The Nanjing states, “To know by observation is called spirit; to know by listening is called sage; to know by questioning is called skill; to know by palpation is called cleverness.”
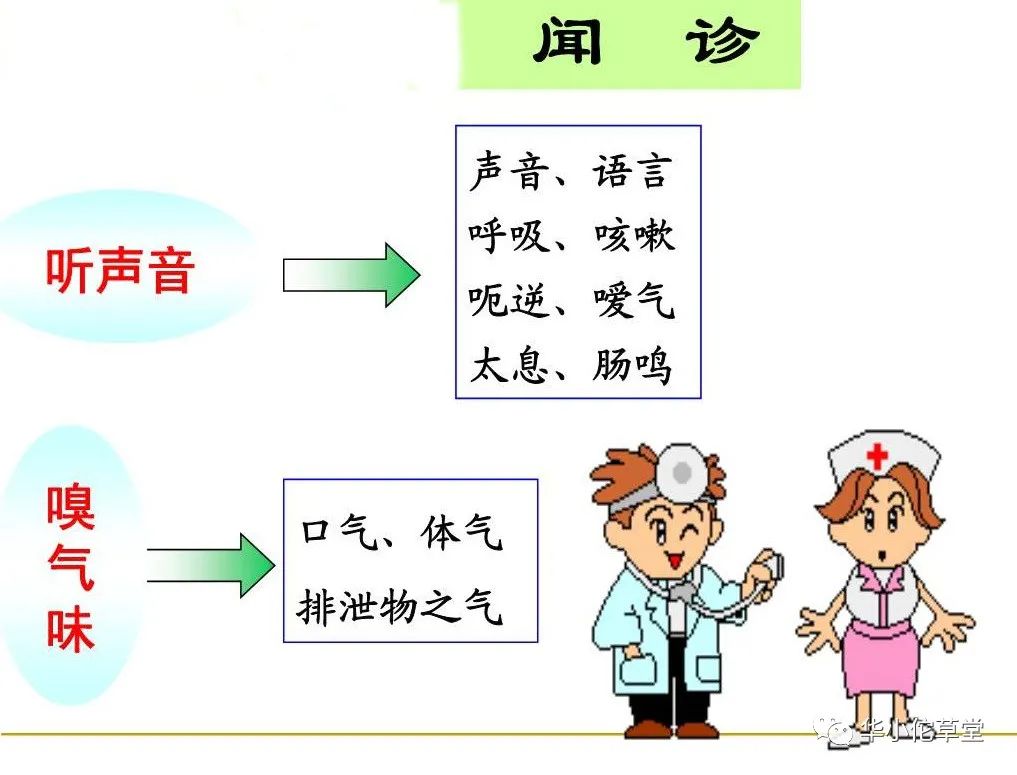
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), diagnosing a condition emphasizes “observation, listening, questioning, and palpation, integrating the four examinations.” So what is “listening diagnosis,” and what does it entail?

Listening diagnosis includes listening (hearing) to sounds and smelling (olfaction) odors. For instance, if a patient’s voice is weak and they speak little, it often indicates a deficiency pattern; a loud voice and excessive talking suggest a full pattern. Wheezing and coarse breathing with phlegm in the throat indicate asthma, while a dry cough without phlegm suggests lung dryness, and a weak cough indicates lung deficiency. Bad breath often relates to stomach heat, sour-smelling breath indicates retained food, foul-smelling stools suggest a heat pattern, fishy odor indicates a cold pattern, and foul-smelling or turbid urine often relates to damp-heat. Profuse and fishy vaginal discharge suggests deficiency-cold.
The Five Sounds Corresponding to the Five Organs
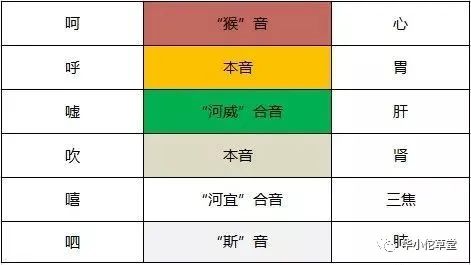
TCM categorizes the common sounds made by humans into five types: crying, laughing, singing, shouting, and groaning, corresponding to the five organs: liver, heart, spleen, lungs, and kidneys. By identifying the sounds produced, one can determine which organ may be problematic and adjust treatment accordingly.
-
Anger and shouting indicate excess liver fire
Individuals with excessive liver qi or rising liver yang often become easily angered and shout loudly. Those with stagnant liver qi may sigh frequently and produce a huffing sound. This is actually an unconscious self-rescue mechanism of the body, using sound to alleviate liver qi stagnation.
Friends with excess liver fire can frequently produce the sound “shh”, which helps regulate emotions and maintain inner peace. TCM herbs such as Chai Hu (Bupleurum), Bo He (Peppermint), and Su Ye (Perilla Leaf) can also help soothe liver qi and prevent qi stagnation, and can be used in moderation.
-
Excessive laughter depletes heart qi
Moderate laughter can help smooth heart qi and enhance health, but excessive laughter can deplete heart qi. If one feels palpitations or short of breath after laughing or talking too much, it often indicates heart qi deficiency, necessitating care for heart qi.
The key to nourishing the heart is to learn to slow down and embrace a slower lifestyle. Regularly producing the sound “he” can replenish heart qi, benefiting conditions like palpitations, insomnia, and forgetfulness. When experiencing emotional fluctuations or mood swings, consuming Hawthorn (Shan Zha) or sour foods can have astringent effects, preventing heart qi from becoming too dispersed and protecting the heart.
(Six Character Secret to Health)
-
Weak voice when singing indicates spleen qi deficiency
If the spleen qi is strong, the voice will be loud and singing will be robust; if spleen qi is deficient, the voice will be weak and singing will lack strength. However, excessive singing or talking can also deplete spleen qi.
Regularly producing the sound “hu” can help cultivate spleen qi, benefiting the prevention of spleen deficiency, abdominal distension, disharmony of the spleen and stomach, and loss of appetite. Elderly individuals who enjoy singing should consume foods that tonify spleen qi, such as Yam (Shan Yao), Red Dates (Da Zao), and Honey.
-
Constant weeping indicates weak lung qi
When lung qi is strong, crying will be loud; if lung qi is deficient, the crying will be soft and only whimpering. Crying is a normal emotional release that can be beneficial to health, but frequent crying can damage lung qi, as the lungs govern the skin, and lung deficiency can lead to skin issues.
Nourishing the lungs emphasizes maintaining a cheerful disposition. Additionally, chewing Walnuts (He Tao) 1-2 pieces every morning and evening can also nourish lung qi.
-
Constant groaning indicates kidney issues
As the saying goes, “No illness, no groaning.” Groaning is the body’s way of adjusting vital energy, which resides in the kidneys. If one frequently groans without illness, it may indicate kidney problems, suggesting a diet rich in Longan (Long Yan) and Yam (Shan Yao) to warm and tonify the kidneys. Regularly producing the sound “chui” can alleviate symptoms like weakness in the lower back and legs, night sweats, dizziness, and tinnitus.
END
Do not keep this to yourself!
Share it with your circle, let your friends see it too!
Previous Highlights
Understanding hospital examination reports, so you won’t have to ask the doctor again!
Save! These inexpensive and effective medicines in pharmacies that most people don’t know about!
Understanding the health benefits of Ganoderma and Ganoderma spore powder is essential! Otherwise, you might be consuming cotton stalks and soil! (Includes methods to identify quality spore powder from CCTV)
Chinese Goji Berries have become a global favorite; there are rules to eating Goji Berries.
TCM Yin-Yang, body weight, and Einstein (Ancient wisdom understood thousands of years ago, discovered by the West in 1905)

