling effects, such as poria, coix seed, yam, adzuki beans, lotus leaves, and cotton flowers.
Additionally, TCM moxibustion can warm yang, tonify qi, strengthen the spleen, and warm the kidneys, alleviating symptoms like poor appetite, abdominal bloating, diarrhea, and fatigue caused by spleen deficiency and damp accumulation. Soaking feet in water boiled with mugwort can help expel cold dampness from the body. Moderate exercise is also an effective method for dispelling dampness, but those with heavy dampness may feel fatigued, so the choice of exercise form and intensity should be appropriate, such as yoga, Ba Duan Jin, or aerobic exercise, where slight sweating can help expel dampness from the body.

