| There are many types of herbs in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that serve dual purposes as both medicine and food. These herbs possess medicinal value and can also be used as ingredients in daily meals. Below are some common medicinal and edible herbs along with brief introductions: |

Shan Yao (Dioscorea opposita)– Strengthens the spleen and benefits the stomach, restores physical strength, lowers blood sugar.

Shan Yao has a sweet taste and neutral nature; it enters the lung, spleen, and kidney meridians; it is neither drying nor greasy; it has the effects of strengthening the spleen, nourishing the lungs, benefiting the stomach, tonifying the kidneys, solidifying essence, strengthening bones, calming the mind, and promoting longevity. It is mainly used to treat symptoms such as spleen and stomach deficiency, poor appetite, chronic diarrhea, lung qi deficiency, kidney qi deficiency, and soreness of the lower back and knees. It can be consumed by the general population.【Properties and Meridian Entry】Neutral in nature, sweet in taste. Enters the spleen, lung, and kidney meridians.【Functions and Indications】Tonifies the spleen and nourishes the stomach, generates fluids and benefits the lungs, tonifies the kidneys and astringes essence. It belongs to the category of tonifying qi herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage: 15-30 grams, decocted for internal use. Used for treating spleen deficiency with poor appetite, chronic diarrhea, lung deficiency with cough, kidney deficiency with nocturnal emissions, leukorrhea, frequent urination, and thirst due to deficiency heat. Fried Shan Yao is used to tonify the spleen and strengthen the stomach, treating spleen deficiency with poor appetite, diarrhea, and excessive leukorrhea.【Contraindications】Use with caution in cases of dampness and fullness or with real pathogens and accumulation.


Shan Zha (Crataegus pinnatifida):Strengthens the stomach, aids digestion, promotes qi circulation, disperses blood stasis, and reduces lipids.

Shan Zha can promote digestion and regulate qi and blood, showing significant efficacy for symptoms such as excessive meat and greasy foods, and abdominal distension. Shan Zha can also be made into jams and candied hawthorn, which are popular among people.【Properties and Meridian Entry】Slightly warm in nature, sour and sweet in taste. Enters the spleen, stomach, and liver meridians.【Functions and Indications】Promotes digestion and strengthens the spleen, regulates qi and disperses blood stasis. It belongs to the category of digestive herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage: 6-12 grams, decocted for internal use; or in pills or powders. For external use: appropriate amount, decocted for washing or applied as a poultice. Used for treating food stagnation from meat, pediatric milk accumulation, abdominal pain, dysentery, diarrhea, dysmenorrhea, postpartum blood stasis abdominal pain, and hyperlipidemia.【Contraindications】Use with caution in those with spleen and stomach deficiency.



Hong Zao (Ziziphus jujuba):Tonifies qi and blood, replenishes vitamin C.

Hong Zao is rich in nutrients, containing vitamin C, iron, calcium, etc., and can nourish blood and qi, calm the heart, and soothe the mind. It is often used in porridge, soups, or eaten directly as a snack.【Properties and Meridian Entry】Warm in nature, sweet in taste. Enters the spleen, stomach, and heart meridians.【Functions and Indications】Tonifies the middle and benefits qi, nourishes blood and calms the mind. It belongs to the category of tonifying qi herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage: 6-15 grams, decocted for internal use. Used for treating spleen deficiency with poor appetite, insufficient qi and blood, fatigue, and diarrhea in women.【Contraindications】Use with caution in cases of excessive dampness, phlegm accumulation, food stagnation, intestinal parasites, and dental pain, as well as in cases of phlegm heat cough.


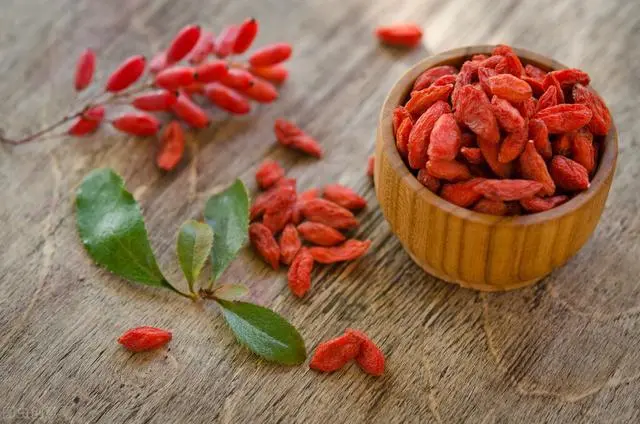
Gou Qi Zi (Lycium barbarum):Nourishes the liver and kidneys, brightens the eyes.

Gou Qi Zi is rich in vitamin C and carotene, commonly used to nourish the liver and kidneys, and improve eyesight. It can be brewed as tea or used as a cooking ingredient.Lotus seeds: Lotus seeds are rich in protein, calcium, phosphorus, etc., and are often used to nourish the heart and spleen, calm the mind, and stabilize the will. Lotus seed soup and lotus seed porridge are common medicinal dishes.【Properties and Meridian Entry】Neutral in nature, sweet in taste. Enters the liver and kidney meridians.【Functions and Indications】Nourishes the liver and kidneys, benefits essence, and brightens the eyes. It belongs to the category of tonifying yin herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage: 6-12 grams, decocted for internal use; or in pills, powders, pastes, or wine. Used for treating deficiency of essence, soreness of the lower back and knees, dizziness, tinnitus, internal heat with thirst, blood deficiency with yellowing, and unclear vision.【Contraindications】Use with caution in cases of external pathogens with real heat, and in those with spleen deficiency and diarrhea.



Qian Shi (Euryale Fox):Strengthens the spleen, benefits the stomach, tonifies qi, and nourishes blood.

Qian Shi is rich in starch and protein, and has the effects of nourishing the spleen and stomach, and tonifying the kidneys. It is often used in porridge or as a filling for pastries.
【Properties and Meridian Entry】Neutral in nature, sweet and astringent. Enters the spleen and kidney meridians.【Functions and Indications】Benefits the kidneys, solidifies essence, tonifies the spleen, stops diarrhea, and eliminates dampness. It belongs to the category of astringent herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage for internal use: decocted, 15-30 grams; or in pills, powders, and can also be cooked in porridge. Used for treating nocturnal emissions, frequent urination, spleen deficiency with chronic diarrhea, leukorrhea, and dampness.【Contraindications】Contraindicated in cases of urinary difficulty and caution in cases of food stagnation.



Long Yan Rou (Dimocarpus longan):Benefits qi and blood, enhances memory, calms the mind.

Long Yan Rou (Longan) has the effects of nourishing the heart and blood, calming the mind, and is very suitable for those with insufficient qi and blood, palpitations, and insomnia. Dried longan and longan porridge are common ways to consume it.【Properties and Meridian Entry】Warm in nature, sweet in taste. Enters the heart and spleen meridians.【Functions and Indications】Tonifies the heart and spleen, nourishes blood and calms the mind. It belongs to the category of tonifying qi herbs.【Clinical Applications】Dosage: 10-15 grams, decocted for internal use; or made into syrup; or soaked in wine; or in pills or powders. Used for treating heart and spleen deficiency with palpitations, forgetfulness, diarrhea, edema, and insomnia due to insufficient qi and blood; dry cough with little phlegm, hoarseness, and dry mouth and throat due to lung yin deficiency. Clinically used for nourishing, inner ear vertigo, digestive system diseases, and coronary heart disease.【Contraindications】Contraindicated in cases of phlegm-heat in the spleen and stomach, damp stagnation, digestive disorders, nausea, and vomiting. Pregnant women, especially in early pregnancy, should avoid consuming longan to prevent fetal movement and premature birth. Additionally, due to its high glucose content, it is not recommended for diabetics.


A happy mood is the first element of health.
A duck and a crab race to the finish line, hard to tell who wins. The referee says: “Let’s play rock-paper-scissors.” The duck angrily replies: “Damn, are you counting on me? I always lose to scissors!”
It is important to note that while these herbs have dual medicinal and edible properties, attention must still be paid to the balance of their medicinal value and safety in consumption. Some herbs may have side effects or contraindications in specific situations, so it is advisable to consult a professional doctor or TCM practitioner before use.
| =====Previous Classics=====TCM – Efficacy and Contraindications of Xiang YuanTCM – Efficacy and Contraindications of Jiang XiangTCM – Efficacy and Contraindications of Bai Jiang CanTCM – Effects and Efficacy of Feng Gui Dou CaoTCM – Efficacy and Functions of Huang BaiTCM – Efficacy and Contraindications of Tan XiangTCM – Efficacy and Functions of Ji Ji CaoTCM Basic Theory (Episodes 1-3) VideoCommon Medications List for ConstipationEffects and Functions of Jin Hua Fu Brick Tea |

Note:Please do not self-medicate; follow medical advice.
If you find this article valuable, feel free to share it with more friends!

