
January 15, 2024, Monday
Article No. 1989

Special Reminder: The articles and images published by this public account are for internal communication purposes only, and the source and origin of the articles are prominently indicated. If there are copyright issues, or if the copyright holder does not wish for their work to be published on this platform, please contact us to request the removal of your work.
On November 17, 2023, the National Health Commission and the State Administration for Market Regulation issued the “Announcement on the Inclusion of Codonopsis and Eight Other Substances as Both Food and Medicinal Materials According to Tradition” (2023 No. 9), which includes Codonopsis (Dang Shen), Cistanche (Rou Cong Rong), Dendrobium (Tie Pi Shi Hu), American Ginseng (Xi Yang Shen), Astragalus (Huang Qi), Ganoderma (Ling Zhi), Cornus (Shan Zhu Yu), Gastrodia (Tian Ma), and Eucommia (Du Zhong Ye) into the list of substances that are traditionally both food and medicinal materials (referred to as food-medicinal substances). Food products must not contain pharmaceuticals, but can include substances that are traditionally both food and medicinal materials.
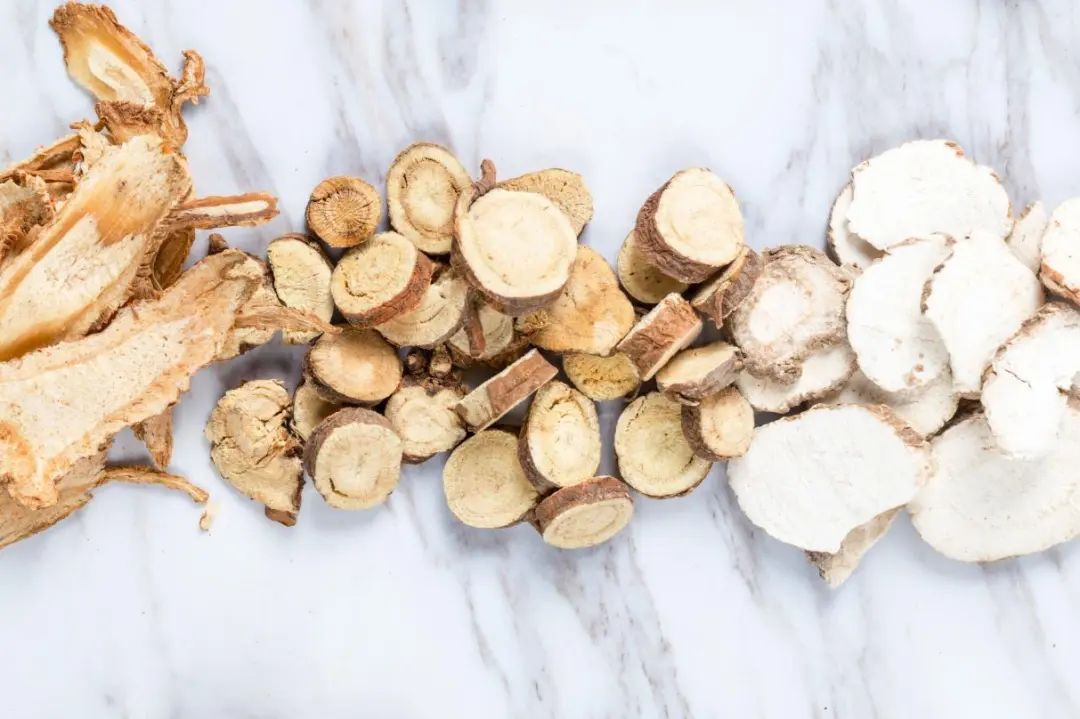
Codonopsis (Dang Shen), also known as Shang Dang Ren Shen, Fang Feng Dang Shen, etc., is the dried root of the plant Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. of the Campanulaceae family, and has various health benefits. There are over 40 species of Codonopsis, mainly distributed in East and Central Asia; among them, 39 species are found in China, primarily in Gansu, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Shanxi, Hubei, and Northeast China. Codonopsis was first recorded in the Qing Dynasty in Wu Yiluo’s “Ben Cao Cong Xin” stating, “The best is the one from Shang Dang. Genuine Codonopsis is now hard to find, and the varieties sold in the market are numerous and mostly ineffective, only Fang Feng Dang Shen is of good quality. The true one has a lion’s head shape, while the hard-textured one is false.” This mentions the characteristic of Codonopsis having a “lion’s head” shape. In the Qing Dynasty, Zhang Lu’s “Ben Jing Feng Yuan” recorded, “The one produced in the Taihang Mountains of Shanxi is called Shang Dang Ren Shen. Although it does not have the strong warming and tonifying effects, it has a mild and clear lung function, unlike Sha Shen which is cold and mainly dispels lung qi.” Here, “Shang Dang Ren Shen” refers to Codonopsis. “De Pei Ben Cao” states that “Shang Dang Shen is sweet and neutral. It enters the Taiyin meridian and nourishes the middle qi, harmonizing the spleen and stomach.” It records the flavor and efficacy of Codonopsis. “Zhi Wu Ming Shi Tu Kao” states, “Codonopsis is a climbing plant, with leaves not opposite, and nodes as large as fingers. Wild ones have white sap, and flowers bloom in autumn like Sha Shen, with blue-white color.” It includes a full image of Codonopsis, which helps in accurate identification, and its description matches modern Codonopsis. There was no record of Codonopsis before the Ming Dynasty, so it may have been confused with ginseng before the Ming Dynasty, and only after the Qing Dynasty was Codonopsis gradually distinguished from ginseng, laying the foundation for further research on Codonopsis.
Codonopsis is neutral in nature, sweet in flavor, and enters the spleen and lung meridians. It has the effects of strengthening the spleen and benefiting the lungs, nourishing blood and generating fluids, and can treat symptoms such as spleen and lung qi deficiency, poor appetite, fatigue, cough with shortness of breath, insufficient qi and blood, pale complexion, palpitations, shortness of breath, thirst due to fluid damage, and internal heat leading to thirst. Therefore, Codonopsis has broad prospects in the application of health foods.


Nutrition Components of Codonopsis
Modern research has found that Codonopsis contains glucose, inulin, fructose, and 17 amino acids including 7 essential amino acids, as well as various trace elements such as Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu, Mn, multiple vitamins including B1 and B2, and various bioactive substances such as flavonoids, steroids, alkaloids, organic acids, coumarins, and ester compounds.
Flavonoids. Multiple flavonoid compounds have been isolated and identified from Codonopsis, with representative components including medicagenic acid, apigenin,
luteolin, and rhein.
Steroids. The steroid compounds isolated from Codonopsis mainly include sitosterol and stigmasterol, including sitosterol, sitosterol-β-D-glucoside, and α-stigmasterol.
Triterpenes. The main triterpene compounds isolated from Codonopsis include triterpenoids, with the most isolated being triterpenoid compounds, including daucosterol, daucosterol acetate, and oleanolic acid.
Lignans. The lignan compounds isolated from Codonopsis include Codonopsis saponins I-VI, eugenin, methyl eugenin, and resin acids, among which Codonopsis saponins I-VI are characteristic components of the Codonopsis genus.
Phenolic acids. Various phenolic acid compounds have been isolated from Codonopsis, such as ferulic acid, eugenic acid, caffeic acid, Codonopsis acid, and chlorogenic acid.
Alkaloids. Alkaloids are a class of nitrogen-containing organic compounds with complex structures, and the main alkaloids isolated from Codonopsis include Codonopsis alkaloids, adenosine, Codonopsis base, choline, and nicotine.
Polysaccharides. Codonopsis is best known for its sweet taste, thus it contains various sugars including monosaccharides, polysaccharides, and oligosaccharides, with polysaccharides being the main component of Codonopsis sugars, exhibiting biological activities such as immune regulation, antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and blood sugar-lowering effects. Currently, various polysaccharides have been isolated from different parts of Codonopsis, mainly types of heteropolysaccharides including CPP, CPP1a, CPP1b, CPP1c, CERP1, WCP-I, S-CPPA1, CPPN, COP-W1, CTPN, CPO, CPSP-1, CTSP-1, CPPS3, RCNP, RCAP-1, and RCAP-2.

Effects and Functions
Neuroprotective Activity
Codonopsis extract can protect nerve cells, improve memory, and prevent or delay Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological effects. Studies have found that Codonopsis saponins have a preventive effect on focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats, and the mechanism is related to the inhibition of mRNA expression of inflammatory-related genes; Codonopsis polysaccharides significantly improve neuronal damage in the hippocampus caused by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice by reducing malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels in brain tissue and decreasing acetylcholinesterase activity, thus protecting against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.
Immune Activity
As a food-medicinal dual-use herb, Codonopsis has immune-regulating effects both in vivo and in vitro. Studies have found that Codonopsis polysaccharides can promote the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), enhance the immune activity of mouse macrophage Ana-1 cells, and boost immune function. Meanwhile, Codonopsis polysaccharides can activate T cells through the T cell receptor/CD28 signaling pathway at the molecular, cellular, and animal levels, exerting immune-regulating effects.
Effects on the Digestive System
Codonopsis enters the spleen meridian and has the effect of strengthening the spleen, which can treat symptoms of spleen and stomach weakness, protect gastric mucosa, treat gastric ulcers, and promote gastrointestinal absorption. Codonopsis polysaccharides have a spleen-tonifying effect, effectively improving the gastrointestinal absorption function of spleen-deficient mice by regulating gastrointestinal hormone secretion; Codonopsis flavonoid extracts can promote the migration of small intestinal epithelial IEC-6 cells and increase intracellular polyamine content; Codonopsis water extracts can repair colonic mucosal damage, possibly related to enhancing the body’s antioxidant capacity; Codonopsis total saponins can protect against ulcerative colitis mucosal damage by reducing the release of inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α through anti-lipid peroxidation and inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Research on Codonopsis in the cardiovascular system has found that Codonopsis extract can protect myocardial cells, improve heart function, and enhance hematopoietic function. After myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits, Codonopsis aqueous solution can reduce the release of lactate dehydrogenase and creatine kinase, lower malondialdehyde levels, and enhance superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, protecting damaged myocardial cells. Codonopsis granules can effectively improve the contractile ability of myocardial cells in heart failure rats by increasing calcium transient peak values and shortening the decline time. Codonopsis polysaccharides can mediate the aging of hematopoietic stem cells in mice induced by X-rays by regulating p53 protein and the p53-p21 pathway, improving B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2-associated X protein.
Blood Lipid Regulation and Blood Sugar Lowering Activity
The active components of Codonopsis that regulate blood sugar and lipids are mainly polysaccharides and saponins. Studies have found that Codonopsis polysaccharides can reduce insulin resistance, lower blood sugar in diabetic mice, and significantly improve insulin resistance in human liver cancer HepG2 cells, achieving a blood sugar-lowering effect. Codonopsis total saponins can reduce serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in hyperlipidemic rats, effectively regulating blood lipids.
Antioxidant and Anti-Aging
A large number of studies have shown that Codonopsis extract has certain antioxidant and anti-aging effects. Codonopsis polysaccharides have strong scavenging ability against DPPH free radicals and superoxide anion radicals, significantly increasing SOD and catalase activity in aging model mice.
Anti-Tumor
Studies have found that Codonopsis polysaccharides can inhibit gastric cancer cell proliferation and promote apoptosis by regulating the miR-361-5p/Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB pathway, while Codonopsis total saponins can reduce the survival rate of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells by upregulating miR-142-3 and downregulating E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH7, promoting apoptosis and inhibiting breast cancer.


Current Applications of Codonopsis
Food
Codonopsis roots and tender stems and leaves are used as food ingredients, often processed into tea, soup, porridge, health wine, pickles, cold dishes, and medicinal pastes, with a long history of consumption in Korea, China, and Southeast Asia.
Since ancient times, people in China have used Codonopsis in medicinal cuisine, such as Codonopsis and Poria porridge, which has warming and spleen-strengthening effects, suitable for those with spleen and stomach weakness; Codonopsis and lily porridge, which moistens the lungs and stops cough, tonifying the spleen and benefiting qi; Codonopsis and red date stew with sea cucumber, which benefits essence and fills marrow, tonifying qi and nourishing blood; and Codonopsis stewed with pig heart, which invigorates blood circulation and nourishes qi and blood.
With the inclusion of Codonopsis in the food-medicinal dual-use catalog, functional foods containing Codonopsis will have broader application value.
Health Foods
There are many health products on the market made from Codonopsis, such as Ejiao Goji Codonopsis Rehmannia oral liquid (National Health Food Approval G20150633), Ejiao Astragalus Codonopsis tablets (National Health Food Approval G20140294), Codonopsis Astragalus Goji oral liquid (National Health Food Approval G20160256), Ejiao Deer Antler Angelica Goji Rehmannia Codonopsis granules (National Health Food Approval G20150097), Ejiao Astragalus Codonopsis cooked Rehmannia Goji iron oral liquid (National Health Food Approval G20080332), Codonopsis Bird’s Nest Astragalus oral liquid (National Health Food Approval G20080250), and Codonopsis Poria capsules (National Health Food Approval G20130555), mainly aimed at improving anemia and enhancing immunity, suitable for those with nutritional anemia and low immunity.
Medicinal Products
Codonopsis plants are used in medicine, including roots, flowers, seeds, aerial parts, or whole herbs, utilized by various ethnic groups including Han, Mongolian, Tibetan, Yi, Bai, and Korean. In clinical applications, Codonopsis and its substitutes are often used as tonifying medicines in combination with other drugs, available in forms such as traditional Chinese medicine slices, oral liquids, mixtures, pills, tablets, medicinal teas, and pastes.
Codonopsis has the effects of strengthening the spleen and benefiting the lungs, nourishing blood and generating fluids, and is used to treat symptoms such as spleen and lung qi deficiency, poor appetite, fatigue, cough with shortness of breath, insufficient qi and blood, pale complexion, palpitations, shortness of breath, thirst due to fluid damage, and internal heat leading to thirst. Among them, the traditional Chinese medicine formula Ba Zhen Yi Mu Tang can tonify qi and blood, regulating menstruation; Ren Shen Wu Wei Zi Tang can strengthen the spleen and benefit qi, treating spleen qi deficiency and middle qi deficiency.
In addition, Codonopsis is the main ingredient in many Chinese patent medicines, such as Shen Mai Yin (Codonopsis formula), Compound Codonopsis tablets, Codonopsis oral liquid, and Codonopsis Li Zhong Wan.

Marks & Spencer x Zoe Launch New Gut Beverage
The British department store Marks & Spencer has announced a collaboration with nutrition science company Zoe to launch a new gut beverage: M&S Food x Zoe Gut Shot. The new product is a kefir fermented milk drink made from whole-fat fermented milk and mixed fruit puree (apple, strawberry, banana, blueberry) along with extracts from ginger, blackcurrant, and pomegranate. Additionally, the product contains 14 types of gut-friendly probiotics, exceeding 5 billion, and is rich in dietary fiber and calcium. Priced at £2 per bottle, it is available in Marks & Spencer stores across the UK.







Professor Zhu Beiwei, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and his team visited the Jiwei Tiancheng Beverage Technology Research Institute for investigation and research.
Academicians and experts gathered to support the integration and service upgrade of Jiwei Tiancheng Research Institute.
The refinement and innovation of functional beverages – the 2018 Functional Beverage Research and Exchange Conference was officially held at Jiwei Tiancheng.
Creating the future of the beverage industry with a holistic approach – the 2019 Beverage Industry Development Seminar was grandly held.
2024 Prediction: The Food and Beverage Industry Will Experience Many Significant Changes

