Codonopsis (Dang Shen) is the dried root of the plants Codonopsis pilosula, Codonopsis tangshen, or Codonopsis lanceolata, belonging to the Campanulaceae family. Codonopsis has a sweet flavor and a neutral nature, entering the Spleen and Stomach meridians. Its effects include tonifying the Spleen, benefiting the Lung, nourishing the blood, and generating fluids.

Codonopsis is neutral and not overly drying or greasy, with effects similar to Ginseng but milder. According to the “Bencao Zhengyi,” it states: “Codonopsis can tonify the Spleen and nourish the Stomach, moisten the Lung and generate fluids, and strengthen the Middle Qi, which is not far from Ginseng. Its most valuable aspect is that it strengthens the Spleen without being drying, nourishes the Stomach Yin without being damp, moistens the Lung without causing cold, nourishes the blood without being overly rich, and avoids the drawbacks of excessive dryness.” Therefore, it is often used clinically as a substitute for Ginseng. However, Ginseng has a stronger Qi-tonifying effect, especially in greatly replenishing the original Qi, reviving Yang, and rescuing from collapse, and it has the functions of calming the spirit, stabilizing the soul, brightening the eyes, and enhancing intelligence, which Codonopsis does not possess. On the other hand, Codonopsis excels in nourishing blood, which is its strength, surpassing Ginseng in this regard.

Distribution
Based on different origins and sources, the mainstream Codonopsis medicinal materials in the market are divided into “Lu Codonopsis,” “White Strip Codonopsis,” “Patterned Codonopsis,” and “Banqiao Codonopsis.”
Lu Codonopsis: Mainly distributed in Huguan County and Ping Shun County of Changzhi City, Shanxi Province, and surrounding areas, sourced from Codonopsis pilosula;
White Strip Codonopsis: Mainly distributed in Weiyuan County, Longxi County, and Lintao County of Dingxi City, Gansu Province, sourced from Codonopsis pilosula;
Patterned Codonopsis: Mainly distributed in Wenxian, Lixian, Wudu District, Dangchang County, and Zhouqu County of Longnan City, Gansu Province, and Jiuzhaigou County and Pingwu County of Sichuan Province, sourced from Codonopsis tangshen;
Banqiao Codonopsis: Mainly distributed in Banqiao Town and surrounding areas of Enshi City, Hubei Province, sourced from Codonopsis lanceolata.



Harvesting
The optimal harvesting time is from late October to early November (after the frost). White Strip Codonopsis (Lu Codonopsis) should be harvested after 2-3 years; Codonopsis lanceolata should be harvested after 3 years for the best yield; Patterned Codonopsis can be harvested after 5 years (including 2 years of seedling growth), generally requiring 6 years to improve the quality of top-grade and first-grade products. After 10 days post-frost, the root skin of Patterned Codonopsis begins to thicken, and the quality declines, so harvesting should not be delayed.

Processing
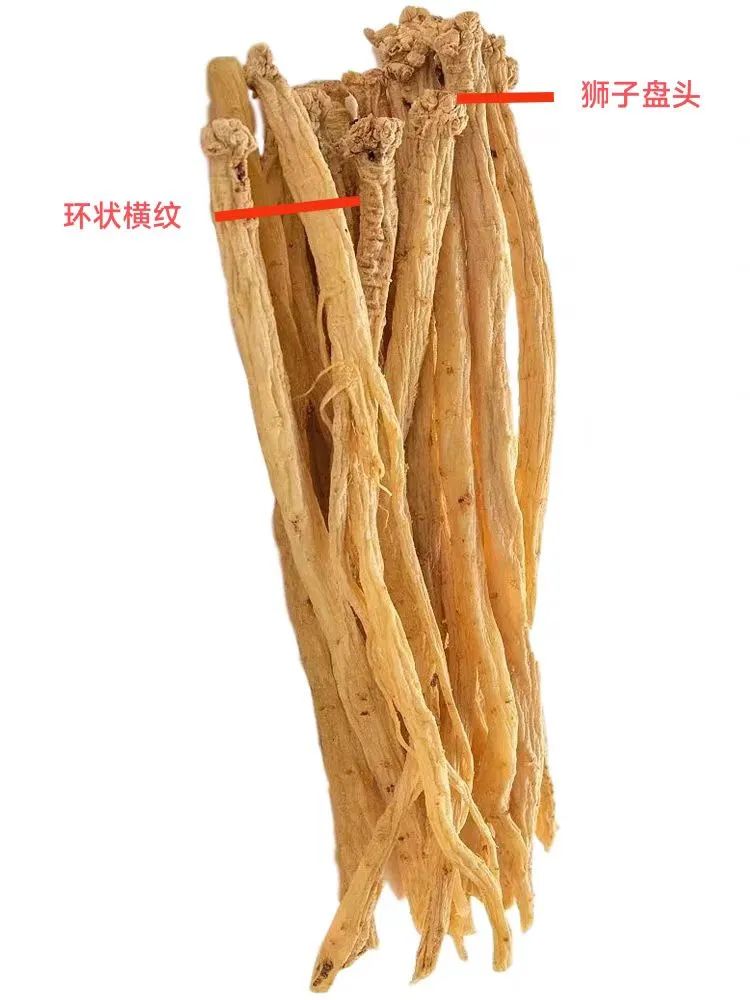
Traditional Drying Process: After classifying by thickness and length, the roots are sun-dried until the surface is slightly moist and soft (able to bend without breaking). The Codonopsis is held and kneaded by hand or with a wooden board, then dried again, repeating this process until fully dried. After each kneading, it should be spread out to prevent mold. Once dried to about 80-90%, it can be stored. Kneading prevents the separation of the medicinal material’s skin, resulting in a product that is “single, independent, pen-like, orange-yellow, with a mudfish head, chicken skin wrinkles, and chrysanthemum heart,” which is of excellent quality and easy to store. “Kneading while drying” prevents the occurrence of hollow sections during the drying process.

Characteristics
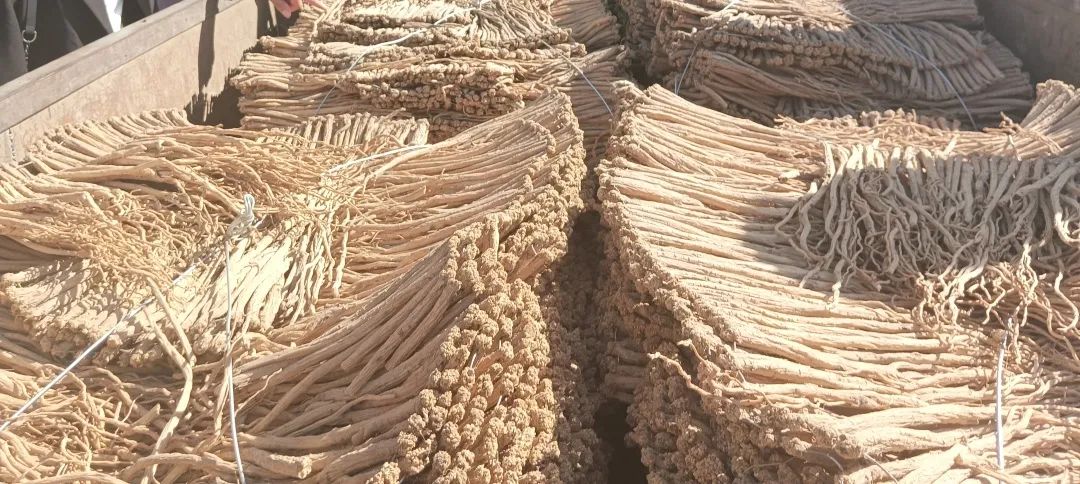
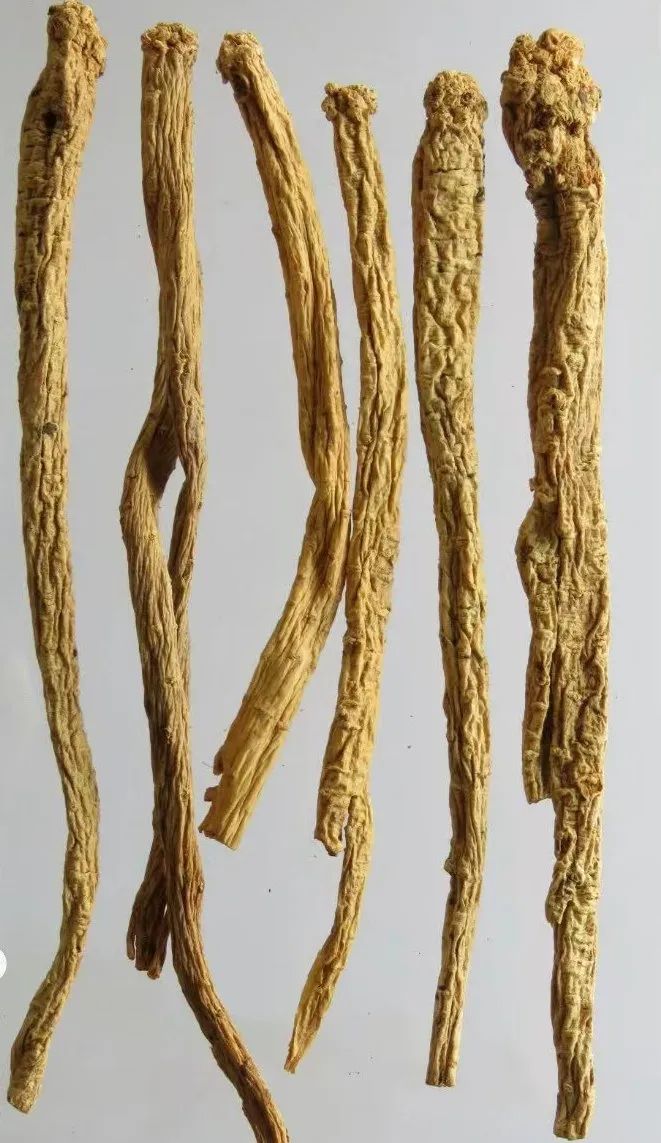
White Strip Codonopsis, Lu Codonopsis:They are long cylindrical, slightly curved, measuring 10-35 cm in length and 0.4-2 cm in diameter. The surface is gray-yellow, yellow-brown to gray-brown, with numerous warty protrusions at the root tip and buds, each bud scar having a depressed round dot at the top; below the root tip, there are dense ring-like transverse wrinkles, gradually becoming sparse downwards, some reaching half the total length, while cultivated varieties have few or no ring-like transverse wrinkles; the entire root has longitudinal wrinkles and scattered transverse long pore-like protrusions, with black-brown gelatinous material often found at the broken root ends. The texture is slightly soft or slightly hard with some toughness, the cross-section is slightly flat, with cracks or radial patterns, the skin part is light brown-yellow to yellow-brown, and the wood part is light yellow to yellow, presenting a “chrysanthemum heart” shape. It has a special aroma and a slightly sweet taste.
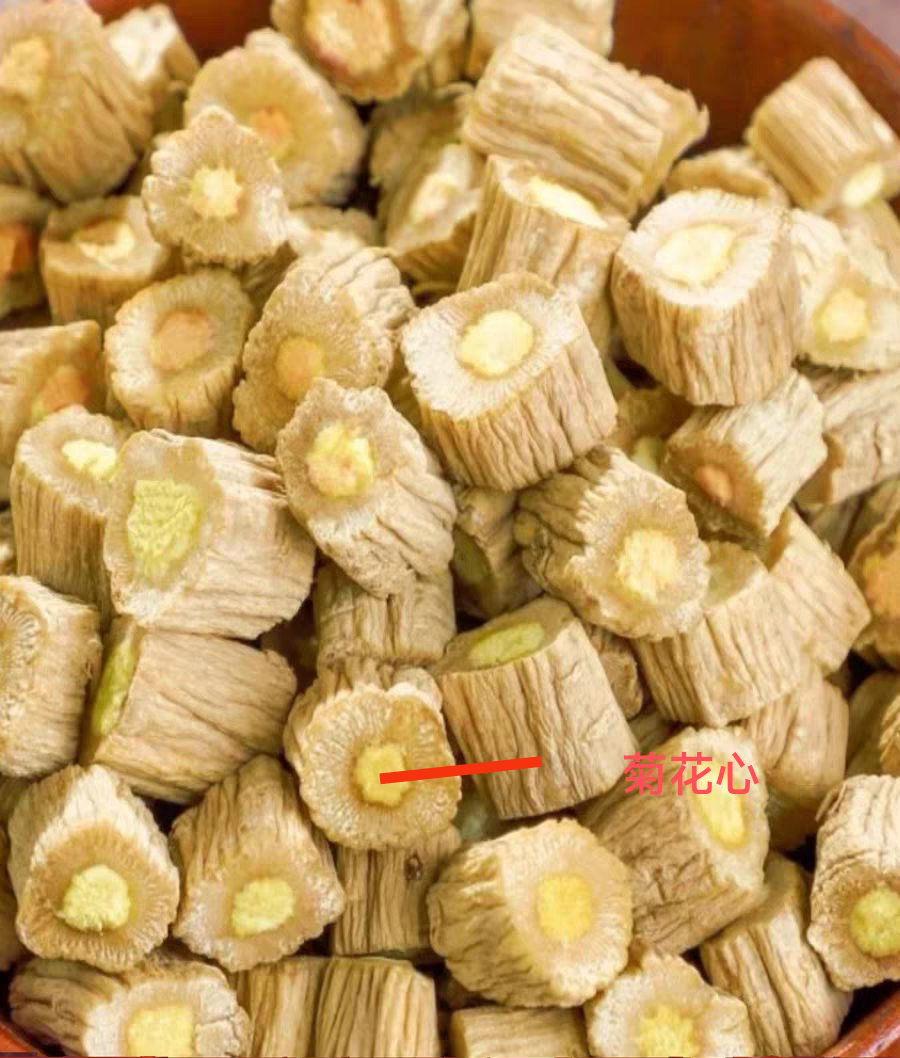


Patterned Codonopsis (Western Codonopsis):Measuring 10-35 cm in length and 0.5-2.5 cm in diameter. The surface is yellow-white to gray-yellow, with a slightly soft or slightly hard texture and some toughness, with dense ring-like transverse wrinkles often reaching more than half the total length. The cross-section has many cracks, the skin part is gray-white to light brown, and the wood part is light yellow.
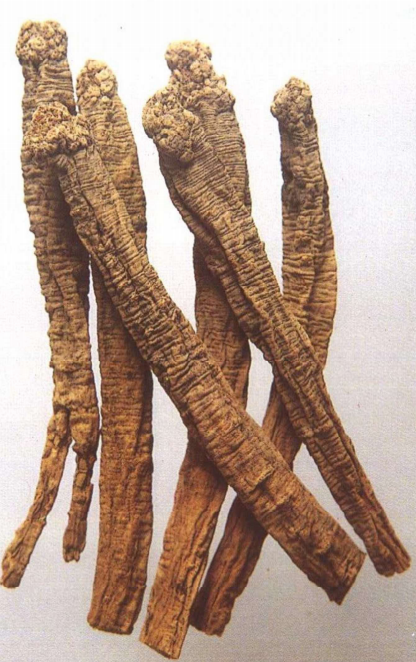


Banqiao Codonopsis:Measuring 10-45 cm in length and 0.5-2 cm in diameter. The surface is gray-yellow to yellow-brown, with obvious irregular longitudinal grooves. The texture is relatively soft yet firm, with fewer cracks in the cross-section, the skin part is yellow-white, and the wood part is light yellow.
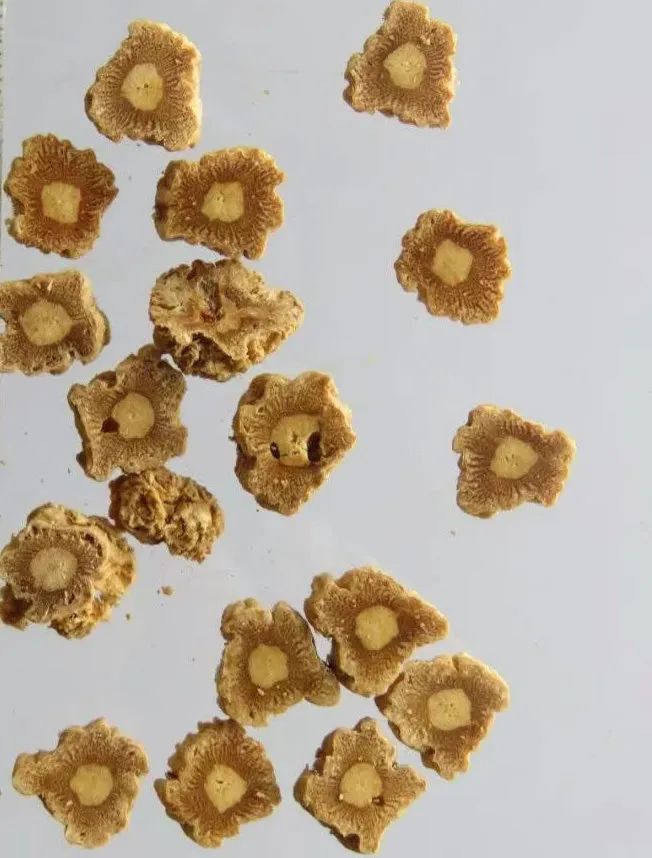



Codonopsis in Dietary Therapy
Health supplements and health foods made primarily from Codonopsis include the following two categories.
Medicinal Dishes
1. Codonopsis Paste: First recorded in “De Pei Bencao.” Use 500 g of Codonopsis, 250 g of Glehnia, and 200 g of longan meat, simmered in water until it can drip into beads. Store in porcelain containers. Take one wine cup’s worth daily, mixed with hot water on an empty stomach, or can be added to other soups or medicines. It has the effects of clearing Lung Qi, tonifying original Qi, improving voice, and strengthening muscles;
2. Codonopsis and Angelica Stewed Chicken: From “Qiankun Shengyi.” Use 15 g of Codonopsis, 15 g of Angelica, and one chicken (about 1000 g), with appropriate amounts of green onion, ginger, yellow wine, and salt. Clean the chicken, remove the skin and internal organs. Wash Codonopsis and Angelica, and stuff them with green onion segments and ginger strips into the chicken’s cavity. Place the chicken in a clay pot, add water, and simmer on low heat until tender. Serve in portions, used for treating Qi and blood deficiency, pale complexion, fatigue, and postpartum blood loss;
3. Codonopsis and Astragalus Stewed Black Chicken: Nourishes Qi, replenishes blood, and strengthens deficiency;
4. Codonopsis and Dried Tangerine Peel Stewed Rooster: Has the function of tonifying deficiency and benefiting Qi;
5. Codonopsis and Red Dates Stewed Pork Ribs: Nourishes Qi and blood, benefits health, used for physical weakness;
6. Codonopsis and Astragalus Pork Soup (also known as “Ten Complete Nourishing Soup”): Ingredients include pork, pig stomach, pig skin, cuttlefish, chicken and duck feet (wings), Codonopsis, roasted Astragalus, cinnamon, cooked Rehmannia, fried Atractylodes, Angelica, etc. It has the effects of warming and tonifying Qi and blood, nourishing, used for Qi and blood deficiency, pale complexion, and chronic illness;
7. Codonopsis, Fox Nut, and Stewed Pig Kidney: Can treat nephritis and proteinuria;
8. Codonopsis, Chinese Yam, and Angelica Stewed Pig Kidney: Nourishes blood and Qi, tonifies the kidney, used for Qi and blood deficiency, palpitations, shortness of breath, insomnia, and spontaneous sweating;
9. Codonopsis and Angelica Steamed Eel: Has the effects of warming and tonifying Qi and blood, promoting blood circulation, and strengthening muscles and bones, used for Liver and Kidney deficiency, lower back pain, and fatigue.
Drinks
1. Codonopsis Porridge: Cook Codonopsis with rice, add an appropriate amount of brown sugar, nourishes Qi, nourishes blood, and strengthens the Spleen. Suitable for those with weak Middle Qi, post-illness weakness, poor appetite, and indigestion;
2. Codonopsis Drink: Boil Codonopsis with Ophiopogon, Schisandra, and red dates for a drink, has certain efficacy for cardiovascular diseases, suitable for the elderly to consume regularly;
3. Codonopsis and Red Dates Tea: Has certain efficacy for Spleen and Stomach weakness, Qi and blood deficiency, and can also beautify the skin;
4. Codonopsis and Fried Rice together boiled as a tea substitute: Can benefit Qi and strengthen the Spleen, aid digestion, used for post-illness weakness, poor appetite, and indigestion; can also regulate chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcers;
5. Double Codonopsis Longan Juice: Use 500 g of Codonopsis, 250 g of Glehnia, and 250 g of longan meat, boil in water for a concentrated juice, take one wine cup daily, mixed with hot water on an empty stomach. Treats original Qi deficiency, low voice, and weakness in limbs;
6. Codonopsis and Longan Wine: Soak Codonopsis and longan meat in white wine, has the effects of tonifying the center, benefiting Qi, nourishing blood, and calming the spirit, used for Qi and blood deficiency, weakness in limbs, insomnia, and forgetfulness.

Is Ming Codonopsis the Same as Codonopsis?
Ming Codonopsis and Codonopsis differ by only one character, leading many to mistakenly believe they are the same herb. However, they have many differences. Let’s understand what Ming Codonopsis is:
Ming Codonopsis is the dried root of the plant of the Apiaceae family. It is slender cylindrical, long fusiform, or irregularly shaped, measuring 6-20 cm in length and 0.5-2 cm in diameter. The surface is yellow-white or light brown, smooth or with longitudinal grooves and root scars, some with reddish-brown spots. The texture is hard and brittle, with a waxy cross-section, the skin part is thin, yellow-white, and may easily separate from the wood part, which is whitish. It has a faint aroma and a bland taste.
Properties and Efficacy: Sweet, slightly bitter, slightly cold. It enters the Lung, Spleen, and Liver meridians. It moistens the Lung, resolves phlegm, nourishes Yin, harmonizes the Stomach, calms the Liver, and detoxifies. It is used for Lung heat cough, vomiting and regurgitation, poor appetite, dry mouth, red eyes, dizziness, and toxic sores.
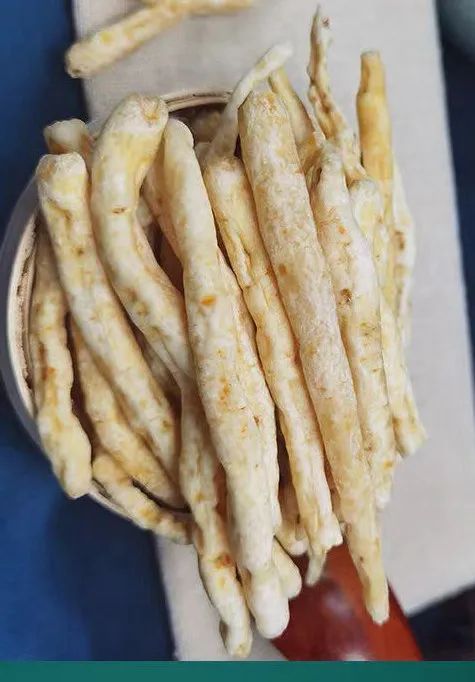
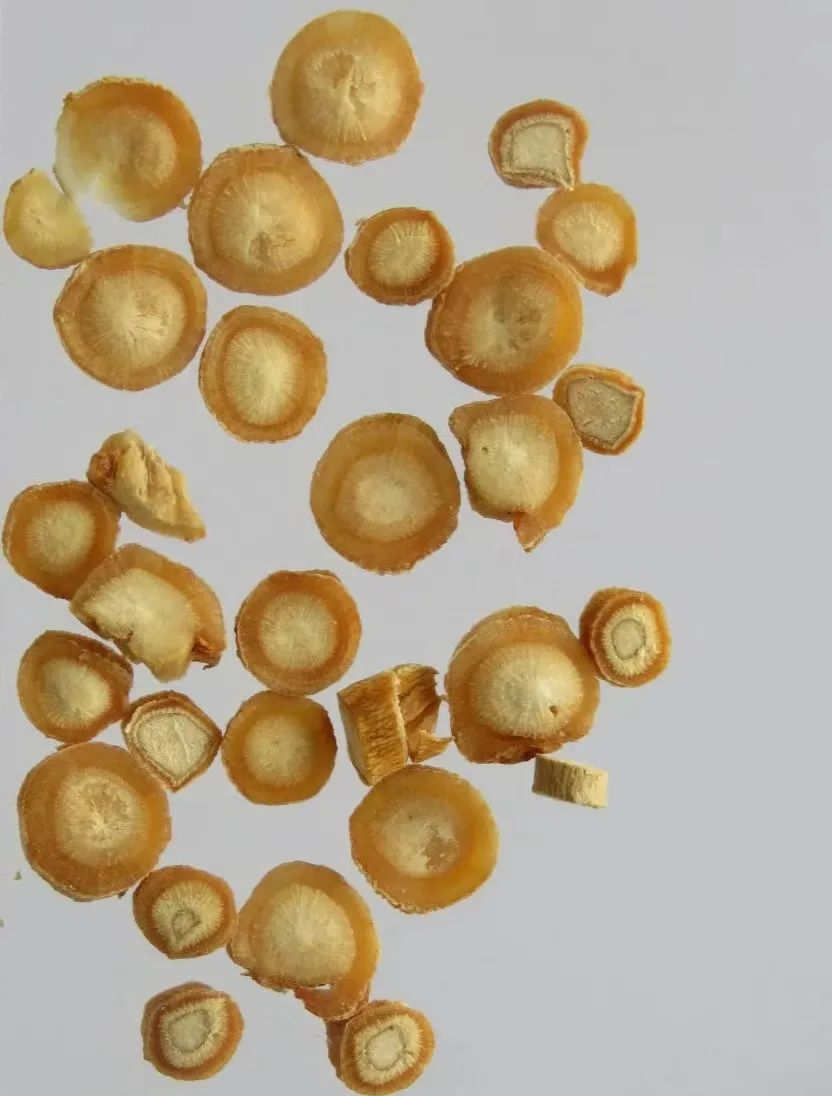


Therefore, we can see that Ming Codonopsis and Codonopsis belong to different plant families, have different properties and effects, and are completely different herbs. Ming Codonopsis clears the Lung and descends, while Codonopsis tonifies the center and benefits Qi, each has its specialty, and they should not be used interchangeably in clinical practice.
END
Written by|He Xinyuan
Edited by|Luo Zheli

