Inheriting the legacy of Qi Huang, a public account with substance and warmth
1. Year of Compilation: Late Eastern Han Dynasty. Author: Zhang Ji, courtesy name Zhongjing. Total: Ten volumes, twenty-two sections, one hundred and twelve formulas. 2. First Compilation; Wei-Jin Wang Shuhe was the first to correct it; Song Dynasty Lin Yi was the first to annotate it; Song Jin Cheng Wujitong’s circulating edition: Song edition of “Shang Han Lun” and “Annotated Shang Han Lun”. 3. Meaning of “Shang Han”: There is a broad and narrow definition of Shang Han. Broadly, Shang Han refers to all externally contracted febrile diseases. Narrowly, Shang Han refers to diseases caused by the invasion of wind-cold. 4. Direct Attack: Refers to the pathogenic factor attacking directly at the three Yin stages without passing through the initial Yang and three Yang stages. Combined Disease: Refers to the simultaneous onset of two or three meridians without a sequence. Concurrent Disease: If the symptoms of one meridian have not resolved, and another meridian’s disease arises, it is called concurrent disease. Two Invasions: Refers to the simultaneous invasion of two meridians with a Yin-Yang relationship, such as the Taiyang and Shaoyin.

Taiyang Disease SectionPathogenic Factor: Cold Pathogen. Eight Principles: Exterior, Excess, Cold – Yang Syndrome. Location: In the exterior. Main Symptoms: Floating pulse, stiff neck, and aversion to cold. Pathogenesis: Wind-cold attacks the exterior, and Ying and Wei are invaded. 【Outline】 Original Text: Taiyang disease manifests with a floating pulse, stiff neck, and aversion to cold. (1) Taiyang disease with fever, sweating, and aversion to wind, with a slow pulse is called wind stroke. (2) Taiyang disease, whether fever has occurred or not, must have aversion to cold, body aches, nausea, and a tight pulse in both Yin and Yang, is called Shang Han. (3) Taiyang disease with fever and thirst, without aversion to cold is classified as warm disease. (6) If there is fever and aversion to cold, it arises from Yang; if there is no fever and aversion to cold, it arises from Yin. (7) 1. Wind-Warm: A variant of warm disease caused by the improper use of acrid-warm herbs for sweating. This differs from the later studies of warm diseases. Direct Vision: Double vision, with difficulty in moving the eyeballs. Secondary Meridian: The second meridian.
【Wind Stroke Exterior Deficiency Syndrome】 Original Text: Taiyang disease, headache, fever, sweating, aversion to wind, Gui Zhi Tang is the main treatment. (13) 2. Gui Zhi Tang Preparation Method: ① Simmer on low heat; ② Sip hot thin porridge; ③ Warm cover; ④ Moderate sweating; ⑤ Adjust medication according to the condition; ⑥ Contraindications. 3. If a patient with Taiyang disease initially takes Gui Zhi Tang and experiences restlessness, first needle Feng Chi and Feng Fu, then administer Gui Zhi Tang for recovery. (Acupuncture and herbs used together) After the Taiyang disease, if the Qi rises, Gui Zhi Tang can be used according to the previous method. If it does not rise, it must not be used. (Flexible application) 4. Gui Zhi Tang-related formulas
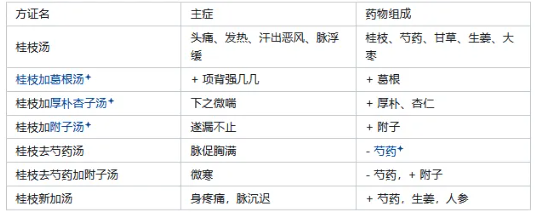
5. Comparison: Gui Zhi Tang vs. Ma Huang Tang. Both syndromes are major types of Taiyang exterior syndromes, characterized by aversion to wind and cold, fever, headache, and floating pulse, caused by wind-cold attacking the exterior and Ying-Wei disharmony. However, the basic pathogenesis of Gui Zhi Tang syndrome is Wei-Yang instability and Ying-Yin loss, characterized by sweating and a floating, slow pulse, hence also called exterior deficiency syndrome, treated with muscle relaxation, wind dispelling, and harmonizing Ying and Wei; the pathogenesis of Ma Huang Tang syndrome is Wei-Yang being obstructed and Ying-Yin stagnation, characterized by no sweating and a floating, tight pulse, hence also called exterior excess syndrome, treated with sweating, exterior resolution, and lung dispersing to relieve wheezing. 【Shang Han Exterior Excess Syndrome】 Original Text: Taiyang disease, headache, fever, body aches, low back pain, joint pain, aversion to wind, and no sweating, Ma Huang Tang is the main treatment. (35) Taiyang disease, stiff neck and back, no sweating, aversion to wind, Ge Gen Tang is the main treatment. (31) Shang Han with floating, slow pulse, body not painful but heavy, occasionally light, without Shaoyin syndrome, Da Qing Long Tang is the main treatment. (39) Ma Huang Tang contraindications: Dry throat, patients with bleeding disorders, those with blood loss, sweating, and patients with cold cannot be treated with sweating. 6. If Taiyang disease does not resolve after eight or nine days, and the exterior syndrome persists, continue to use Ma Huang Tang. 7. If the pulse is floating and tight, the method should be to relieve pain with sweating. If the pulse at the wrist is slow, it must not be treated with sweating. How do we know this? Because of insufficient Ying Qi and little blood. (Slow pulse at the wrist: a pulse that is less than four beats per breath is considered slow. Here it refers to the wrist pulse being slow and weak.) 8. Ma Huang Tang-related formulas
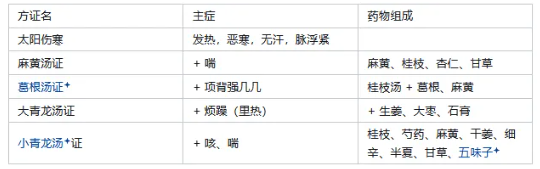
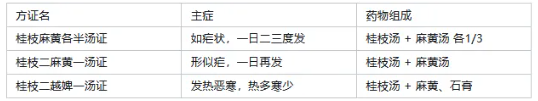
Da Qing Long Tang: The formula with the largest dosage of Ma Huang (six taels) in “Shang Han”. 9. Comparison: Da Qing Long Tang vs. Xiao Qing Long Tang. Both Da and Xiao Qing Long Tang syndromes are Taiyang Shang Han with interior syndromes, both have fever, aversion to cold, no sweating, and floating tight pulse, using acrid-warm herbs to resolve the exterior, derived from the modification of Ma Huang Tang. However, Da Qing Long Tang syndrome is characterized by external cold and internal heat, with irritability and heat, treated with sweating to resolve the exterior and clear internal heat, primarily focusing on resolving the exterior; Xiao Qing Long Tang syndrome is characterized by external cold and internal fluid, with cough, wheezing, and nausea, treated with sweating to resolve the exterior and warm to transform water fluids, primarily focusing on draining fluids. 【Exterior Stagnation Light Syndrome】 10. Exterior Stagnation Light Syndrome
【Water Accumulation Syndrome】 Taiyang disease, after sweating, excessive sweating, dry stomach, restlessness, and desire for water, give a little water to drink, to harmonize the stomach Qi for recovery. If the pulse is floating, urination is not smooth, and there is slight heat and thirst, Wu Ling San is the main treatment. (71) Wu Ling San: The formula with the largest dosage of Ze Xie. Water Reversal: A symptom of water retention in the body, causing thirst and vomiting upon drinking, is a manifestation of severe water accumulation syndrome. 【Blood Accumulation Syndrome】 11. Blood Accumulation Syndrome
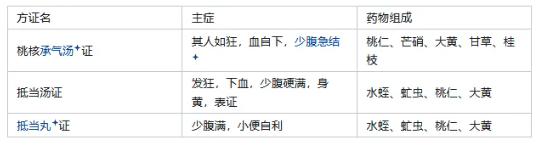
The use of Gui Zhi in Tao He Cheng Qi Tang: Warms and unblocks the meridians, not for resolving the exterior. 12. Comparison: Tao He Cheng Qi Tang vs. Di Dang Tang vs. Di Dang Wan. All three syndromes are blood-heat accumulation, with the disease located in the lower jiao blood division, but they differ in severity. Tao He Cheng Qi Tang syndrome is a light blood accumulation syndrome, with initial blood-heat accumulation, characterized by urgent lower abdominal pain, and the person appears manic, treated with invigorating blood and resolving stasis, unblocking the heat below, using Tao He Cheng Qi Tang, which has a strong purging effect due to the combined use of Niu Huang and Huang Lian. Di Dang Tang syndrome is an acute heavy blood accumulation syndrome, with heavier stasis, characterized by hard fullness in the lower abdomen, and the person appears manic, treated with breaking blood and resolving stasis, purging heat and removing excess, using Di Dang Tang, which has a greatly enhanced ability to break stasis due to the use of water leeches and flies. Di Dang Wan syndrome is a chronic blood accumulation syndrome, with heavier stasis but a slower disease progression, treated with purging heat and breaking stasis, using strong medicine for gentle attack, using Di Dang Wan, intending to reduce the dosage, changing from decoction to pill for a gentler attack. 【Combined and Concurrent Diseases】 Original Text: Taiyang and Yangming combined disease, with wheezing and fullness in the chest, must not be purged, should use Ma Huang Tang. (36) Taiyang and Yangming combined disease must have diarrhea, Ge Gen Tang is the main treatment. (32) Taiyang and Yangming combined disease, with no diarrhea but vomiting, Ge Gen plus Ban Xia Tang is the main treatment. (33) Taiyang and Shaoyang combined disease, with diarrhea, use Huang Qin Tang; if vomiting, Huang Qin plus Ban Xia Sheng Jiang Tang is the main treatment. (172) 【Variant Syndrome Outline】 13. Bad Disease: Variant Syndrome. Refers to abnormal changes in the original disease due to improper treatment, with complex symptoms that no longer exhibit the clinical characteristics of the six meridian diseases. Treatment for variant syndrome: Observe the pulse and symptoms, understand what is violated, and treat according to the symptoms. Contraindications for Gui Zhi Tang: If Taiyang disease has lasted three days, has already sweated, and if there is vomiting, diarrhea, or warm needling, and it still does not resolve. 14. Examples illustrate the sequence of exterior to interior, interior to exterior, and simultaneous treatment of both. 【Heat Syndrome】 15. Heat Syndrome – Zhi Zi Chi Tang-related syndromes
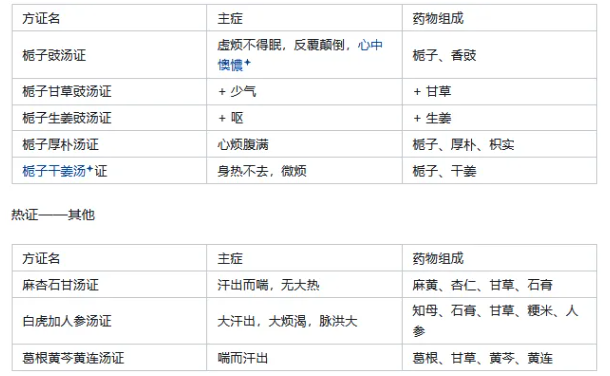
Chest Congestion → Zhi Zi Chi Tang, Heart Pain → Zhi Zi Chi Tang 【Deficiency Syndrome】 16. Deficiency Syndrome – Gui Zhi Gan Cao Tang-related formulas
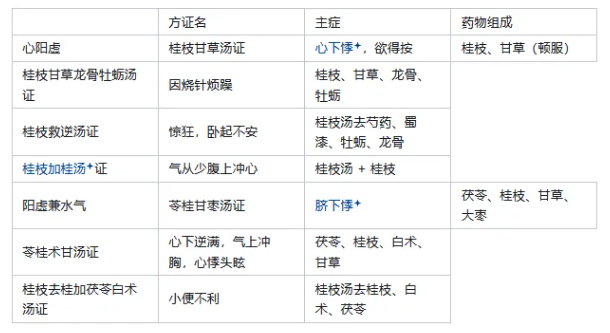
Gui Zhi plus Gui Tang: The largest dosage of Gui Zhi (five taels) in “Shang Han”. “Plus Gui” function: Calms the Qi and lowers the counterflow (relieves the rebellious Qi). Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang: A representative formula for strengthening the spleen and promoting water metabolism (a representative formula for promoting Yang and benefiting water: Wu Ling San). 17. Comparison: Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang vs. Ling Gui Gan Jiao Tang. The two formulas differ by only one ingredient, although both are designed for water-related diseases, they have many differences in pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang syndrome is primarily due to spleen Yang deficiency, with fluid retention in the middle jiao, symptoms primarily in the middle jiao, characterized by fullness below the heart, with Qi rising from below the heart to the chest; Ling Gui Gan Jiao Tang syndrome is primarily due to heart Yang deficiency, with fluid retention in the lower jiao, symptoms primarily in the lower jiao, characterized by movement below the navel, with a counterflow tendency. Although both treat warming Yang, transforming Qi, and promoting water metabolism, Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang focuses on treating the middle jiao, using Bai Zhu to strengthen the spleen. Ling Gui Gan Jiao Tang focuses on treating the lower jiao, heavily using Fu Ling for diuresis. 18. Deficiency Syndrome – Others
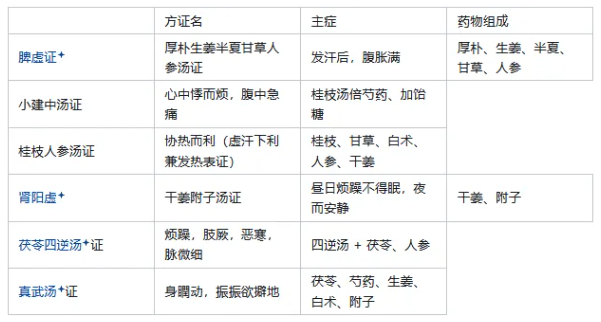
Hou Po Sheng Jiang Ban Xia Gan Cao Ren Shen Tang Syndrome: Hou Po: Ren Shen = 8:1 (indicating Qi stagnation is the main issue). Zhen Wu Tang Syndrome: A representative formula for warming Yang and promoting water metabolism. 19. What are the main symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment methods of Xiao Jian Zhong Tang Syndrome? Main Symptoms: Urgent abdominal pain, palpitations, preference for warmth and pressure, may also have slight aversion to cold and fever. Pathogenesis: Middle jiao deficiency cold, insufficient Qi and blood, disturbed by pathogens. Treatment Method: Warm the middle, strengthen the spleen, and harmonize Qi and blood. 20. What are the main symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment methods of Zhen Wu Tang Syndrome? Main Symptoms: Palpitations, dizziness, body tremors, feeling like falling to the ground or edema, difficulty urinating, white tongue coating, deep pulse. Pathogenesis: Sinking Yang deficiency, excessive water evil. Treatment Method: Warm Yang and promote water metabolism.
21. Deficiency Syndrome – Both Yin and Yang Deficiency.

【Chest Congestion Syndrome】 Original Text: Shang Han for six or seven days, chest heat and fullness, pulse deep and tight, pain below the heart, pressing it feels like a stone, Da Xian Xiong Tang is the main treatment. (135) Shang Han for more than ten days, heat accumulation in the interior, with alternating cold and heat, use Da Chai Hu Tang; but if there is chest fullness without significant heat, this is water accumulation in the chest, Da Xian Xiong Tang is the main treatment. (136) Taiyang disease, excessive sweating and then purging, not having a bowel movement for five or six days, dry tongue and thirst, slight heat in the afternoon, with fullness and pain below the heart, Da Xian Xiong Tang is the main treatment. (137) Small chest congestion disease, located below the heart, pressing it causes pain, pulse floating and slippery, Xiao Xian Xiong Tang is the main treatment. (138) 22. Chest Congestion: A type of disease characterized by the presence of a tangible pathogenic factor in the chest, primarily manifesting as chest, stomach, and abdominal pain. (Floating pulse, deep pulse) Cang Jie: Clinical manifestations similar to chest congestion, but of different nature, characterized by internal cold and excess Yin, with mixed deficiency and excess. (Floating pulse, small, thin, deep, tight pulse) Tide Heat: A type of heat pattern, fever occurs like a tide, regularly appearing and subsiding. 23. Chest Congestion Syndrome.
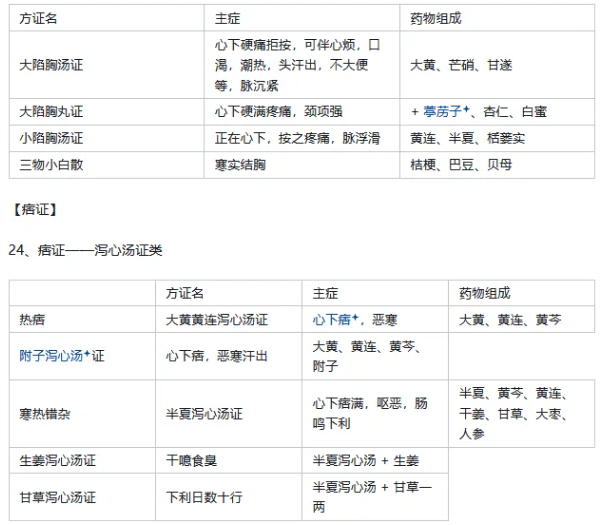 25. Comparison: Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang Syndrome vs. Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang vs. Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang. All three syndromes primarily manifest as hardness below the heart, and can also present with vomiting, diarrhea, and borborygmi, all due to damage to the spleen and stomach, with water and dampness obstructing, causing dysfunction in ascending and descending, and Qi stagnation. Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang syndrome primarily manifests with Qi rising from the stomach, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart and vomiting; Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang syndrome has water and food stagnation, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart, dry belching with foul odor; Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang syndrome has spleen and stomach weakness, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart, abdominal rumbling, severe diarrhea, inability to digest food, dry vomiting, and restlessness. Although the pathogenesis and symptoms of the three are generally similar, they differ in focus, with the treatment methods primarily using a combination of cold and warm, acrid opening and bitter descending, harmonizing the stomach and resolving fullness, with Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang as the representative formula, Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang focusing on dispersing water Qi, and Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang focusing on tonifying and harmonizing the stomach.
25. Comparison: Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang Syndrome vs. Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang vs. Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang. All three syndromes primarily manifest as hardness below the heart, and can also present with vomiting, diarrhea, and borborygmi, all due to damage to the spleen and stomach, with water and dampness obstructing, causing dysfunction in ascending and descending, and Qi stagnation. Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang syndrome primarily manifests with Qi rising from the stomach, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart and vomiting; Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang syndrome has water and food stagnation, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart, dry belching with foul odor; Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang syndrome has spleen and stomach weakness, hence the main symptoms are hardness below the heart, abdominal rumbling, severe diarrhea, inability to digest food, dry vomiting, and restlessness. Although the pathogenesis and symptoms of the three are generally similar, they differ in focus, with the treatment methods primarily using a combination of cold and warm, acrid opening and bitter descending, harmonizing the stomach and resolving fullness, with Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang as the representative formula, Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang focusing on dispersing water Qi, and Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang focusing on tonifying and harmonizing the stomach.
26. Fullness Syndrome – Others
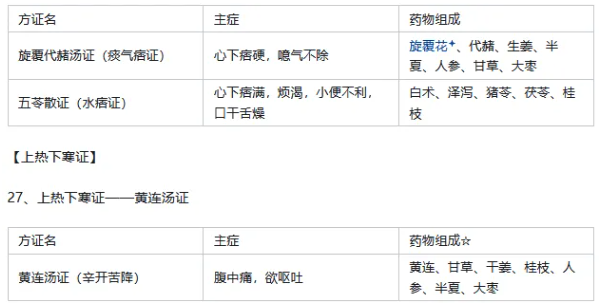
【Recovery Indicators】 Original Text: For any illness, if there is sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, blood loss, or loss of body fluids, and Yin and Yang harmonize, it will surely recover. (58) 【Similar Syndromes of Taiyang Disease】 28. Similar Syndromes of Taiyang Disease 1) Fluid Stagnation in the Chest and Flank Syndrome – Shi Zao Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Hard fullness below the heart, pain radiating to the flank, dry vomiting, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. Pathogenesis: Water and fluid stagnation in the chest and flank, causing dysfunction in Qi movement (the syndrome belongs to suspended fluid). Treatment Method: Attack and expel water and fluid. Formula: Yuan Hua, Gan Sui, Da Ji. 2) Phlegm Stagnation in the Chest Syndrome – Gua Di San Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Hardness in the chest, Qi rising to the throat, shortness of breath, and a slightly floating pulse. Pathogenesis: Phlegm stagnation obstructing the chest. Treatment Method: Eject phlegm. Formula: Gua Di, Chi Xiao Dou.
Yangming Disease Section Pathogenic Factor: Heat Pathogen. Eight Principles: Interior, Excess, Heat – Yang Syndrome. Location: In the stomach, intestines, and stomach meridian.
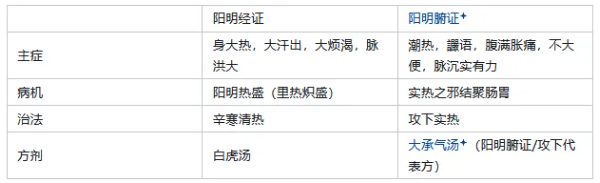
【Outline】 1. Yangming disease is characterized by fullness in the stomach. (180) Fullness in the stomach: Refers to the pathogenesis of Yangming disease. There is an accumulation of pathogenic heat in the stomach and intestines. 2. Taiyang Yangming → Spleen Constraint → Ma Zi Ren Wan Syndrome. Spleen Constraint: Stomach heat and intestinal dryness, damaging body fluids, insufficient spleen Yin, the spleen’s function of transporting body fluids is constrained, symptoms include hard stools and frequent urination. Sweating profusely → shifts to Yangming. 3. Question: What are the external symptoms of Yangming disease? Answer: Body heat, sweating, no aversion to cold, but aversion to heat. (182) Shang Han for three days, Yangming pulse is large. (186) 【Heat Syndrome】 4. Heat Syndrome
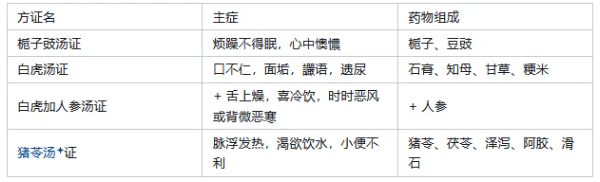
5. Bai Hu Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Fever, sweating, thirst, floating and slippery pulse. Pathogenesis: Yangming heat is excessive, filling both inside and outside. Treatment Method: Acrid cold to clear heat. Ingredients: Shi Gao, Zhi Mu, Gan Cao, Jing Mi. 6. If the pulse is floating and there is fever, thirst, and difficulty urinating, Zhu Ling Tang is the main treatment. (223) Zhu Ling Tang: A representative formula for nourishing Yin and promoting water metabolism. 【Excess Syndrome】 7. Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Abdominal distension, constipation, steaming heat, and irritability. Pathogenesis: Dry heat is excessive, with initial accumulation in the bowels. Treatment Method: Purge heat, harmonize the stomach, moisten dryness, and soften hardness. Ingredients: Mang Xiao, Da Huang, Gan Cao. Yangming disease, if there is no vomiting or diarrhea, and irritability, Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (207) If Taiyang disease has lasted three days, and sweating does not resolve, steaming heat indicates it belongs to the stomach, Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (248) After vomiting in Shang Han, if there is abdominal distension, Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (249) 8. Xiao Cheng Qi Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Hard stools, abdominal distension, tidal heat, irritability, and slippery rapid pulse. Pathogenesis: Excess heat is accumulated internally, obstructing the bowels. Treatment Method: Unblock the bowels, guide stagnation, and move Qi to relieve fullness. Ingredients: Da Huang, Hou Po, Zhi Shi. Yangming disease, if the person sweats a lot, body fluids are lost, the stomach is dry, and hard stools are inevitable, Xiao Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. If one dose stops the symptoms, do not take it again. (213) Yangming disease, if there is irritability and tidal heat, with a slippery rapid pulse, Xiao Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. If one dose causes gas to move in the abdomen, take another dose; if it does not move, do not take it again. If the next day there is still no bowel movement, and the pulse is slightly slippery, it indicates internal deficiency, which is difficult to treat, and do not take Cheng Qi Tang again. (214) If Taiyang disease has vomiting, diarrhea, or sweating, and there is slight irritability, frequent urination, and hard stools, Xiao Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (250) 9. Da Cheng Qi Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Heat: tidal heat (fever with sweating, no aversion to cold, fever occurs in the afternoon). Irritability: irritability (restlessness, speaking as if seeing ghosts). Distension: abdominal distension (abdominal fullness, distension). Constipation: no bowel movement (difficulty in defecation, hard stools, dry feces, undigested food). Excess: pulse is deep, solid, and strong. Pathogenesis: Excess heat pathogenic factors severely accumulate in the stomach and intestines. A typical Yangming bowel excess syndrome. Treatment Method: Attack and purge excess heat. Ingredients: Da Huang, Mang Xiao, Zhi Shi, Hou Po. If the patient has difficulty urinating, bowel movements are sometimes difficult, and there is slight heat, and they cannot lie down, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (242) Abdominal fullness does not decrease, and if it is insufficient, it must be purged, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (255) 10. Yangming Three Urgents. ☆ Shang Han for six or seven days, if the eyes are not clear, and there are no exterior or interior symptoms, with difficulty in defecation, slight heat in the body, this is excess, and it must be purged urgently, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (252) Yangming disease, with fever and excessive sweating, must be purged urgently, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (253) If sweating does not resolve, and there is abdominal fullness and pain, it must be purged urgently, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (254) Mechanism: Eyes not clear, and not harmonious – internal heat is excessive, damaging Yin, with no exterior or interior symptoms – no exterior symptoms, difficulty in defecation, slight heat – heat evil is hidden, causing damage to body fluids, excessive sweating – internal heat is excessive, damaging body fluids, excessive sweating does not resolve, abdominal fullness and pain – bowel excess has formed, heat disease transforms rapidly. 11. If the pulse is slippery and rapid, it indicates there is undigested food, and it must be purged, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (256) 【Moistening and Guiding Method Syndrome】 12. Ma Zi Ren Wan Syndrome. The pulse is floating and slippery, indicating the stomach Qi is strong, but slippery indicates frequent urination, floating and slippery are in conflict, leading to hard stools, indicating spleen constraint, Ma Zi Ren Wan is the main treatment. (247) Ingredients: Ma Zi Ren, Shao Yao, Zhi Shi, Hou Po, Xing Ren, Da Huang. 【Purge Method Differentiation】 13. If there is abdominal distension and no bowel movement, Xiao Cheng Qi Tang can be used to gently harmonize the stomach Qi. If there is subsequent fever, it must be due to hard stools, and Xiao Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. 【Purge Method Contraindications】 14. If there is excessive vomiting in Shang Han, even if there are Yangming symptoms, it must not be purged. Yangming disease, if there is hardness and fullness below the heart, it must not be purged. Yangming disease, if the face is red, it must not be purged. Yangming wind, with bitter mouth and dry throat, abdominal fullness, slight wheezing, fever, and aversion to cold, pulse is floating and tight, it must not be purged. Yangming disease, if unable to eat, it must not be purged. 【Cold Syndrome】 15. If there is a desire to vomit food, it belongs to Yangming, Wu Zhu Yu Tang is the main treatment. If the soup worsens, it belongs to the upper jiao. (243) Wu Zhu Yu Tang: Wu Zhu Yu, Ren Shen, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao. 【Jaundice Syndrome】 16. Yin Chen Hao Tang Syndrome (damp-heat jaundice) Main Symptoms: Body yellow like orange, yellow eyes, deep yellow urine, body heat, no sweating or sweating on the head, reaching the neck, thirst, slight abdominal fullness, red tongue with yellow greasy coating, pulse is wiry and rapid or slippery and rapid. Pathogenesis: Excess heat accumulates, steaming the liver and gallbladder, causing Qi stagnation. Treatment Method: Clear heat, promote dampness, and reduce jaundice. Ingredients: Yin Chen Hao, Zhi Zi, Da Huang. Yangming disease, with fever and sweating, this is heat exceeding, cannot cause jaundice. However, if sweating occurs on the head, and the body does not sweat, with thirst and desire for water, this indicates that the heat is trapped internally, and the body will surely turn yellow, Yin Chen Hao Tang is the main treatment. (236) Shang Han for seven or eight days, body yellow like orange, deep yellow urine, and slight abdominal fullness, Yin Chen Hao Tang is the main treatment. (260) 17. Zhi Zi Bai Pi Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Body yellow, eyes yellow like orange, fever, yellow urine, thirst, irritability, red tongue with yellow coating. Pathogenesis: Damp-heat combined, with heat heavier than dampness, obstructing the three jiao. Treatment Method: Clear internal heat, drain dampness, and reduce jaundice. Ingredients: Zhi Zi, Gan Cao, Huang Bai. Yangming disease, with body yellow and fever, Zhi Zi Bai Pi Tang is the main treatment. (261) 18. Ma Huang Lian Qiao Chi Xiao Dou Tang Syndrome. Main Symptoms: Body yellow, eyes yellow like orange, yellow urine, fever, aversion to cold, no sweating, or itching. Pathogenesis: Damp-heat obstructing internally, with wind-cold binding externally. Treatment Method: Clear heat, promote dampness, resolve the exterior, and disperse evil. Ingredients: Ma Huang, Lian Qiao, Chi Xiao Dou, Xing Ren, Da Zao, Zi Bai Pi, Sheng Jiang, Gan Cao. Yangming disease, with trapped heat internally, the body will surely turn yellow, Ma Huang Lian Qiao Chi Xiao Dou Tang is the main treatment. (262) 19. Comparison: Yin Chen Hao Tang Syndrome vs. Zhi Zi Bai Pi Tang Syndrome vs. Ma Huang Lian Qiao Chi Xiao Dou Tang Syndrome. These three syndromes are commonly referred to as Yangming damp-heat jaundice syndromes. All three syndromes share common characteristics of body yellow, eyes yellow, bright orange color, and yellow urine that is not smooth. Yin Chen Hao Tang Syndrome is the heaviest of the damp-heat jaundice syndromes, with abdominal Qi stagnation, and may also present with fever, sweating not smooth, abdominal fullness, constipation, red tongue with yellow greasy coating, hence the treatment is primarily focused on clearing and draining. Zhi Zi Bai Pi Tang Syndrome is lighter, with heat heavier than dampness, and may also present with thirst, red tongue with yellow coating, hence the treatment is primarily focused on clearing internal heat and draining dampness. Ma Huang Lian Qiao Chi Xiao Dou Tang Syndrome is damp-heat jaundice with concurrent wind-cold binding externally, presenting with fever, aversion to cold, no sweating, or itching, hence the treatment is primarily focused on clearing and draining damp-heat while resolving the exterior and dispersing evil. 20. Gu Dan: A type of jaundice caused by improper diet and dysfunction of the middle jiao, hence called Gu Dan. There are distinctions between cold-damp and damp-heat. 【Yangming Disease Prognosis】 21. Irritability: Loud voice and rough speech, mostly belong to excess. Zheng voice: Repetitive speech, low voice and weak, mostly belong to deficiency.
Shaoyang Disease Section Pathogenic Factor: Heat Pathogen. Eight Principles: Interior, Excess, Heat – Yang Syndrome (Half Exterior, Half Interior). Location: In the gallbladder, gallbladder meridian. Main Symptoms: Bitter mouth, dry throat, dizziness; alternating cold and heat, fullness in the chest and flank, dislike of food, irritability, and nausea, with a wiry and thin pulse. Pathogenesis: Evil enters Shaoyang, causing conflict between the righteous and the evil, affecting the stomach. Treatment Method: Harmonize and resolve Shaoyang, support the righteous and expel the evil. Formula: Xiao Chai Hu Tang. 【Outline】 1. Shaoyang disease is characterized by bitter mouth, dry throat, and dizziness. (263) 2. Shang Han, with wiry and thin pulse, headache, and fever, belongs to Shaoyang. (265) 【Xiao Chai Hu Tang Syndrome】 3. Xiao Chai Hu Tang Syndrome Main Symptoms: Alternating cold and heat, fullness in the chest and flank, irritability, dislike of food, bitter mouth, dry throat, dizziness, and wiry pulse. Pathogenesis: Evil invades Shaoyang, gallbladder fire accumulates, and the pivot is not smooth. Treatment Method: Harmonize and resolve Shaoyang, and smooth the pivot. Ingredients: Chai Hu, Ban Xia, Ren Shen, Gan Cao, Huang Qin, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao. 4. Shang Han for five or six days, with wind stroke, alternating cold and heat, fullness in the chest and flank, dislike of food, irritability, or fullness in the chest without nausea, or thirst, or abdominal pain, or fullness in the flank, or palpitations, or difficulty urinating, or no thirst, slight heat in the body, or cough, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (96) Blood weak and Qi exhausted, the pores open, the evil Qi conflicts with the righteous Qi, and accumulates in the flank. The conflict between the righteous and the evil causes alternating cold and heat, and the fullness must be relieved, hence causing nausea, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. If after taking Chai Hu Tang, the patient is thirsty, it belongs to Yangming, and should be treated accordingly. (97) 5. How to understand “If one symptom is seen, it is sufficient, not all must be present”? “If one symptom is seen, it is sufficient, not all must be present” is indeed semantically related and difficult to separate, but from the spirit of differentiation and treatment, it emphasizes the importance of “not all must be present”. That is, if any of the main symptoms of Shaoyang disease is observed, Xiao Chai Hu Tang can be administered to harmonize. 6. Shang Han, with Yang pulse being thin, Yin pulse being wiry, the method should be to treat urgent abdominal pain first with Xiao Jian Zhong Tang; if there is no difference, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (100) 7. Yangming disease, with tidal heat, loose stools, and normal urination, but fullness in the chest and flank that does not resolve, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (229) (Yangming and Shaoyang share the same disease, treated with Shaoyang methods) 8. Yangming disease, with fullness in the flank, no bowel movement but nausea, and a white coating on the tongue, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment, allowing the upper jiao to be unblocked, the body fluids to descend, the stomach Qi to harmonize, and the body to sweat and resolve. (230) 9. Later, there must be heavy bowel movements: a feeling of heaviness at the anus during bowel movements.
【Chai Hu Gui Zhi Tang Syndrome】 10. Shang Han for six or seven days, with slight fever and aversion to cold, joint pain, slight nausea, and fullness below the heart, if the exterior symptoms have not resolved, Chai Hu Gui Zhi Tang is the main treatment. (146) 【Da Chai Hu Tang Syndrome】 11. Da Chai Hu Tang Syndrome Main Symptoms: Alternating cold and heat, persistent vomiting, urgent fullness below the heart, slight irritability, fullness in the heart, diarrhea or no bowel movement. Pathogenesis: Shaoyang evil heat, combined with Yangming interior excess. Treatment Method: Harmonize Shaoyang, unblock the Yangming interior excess. Ingredients: Chai Hu, Da Huang, Huang Qin, Ban Xia, Zhi Shi, Shao Yao, Da Zao, Sheng Jiang. 12. If Taiyang disease has lasted more than ten days, and there are still symptoms of Chai Hu, first administer Xiao Chai Hu Tang. If there is persistent vomiting, urgent fullness below the heart, slight irritability, it indicates it has not resolved, and Da Chai Hu Tang should be used to purge. (103) Shang Han with fever, sweating, and unresolved symptoms, fullness below the heart, vomiting, and diarrhea, Da Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (165) 13. Comparison: Xiao Chai Hu Tang vs. Da Chai Hu Tang. Both syndromes belong to Shaoyang gallbladder fire accumulation, with the pivot not smooth. However, Xiao Chai Hu Tang syndrome is a typical Shaoyang disease, while Da Chai Hu Tang syndrome is a combination of Shaoyang and Yangming interior excess. Clinically, in addition to the symptoms of Xiao Chai Hu Tang syndrome, such as alternating cold and heat, fullness in the chest and flank, bitter mouth, dry throat, dizziness, irritability, and vomiting, the vomiting is more severe, and the disease affects the stomach and abdominal area, with urgent fullness and pain below the heart, constipation or heat diarrhea, red tongue with yellow coating, and wiry rapid pulse. Xiao Chai Hu Tang syndrome is only suitable for harmonizing Shaoyang, supporting the righteous and expelling the evil; Da Chai Hu Tang syndrome requires harmonizing Shaoyang while also unblocking the Yangming interior excess. The medication is based on Xiao Chai Hu Tang, adding Ren Shen and Zhi Gan Cao to support the righteous; increasing Sheng Jiang to stop nausea, and adding Da Huang and Zhi Shi to purge, forming a formula that resolves both Shaoyang and Yangming. 【Chai Hu plus Mang Xiao Tang Syndrome】 (General understanding) 14. Chai Hu plus Mang Xiao Tang Syndrome Main Symptoms: Fullness in the chest and flank with nausea, tidal heat in the afternoon, slight diarrhea. Pathogenesis: Shaoyang combined with Yangming interior excess, with mild dryness and excess, and the righteous Qi is slightly deficient. Treatment Method: Harmonize Shaoyang, purge heat, and moisten dryness. Ingredients: Xiao Chai Hu Tang + Mang Xiao. 15. Understanding: Da Chai Hu Tang syndrome, which combines Shaoyang and Yangming interior excess, mistakenly uses pill medicine to purge. Pill medicine is slow-acting and light, but has a lasting effect, and cannot clear the stomach and intestines of dryness and excess; the purging nature instead remains in the middle, causing slight diarrhea, hence although there is diarrhea, the tidal heat does not resolve. (Distinction from Da Chai Hu Tang: In Da Chai Hu Tang syndrome, the excess is based on the foundation of Yangming interior excess.) 【Chai Hu Gui Zhi Gan Jiang Tang Syndrome】 (General understanding) 16. Chai Hu Gui Zhi Gan Jiang Tang Syndrome Main Symptoms: Alternating cold and heat, slight fullness in the chest and flank, thirst, irritability, difficulty urinating, but sweating on the head. Pathogenesis: Shaoyang evil heat, water and fluid accumulation, Qi transformation is lost. Treatment Method: Harmonize Shaoyang, warm and transform water and fluid. Ingredients: Chai Hu, Gui Zhi, Gan Jiang, Gua Lou Gen, Huang Qin, Mu Li, Gan Cao. 17. Shang Han for five or six days, has already sweated and then purged, with slight fullness in the chest and flank, difficulty urinating, thirst but not nausea, but sweating on the head, alternating cold and heat, irritability, this indicates it has not resolved, and Chai Hu Gui Zhi Gan Jiang Tang is the main treatment. (147) 【Chai Hu plus Long Gu Mu Li Tang Syndrome】 (General understanding) 18. Chai Hu plus Long Gu Mu Li Tang Syndrome Main Symptoms: Fullness and oppression in the chest and flank, irritability, fear and anxiety, severe cases may lead to delirium, difficulty urinating, heaviness throughout the body, and inability to turn over. Pathogenesis: Evil enters Shaoyang, spreading through the three jiao, causing disturbance to the heart and spirit. Treatment Method: Harmonize Shaoyang, unblock Yang, clear heat, and calm the spirit. Ingredients: Xiao Chai Hu Tang minus Gan Cao, plus Long Gu, Mu Li, Gui Zhi, Fu Ling, Qian Dan, Da Huang. 【Transmission and Prognosis】 19. Shang Han for six or seven days, with no significant heat, and the person is irritable, this indicates that Yang has entered Yin. Yang entering Yin: Exterior symptoms have entered the interior.
太阴病篇Pathogenic Factor: Cold Pathogen. Eight Principles: Interior, Deficiency, Cold – Yin Syndrome. Location: In the spleen (stomach) – localized deficiency cold syndrome. Main Symptoms: Abdominal fullness and vomiting, inability to eat, frequent diarrhea, occasional abdominal pain, weak pulse. Pathogenesis: Spleen Yang deficiency, cold dampness obstructing. Treatment Method: Tonify Qi, warm Yang, disperse cold, and eliminate dampness. Formula: Si Ni San. (Later generations have used Li Zhong Tang) (Li Zhong Tang is purely for spleen Qi deficiency, Si Ni Tang has Yang deficiency.) 【Outline】 1. Taiyin disease is characterized by abdominal fullness and vomiting, inability to eat, frequent diarrhea, and occasional abdominal pain. (273) 【Taiyin Disease Syndrome】 2. If there is diarrhea without thirst, it belongs to Taiyin, due to the presence of cold in the spleen, it should be warmed, and Si Ni San should be taken. (277) Characteristics of diarrhea: diarrhea without thirst. Pathogenesis: Presence of cold (spleen Yang deficiency, cold dampness obstructing). Treatment Method: Warm it (warming method). Representative Formula: Si Ni Tang 【Combined Variant Syndrome】 3. Taiyin combined with exterior syndrome. If Taiyin disease has a floating pulse, sweating can be induced, Gui Zhi Tang is appropriate. (276) 4. Taiyin abdominal pain syndrome is originally a Taiyang disease, if treated with purging, it leads to abdominal fullness and pain, which belongs to Taiyin, Gui Zhi plus Shao Yao Tang is the main treatment; if there is significant pain, Gui Zhi plus Da Huang Tang is the main treatment. (279) Gui Zhi plus Shao Yao Tang Formula: Gui Zhi Tang + three taels of Shao Yao. Gui Zhi plus Da Huang Tang Formula: Gui Zhi Tang + three taels of Shao Yao + Da Huang. 5. If Taiyin is present, the pulse is weak, and the person continues to have frequent diarrhea, if one intends to use Da Huang and Shao Yao, it should be reduced, as the person’s stomach Qi is weak and easily disturbed. Mastery: Weak stomach Qi → should be reduced. 【Prognosis】 6. Spleen fullness: This refers to the righteous Qi being full. It can be understood as the recovery of spleen Yang, hence the foulness should be expelled (expel the evil outward).
少阴病篇 Pathogenic Factor: Cold Pathogen (Cold Transformation Syndrome); Heat Pathogen (Heat Transformation Syndrome). Eight Principles: Interior, Deficiency, Cold (Cold Transformation); Interior, Deficiency, Heat (Heat Transformation). Location: Heart, Kidney.
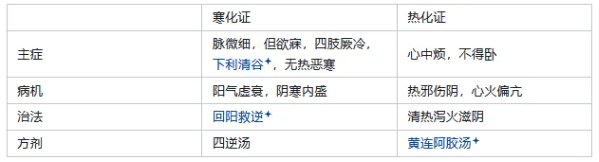
【Outline】 1. Shaoyin disease is characterized by a thin pulse, desiring sleep. (281) 【Shaoyin Cold Transformation Syndrome】 2. Key points for differentiation: diarrhea with thirst → Shaoyin diarrhea characteristics. Shaoyin disease: diarrhea with thirst. Taiyin disease: diarrhea without thirst (different degrees of severity). 3. Si Ni Tang Syndrome (Organ Reversal) ☆ Shaoyin disease, with a deep pulse, must be urgently warmed, Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. Main Symptoms: Thin pulse, desiring sleep, cold limbs, frequent clear diarrhea, no heat or aversion to cold. Pathogenesis: Yang Qi is weak, internal cold is excessive. Treatment Method: Revive Yang and rescue the reversal. Ingredients: Sheng Fu Zi, Gan Cao, Gan Jiang. 4. Tong Mai Si Ni Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, with frequent clear diarrhea, internal cold and external heat, cold limbs, thin pulse, and the body does not have aversion to cold, the face is red, or abdominal pain, or dry vomiting, or sore throat, or difficulty urinating, or no thirst, the body has slight heat, or cough, Tong Mai Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. (317) Ingredients: Same as Si Ni Tang, but with different dosages, increasing the amount of ginger and Fu Zi to enhance the warming and Yang-reviving effect. When the cold is removed, Yang returns, and when Yang returns, the pulse is unblocked. 5. Bai Tong Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, with diarrhea, Bai Tong Tang is the main treatment. Ingredients: Scallion white (warm Yang), Gan Jiang, Fu Zi. 6. Bai Tong plus Pig Gallbladder Juice Tang Syndrome. Ingredients: Bai Tong Tang to unblock Yang and stop diarrhea. Add human urine and pig gallbladder juice to nourish Yin and harmonize Yang, salty, cold, and bitter to descend, assisting the Yang medicine to enter without resistance. 7. Zhen Wu Tang Syndrome ☆ Shaoyin disease, if it has not resolved after two or three days, and after four or five days, abdominal pain, difficulty urinating, heavy and painful limbs, and frequent diarrhea, this indicates the presence of water Qi. The person may cough, have frequent urination, diarrhea, or vomiting, Zhen Wu Tang is the main treatment. (316) Main Symptoms: Palpitations, dizziness, body tremors, feeling like falling to the ground, or edema, difficulty urinating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, heavy and painful limbs, fever, etc. Pathogenesis: Yang Qi is weak, water Qi is excessive. Treatment Method: Warm Yang and promote water metabolism. Ingredients: Fu Ling, Shao Yao, Bai Zhu, Sheng Jiang, Fu Zi. 8. Fu Zi Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, if it has been known for one or two days, with warmth in the mouth, and cold in the back, it should be moxibustioned, Fu Zi Tang is the main treatment. Shaoyin disease, with body pain, cold limbs, joint pain, and deep pulse, Fu Zi Tang is the main treatment. (305) Main Symptoms: Body pain, joint pain, back cold, cold limbs, warmth in the mouth, deep pulse. Pathogenesis: Yang Qi is weak, cold dampness obstructing the muscles and bones. Treatment Method: Warm and tonify the original Yang, disperse cold and eliminate dampness. Ingredients: Fu Zi, Fu Ling, Ren Shen, Bai Zhu, Shao Yao. 9. Comparison: Zhen Wu Tang Syndrome vs. Fu Zi Tang Syndrome (one with excessive water Qi, one with body pain and Yang deficiency). The ingredients of the two formulas are mostly the same, both using Fu Zi, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, and Shao Yao. The difference is that Fu Zi Tang uses double the amount of Bai Zhu and adds Ren Shen, focusing on tonifying Yang Qi and dispersing dampness; Zhen Wu Tang uses half the amount of Bai Zhu, adding Sheng Jiang, focusing on warming and dispersing water and fluid. The former primarily supports the righteous, while the latter primarily expels evil. 10. Wu Zhu Yu Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, with vomiting and diarrhea, cold limbs, irritability, and a desire to die, Wu Zhu Yu Tang is the main treatment. (309) Main Symptoms: Desire to vomit food; vomiting and diarrhea, cold limbs, irritability, and a desire to die; dry vomiting with foamy saliva, headache, etc. Pathogenesis: Stomach Qi is cold and weak, liver Qi invades the stomach, causing counterflow of turbid Yin. Treatment Method: Warm the liver, warm the stomach, lower counterflow, and tonify Qi. Ingredients: Wu Zhu Yu, Sheng Jiang, Ren Shen, Da Zao. 11. Tao Hua Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, with frequent diarrhea with pus and blood, Tao Hua Tang is the main treatment. (306) Shaoyin disease, if it has lasted two or three days to four or five days, with abdominal pain, difficulty urinating, and persistent diarrhea with pus and blood, Tao Hua Tang is the main treatment. (307) Main Symptoms: Frequent diarrhea with pus and blood, dark blood color, slippery and unrestrained, difficulty urinating, pale tongue with white coating, deep weak pulse. Pathogenesis: Spleen and kidney Yang deficiency, unable to control. Treatment Method: Warm Yang, consolidate the loss, and bind the intestines to stop diarrhea. Acupuncture may also be used. Ingredients: Chi Shi Zhi, Gan Jiang, Jing Mi. 【Shaoyin Heat Transformation Syndrome】 12. Huang Lian A Jiao Tang Syndrome ☆ Shaoyin Heat Transformation Syndrome. Syndrome Type: Heart irritation, unable to sleep. Main Symptoms: Heart irritation, unable to sleep, may accompany dry throat and mouth, red tongue with little coating or thin yellow, deep thin rapid pulse. Pathogenesis: Heat evil injures Yin, heart fire is excessive. Treatment Method: Clear heat, drain fire, nourish Yin. Ingredients: Huang Lian, Huang Qin, Shao Yao, Ji Zi Huang, A Jiao. 13. Zhu Ling Tang Syndrome. Shaoyin disease, with diarrhea for six or seven days, cough and nausea, irritability, and inability to sleep, Zhu Ling Tang is the main treatment. (319) (Familiarize with) Zhu Ling Tang vs. Wu Ling San can both treat water Qi diseases, but their pathogenesis, symptoms, and treatment methods differ. Zhu Ling Tang syndrome’s pathogenesis is Yin deficiency with water and heat intermingling, treated with nourishing Yin and promoting water metabolism; Wu Ling San syndrome’s pathogenesis is water accumulation in the lower jiao, with bladder Qi transformation being ineffective, treated with transforming Qi and promoting water metabolism, along with resolving the exterior. 【Shaoyin Yang Stagnation Syndrome – Si Ni San Syndrome (Qi Reversal)】 14. Si Ni San Syndrome (Qi Reversal) ☆ Main Symptoms: Cold limbs, accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea, heavy sensation at the anus, or accompanied by cough, palpitations, and difficulty urinating. Pathogenesis: Liver Qi stagnation, Qi movement is obstructed, Yang Qi is internally stagnant. Treatment Method: Soothe the liver, regulate Qi, and unblock the stagnant Yang. Ingredients: Chai Hu, Shao Yao, Zhi Shi, Gan Cao. 【Shaoyin Combined with Exterior Syndrome】 15. Comparison: Ma Huang Xi Xin Fu Zi Tang vs. Ma Huang Fu Zi Gan Cao Tang. Both are Shaoyin combined with exterior, but the urgency of the syndrome differs. Ma Huang Xi Xin Fu Zi Tang syndrome is an early stage of the disease, with more urgent symptoms, characterized by aversion to cold, and more severe cold limbs, pale tongue with white slippery coating, etc. At this time, the righteous Qi is relatively strong, hence Ma Huang Xi Xin Fu Zi Tang is used to warm the meridians and resolve the exterior to induce sweating; Ma Huang Fu Zi Gan Cao Tang syndrome has lasted several days, with weaker righteous Qi, and the disease is slower, with atypical clinical symptoms, hence Ma Huang Fu Zi Gan Cao Tang is used to induce slight sweating. In terms of medication, the former uses Xi Xin to warm the meridians and disperse cold; the latter uses Gan Cao to gently induce slight sweating, and can also tonify Qi and harmonize the middle, protecting the righteous Qi. 【Shaoyin Urgent Downward Syndrome】 ☆ 16. Shaoyin disease, if known for two or three days, with dry mouth and dry throat, it must be purged urgently, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (320) Mechanism: Dry heat accumulates, injuring body fluids, kidney Yin is damaged → urgent downward Yangming dry heat, to preserve Shaoyin’s body fluids. Shaoyin disease, with clear diarrhea, pure blue color, and abdominal pain, may be purged, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (321) Mechanism: Shaoyin heat transformation, body fluids are lost, heat enters Yangming, heat accumulates and flows → urgent downward Yangming excess, to extinguish the fire and preserve the body fluids (common cause and common use). Shaoyin disease, for six or seven days, with abdominal distension and no bowel movement, must be purged urgently, Da Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. (322) Mechanism: Shaoyin heat transformation, evil heat combines with Yangming, dry heat injures kidney Yin → urgent downward to preserve body fluids. 17. The connection and distinction between Yangming Three Urgents and Shaoyin Three Urgents. ① Yangming Three Urgents is discussed in terms of Yangming bowel excess syndrome, with urgent disease progression, having the potential to injure Shaoyin true Yin, hence it should be urgently purged with Da Cheng Qi Tang to drain heat and preserve Yin; Shaoyin Three Urgents is discussed in terms of Shaoyin’s Yin being burned by dry heat, with the potential to lose Yin body fluids, hence it should be urgently purged with Da Cheng Qi Tang to drain dry heat, extinguishing the fire to preserve body fluids. ② Yangming Three Urgents is discussed from the perspective of bowel heat injuring organ Yin, discussing the evil; Shaoyin Three Urgents is discussed from the perspective of organ Yin being injured by bowel heat, discussing the righteous. ③ One discusses from the perspective of excessive dry heat, while the other discusses from the perspective of true Yin being injured, but both involve purging Yangming’s dry heat and preserving the body’s Yin. Considering both can remind practitioners to balance expelling evil and supporting the righteous. ④ Both methods of expelling evil are means, while protecting the righteous is the goal. In Yangming, the aim is to save the stomach’s body fluids; in Shaoyin, the aim is to save the kidney’s water. ⑤ Regardless of Yangming or Shaoyin, any urgent purging must show signs of internal dry heat accumulation.
Jueyin Disease Section【Outline】 1. Jueyin disease is characterized by thirst, Qi rising to the heart, heart pain and heat, hunger without desire to eat, vomiting of roundworms, and persistent diarrhea. (326) 【Cold-Heat Mixed Syndrome】 2. Wu Mei Wan Syndrome (Roundworm Reversal) (also for chronic diarrhea) Main Symptoms: Alternating between calm and agitation, vomiting, abdominal pain, occurring intermittently, related to food intake, severe pain with cold limbs, with a history of roundworm vomiting. Pathogenesis: Upper heat and lower cold, roundworms disturb the body. Treatment Method: Clear the upper, warm the lower, calm the roundworms, and stop pain. Ingredients: Wu Mei, Xi Xin, Gui Zhi, Huang Lian, Huang Bai, Dang Gui, Ren Shen, Shu Jiao, Gan Jiang, Fu Zi. Combination Characteristics: Sour, bitter, acrid, and sweet are all included, with both cold and warm, attacking and tonifying used together. 3. Gan Jiang Huang Qin Huang Lian Ren Shen Tang Syndrome: Cold reverses and vomits, food intake leads to vomiting. 【Jueyin Cold Syndrome】 4. Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Syndrome (Blood Deficiency Cold Reversal) ☆ Cold limbs, thin pulse, and desire to die, Dang Gui Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. (351) Main Symptoms: Cold limbs, thin pulse, and desire to die. Pathogenesis: Blood deficiency and cold congealing, Qi and blood movement is obstructed. Treatment Method: Nourish blood, unblock the pulse, warm the meridians, and disperse cold. Ingredients: Dang Gui, Shao Yao, Gui Zhi, Xi Xin, Gan Cao, Da Zao, Tong Cao. 5. Wu Zhu Yu Tang Syndrome. Dry vomiting with foamy saliva, headache, Wu Zhu Yu Tang is the main treatment. (378) (Main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, ingredients see Shaoyin 10) Memorize 243, 309, 378, reflecting the same treatment for different diseases. 【Jueyin Heat Syndrome】 6. For severe diarrhea with heat, Bai Tou Weng Tang is the main treatment. Heavy diarrhea: refers to urgent bowel movements, characterized by abdominal pain and a strong urge to defecate, but difficulty in passing stool. 7. Comparison: Tao Hua Tang Syndrome vs. Bai Tou Weng Tang Syndrome. Both can present with diarrhea with pus and blood, but the pathogenesis differs between cold and heat, and deficiency and excess. Tao Hua Tang Syndrome is caused by spleen and kidney Yang deficiency, leading to inability to control the lower jiao, hence the diarrhea is slippery and unrestrained, with dark blood color, foul odor, and often accompanied by continuous abdominal pain, preference for warmth and pressure, no thirst, pale tongue with white coating, hence the treatment should warm the middle and dispel cold, and bind the intestines to stop diarrhea. Bai Tou Weng Tang Syndrome is caused by liver damp-heat, pressing on the large intestine, hence the diarrhea is characterized by urgency and heaviness, with bright red pus and blood, foul-smelling stools, often accompanied by severe abdominal cramping, thirst for cold drinks, red tongue with yellow coating, hence the treatment should clear heat, dry dampness, cool the liver, and detoxify. 【Differentiating Jueyin Heat Excess Syndrome】 8. Be able to judge: first cold then heat, less cold and more heat – good prognosis; first heat then cold, more heat and less cold – poor prognosis. 9. Exclusion: The syndrome name, the danger of the middle Qi collapsing and desiring food.
【Differentiating Jueyin Reversal Syndrome】 10. The pathogenesis and characteristics of reversal: Any reversal indicates that Yin and Yang Qi are not in harmony, leading to reversal. Reversal is characterized by cold limbs. (337) 11. Heat Reversal ☆ Characteristics: The deeper the reversal, the deeper the heat; the milder the reversal, the milder the heat. (335) Treatment Method: Purging method (including clearing method). Treatment Contraindications: Acrid warm sweating. If the pulse is slippery and there is reversal, it indicates internal heat, Bai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (350) 12. Cold Reversal ☆ If there is excessive sweating, heat does not dissipate, internal tension, limb pain, and diarrhea with reversal and aversion to cold, Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. (353) If there is excessive sweating, and reversal occurs, Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. (354) 13. Comparison: Heat Reversal vs. Cold Reversal. 14. Phlegm Reversal (Familiarize with) If the patient has cold limbs, and the pulse is occasionally tight, it indicates that the evil is obstructing the chest, fullness below the heart, and agitation, with inability to eat, the disease is in the chest, and it must be purged, Gua Di San is the main treatment. If it resembles Gui Zhi syndrome, with no headache, no stiff neck, and a floating pulse, it indicates that there is cold in the chest, and it must be purged, Gua Di San is the main treatment. Gua Di San: Gua Di, Chi Xiao Dou, Xiang Chi, a representative formula for purging. 15. Water Reversal → Fu Ling Gan Cao Tang ☆ Main Symptoms: Reversal and palpitations. It may accompany cold pain in the stomach and back, pale tongue, white slippery or greasy coating. Pathogenesis: Middle Yang deficiency, water retention. Treatment Method: Warm and transform water and fluid. Ingredients: Fu Ling, Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang. 【Differentiating Vomiting and Diarrhea Syndromes】 16. Differentiating Vomiting Syndromes: If there is vomiting and fever, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. (379) 17. Differentiating Diarrhea Syndromes: If there is diarrhea with irritability, it indicates dry stools, and Xiao Cheng Qi Tang is the main treatment. Heat accumulates and flows, common cause and common use: This article, Da Chai Hu Tang syndrome (165), Da Cheng Qi Tang syndrome (321). 18. Shang Han with diarrhea, lasting for more than ten days, and the pulse is still solid indicates death. (369) – Pulse and symptoms do not match. 19. Dai Yang: Deficiency of Yang Qi in the lower jiao, with excessive internal cold, floating above, presenting as a floating red face, and a floating large pulse, indicating true cold and false heat.
Huo Luan Disease Section 【Pulse and Symptoms】 1. Main Symptoms: Vomiting and diarrhea alternating, with exterior symptoms. Pathogenesis: Spleen and stomach ascending and descending dysfunction, with clear and turbid intermingling. 2. Huo Luan, headache, fever, body pain, with more heat and desire for water, Wu Ling San is the main treatment; with more cold, do not use water. Li Zhong Wan is the main treatment. (386) 3. Vomiting and diarrhea, sweating, fever, aversion to cold, with cold limbs, and reversal, Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. If vomiting has stopped and diarrhea occurs, sweating and reversal, with cold limbs, and the pulse is thin and about to disappear, Tong Mai Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. If there is aversion to cold, the pulse is thin and there is diarrhea, it indicates blood loss, and Si Ni Tang is the main treatment. If vomiting and diarrhea stop, but body pain persists, it is necessary to harmonize and resolve the exterior, Gui Zhi Tang is the main treatment for slight harmonization. 【Yin and Yang Reversal After Labor Recovery Disease Section】 1. After a major illness, if there is a reversal, Zhi Shi Zhi Zi Chi Tang is the main treatment. (393) Reversal: Refers to the recurrence of a major illness due to overexertion after initial recovery. 2. After Shang Han, if there is a recurrence of fever, Xiao Chai Hu Tang is the main treatment. If the pulse is floating, it should be resolved with sweating; if the pulse is deep and solid, it should be resolved with purging. (394) 3. After a major illness, if there is water retention below the waist, Mu Li Ze Xie San is the main treatment. (395) 4. After a major illness, if there is excessive salivation, and it has not resolved for a long time, with cold in the chest, it should be treated with pill medicine, Li Zhong Wan is the main treatment. (396) 5. After Shang Han, if there is weakness, low energy, Qi reversal, and desire to vomit, Zhu Ye Shi Gao Tang is the main treatment. (397)
The content of this article is for reference only,not for professionaldoctorsplease do not attempt acupuncture or medication

