Observation of Tongue Shape
The shape of the tongue refers to the characteristics of the tongue body, including aspects such as age (old or young), thickness (fat or thin), spots, cracks, and teeth marks.
1. Old Tongue vs. Young Tongue
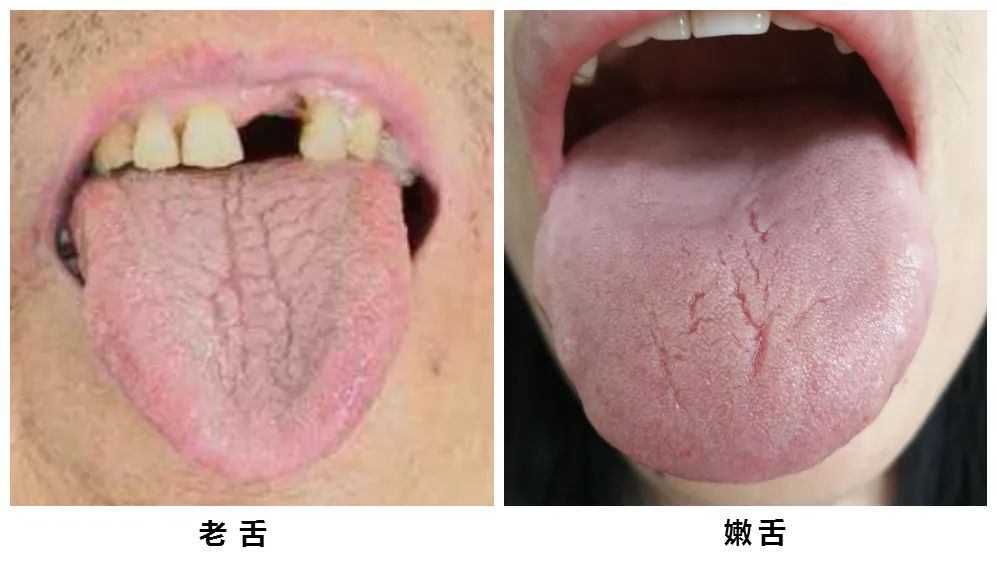
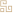
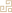
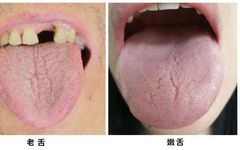
【Tongue Characteristics】
The tongue body has a rough or shriveled texture, appears firm and aged, and has a darker color, indicating an old tongue.
The tongue body has a delicate texture, appears plump and tender, and has a lighter color, indicating a young tongue.
【Clinical Significance】
An old tongue often indicates a pattern of excess.
A young tongue often indicates a pattern of deficiency.
【Mechanism Analysis】
The age of the tongue body is one of the signs of the deficiency or excess of disease. When the pathogenic factors are strong and fill the body, while the righteous qi is not weakened, the evil and righteous qi conflict, causing the tongue body to appear old.
When there is insufficient qi and blood, the tongue body and vessels are not filled, or when yang qi is deficient, leading to weak blood circulation, and internal cold dampness arises, the tongue appears tender and pale.
As stated in the “Guide to Tongue Diagnosis”: “If the tongue body is firm and aged, regardless of the coating color being white, yellow, gray, or black, the condition is mostly excess; if the tongue body is plump and tender, regardless of the coating color being gray, black, yellow, or white, the condition is mostly deficiency.”
2. Fat Tongue vs. Thin Tongue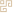
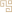
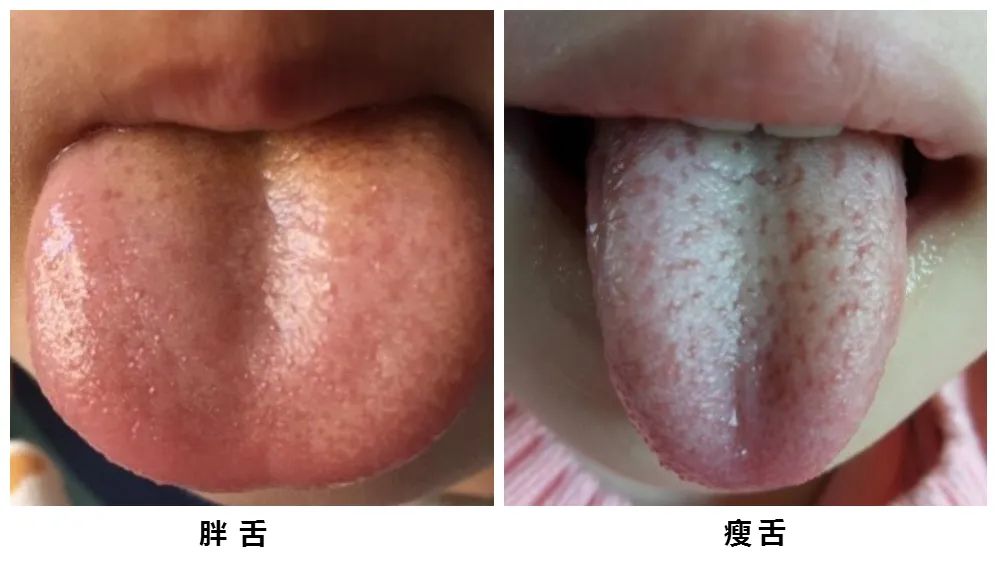
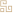
【Tongue Characteristics】:
A fat tongue can be classified into two types: a plump tongue, which is larger and thicker than a normal tongue, filling the mouth, referred to as a fat tongue.
A swollen tongue fills the mouth and may even be unable to close, and when extended, it is difficult to retract, referred to as a swollen tongue.
A thin tongue is smaller and thinner than a normal tongue, referred to as a thin tongue.
【Clinical Significance】
A plump tongue often indicates internal dampness or phlegm retention.
A swollen tongue often indicates damp-heat or heat toxin accumulation.
A thin tongue often indicates deficiency of both qi and blood, or excess heat from yin deficiency.
【Mechanism Analysis】
A pale and plump tongue is often due to spleen and kidney yang deficiency, leading to obstruction in the distribution of fluids, causing dampness to stagnate in the body.
A red and plump tongue is often due to damp-heat in the spleen and stomach, combined with phlegm-heat rising.
A swollen tongue that is red indicates causes such as excessive heat in the heart and spleen, heat toxin accumulation; or a history of alcohol consumption combined with heat illness, leading to heat toxin accumulation; or poisoning leading to blood stasis.
Additionally, patients with congenital tongue hemangiomas may present with localized blood vessel obstruction, resulting in a bluish-purple swelling.
A thin tongue is generally due to insufficient qi, blood, and yin fluids, leading to an inability to nourish the tongue body. A thin and pale tongue often indicates deficiency of both qi and blood;
A thin tongue that is red and dry, with little or no coating, is often seen in cases of excess heat from yin deficiency.

Zhao Lianguo, a native of Jilin Province, a member of the Communist Party, graduated from Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. He has studied under renowned TCM experts, including Professor Li Yueqing, a famous TCM master in the capital, and Professor Jing Xiaodong, one of the top ten doctors in Jilin City. He is a special lecturer in the Green Therapy Department of Mo Mei De Qi and Blood, and a top 100 lecturer on the Chinese Lecturer Network, specializing in the use of herbal plaster therapy for pediatric and internal medicine diseases, as well as blade needle therapy for pain management.


People who click here are very good-looking