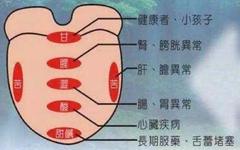
1. Tongue
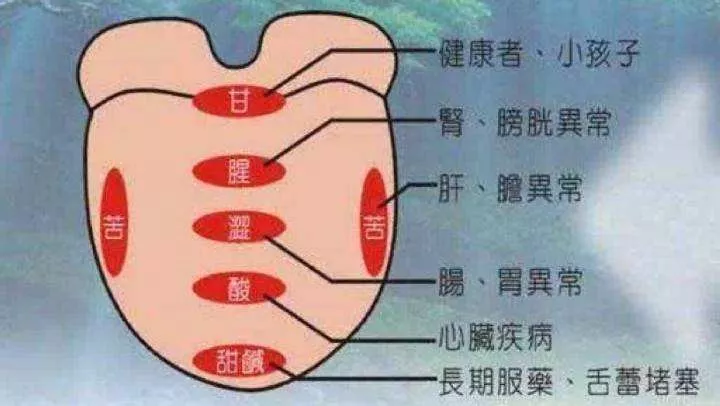
1. The tongue is light red and moist, with a thin white coating, without cracks or indentations: indicates good health.2. Thick tongue coating: indicates indigestion, excessive putrefactive substances in the intestines, or fever and headache.3. Pale tongue color: may indicate anemia.4. Purple tongue color: indicates body hypoxia, commonly seen in patients with pulmonary heart disease, liver disease, and cancer.5. Bright red and dry tongue, with cracks: indicates the patient may have diabetes.6. Bright red tongue: indicates a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid.7. Purple or magenta tongue: indicates a deficiency of vitamin B2.8. Trembling tongue when extended: may indicate neurasthenia, chronic illness, encephalitis, hyperthyroidism, etc.9. Swollen red tongue with prickles: may indicate severe pneumonia, scarlet fever, or other high fever diseases.10. Inflexible tongue movement, slurred speech: is a precursor to cerebral vascular rupture.11. Fat and tender tongue with teeth marks on the sides: indicates the patient has edema and a deficiency of vitamin B1.12. Enlarged tongue: may indicate hypothyroidism.13. White coating on the tip of the tongue: may indicate gastric mucosal inflammation.14. White coating on the back of the tongue: may indicate enteritis.15. Swollen and red tongue: may indicate problems with the gallbladder or pancreas.16. Yellow tongue coating: indicates possible liver dysfunction or indigestion.

2. Taste Sensation
“Smell the fragrance and odor, taste the five flavors.” If there is an unusual taste in the mouth while eating, or if there is an unusual taste in the mouth even when not eating, it may indicate a certain disease.
1. Bitter taste: often caused by heat in the liver and gallbladder, related to abnormal bile secretion.2. Sweet taste: due to damp-heat stagnation in the spleen and stomach, related to digestive system dysfunction.3. Sour taste: commonly seen in gastritis and gastrointestinal ulcers.4. Spicy taste: often belongs to excessive liver fire or phlegm-heat, can also occur in hypertension, neuroses, menopausal syndrome, and chronic low-grade fever patients.5. Salty taste: commonly seen in chronic pharyngitis and oral ulcers, can also appear in chronic nephritis and renal dysfunction.6. Bland taste: commonly seen in spleen and stomach deficiency or post-illness spleen deficiency with weak transport function. Digestive system diseases, endocrine diseases, and long-term febrile consumptive diseases, malnutrition, protein, and caloric deficiency can all cause a bland taste.7. Astringent taste: commonly seen in neuroses or those who have not slept all night; some patients with malignant tumors, especially in late stages, often have astringent taste.8. Fragrant taste: often seen in diabetic patients.9. Bad breath: often due to indigestion, retained food in the stomach, periodontal disease, dental caries, oral ulcers, and nasopharyngeal diseases can also cause bad breath.
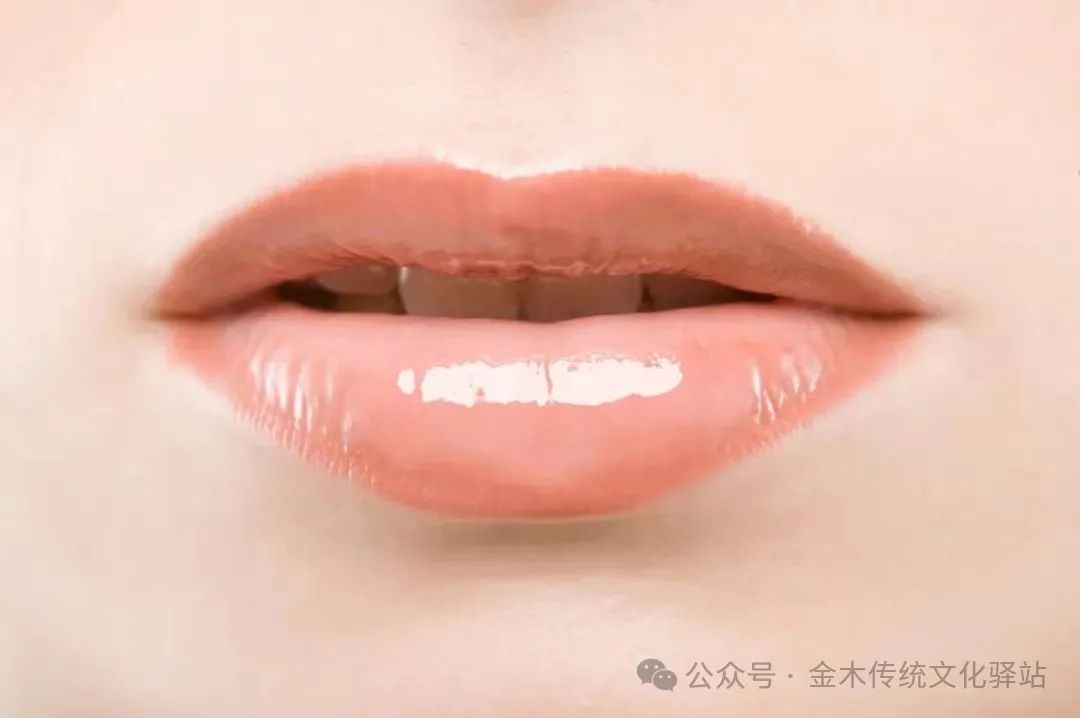

3. Lips
Normal lips are rosy, with appropriate moisture, smooth and shiny.
1. Pale lips: pale lips often indicate spleen and stomach weakness, insufficient qi and blood, commonly seen in anemia and asthenia;
pale upper lip often indicates large intestine deficiency and cold, diarrhea, bloating, abdominal cramping, fear of cold, and mixed symptoms of heat and cold;
pale lower lip indicates stomach cold, which may lead to vomiting and diarrhea, stomach cold, and abdominal pain.
2. Light red lips: often indicate blood deficiency or both qi and blood deficiency. This lip color can be seen in individuals with weak constitutions but no disease.3. Deep red lips: lips that are bright red often indicate fever. In patients with pulmonary heart disease and heart failure, they may appear purplish-red when hypoxic, clinically referred to as cyanosis. Lips that are peach-red are often seen in carbon monoxide poisoning.4. Blue lips: indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis, often due to poor blood flow, which can lead to acute diseases, especially vascular diseases such as embolism and stroke.5. Black lips: black lips indicate kidney failure, and dry, dark purple lips are a bad sign. If the lips are dark and murky, it often indicates digestive system diseases, sometimes accompanied by constipation, diarrhea, lower abdominal pain, headache, insomnia, and loss of appetite; if black spots appear on the lips, and pigmentation occurs at the edges, it is often seen in chronic adrenal cortex insufficiency; if black spots appear on the lips, especially on the lower lip and oral mucosa, densely packed without discomfort, it may indicate multiple polyps in the gastrointestinal tract.

4. Eyes
The eyes are the windows to the soul and are one of the most important sensory organs in the body. The spirit of the eyes is key to observing the fullness or depletion of the body’s vital energy.1. Bright eyes: the eyes must be clear and bright, moving flexibly, with clear vision and rich inner content. This indicates that the body’s qi and blood are abundant, and the functions of the organs are active.2. Dull eyes: refers to a scattered gaze, cloudy cornea, and dull sclera, with a vacant expression. This indicates that the body’s qi and blood are depleted, and the organs are failing, often seen in critically ill patients or elderly individuals.3. Eye diseases or systemic diseases can cause changes in the color of the eyes.4. Red color: red eyes are mainly due to local inflammation and congestion. Systemic inflammatory diseases can also cause red and swollen eyes, such as blood disorders, whooping cough, viral pneumonia, meningitis, tuberculosis, and viral mumps.5. Yellow color: yellow spots or yellow nodules on the eyelids indicate the possibility of yellow tumors or liver cirrhosis. If yellow tumors or yellow nodules are found on the inner side of the upper eyelid, symmetrical and yellowish raised spots, it is often a sign of diabetes.6. White color: pale conjunctiva can be seen in anemia or chronic blood loss diseases.7. Green color: patients with greenish pupils may have intestinal obstruction. The sclera may appear green, indicating a possible sign of intestinal obstruction.8. Blue color: patients with intestinal parasites may have bluish-gray spots on the sclera.9. Black color: often due to insufficient sleep, menstrual irregularities, or excessive sexual activity.10. Observing the shape of the eyes involves checking for any abnormal changes in the eyelids, eye sockets, and eyeballs.11. Swollen eyelids: if the eyelids remain swollen for a long time and are accompanied by other discomforts, this is a sign of disease. Swelling of the lower eyelids in elderly individuals, known as “senile bags,” is a normal physiological change in the elderly.12. Sunken eyes: sunken eyes are often seen in patients with diarrhea and vomiting due to severe dehydration. Severe chronic wasting diseases, such as tuberculosis, diabetes, liver disease, and late-stage tumors, can also cause sunken eyes.13. Protruding eyes: if both eyes protrude, with sharp gaze and symmetrical swelling of the neck, this indicates hyperthyroidism. In patients with high myopia, the eyeballs may protrude due to an elongated axial length, which is a form of pseudo-protrusion.14. Healthy sclera should be white and shiny, without any other colors. If there are unusual colors or spots, it indicates that there may be a disease in the internal organs.15. Bluish-white sclera: this is a sign of anemia.16. Greenish sclera: often indicates intestinal obstruction.17. Yellow sclera: indicates jaundice, which is caused by liver disease or biliary disease, pregnancy toxemia, and some hemolytic diseases.18. Scleral hemorrhage: this is a signal of arteriosclerosis, especially cerebral arteriosclerosis.19. Small red spots on the sclera: this is the result of capillary dilation, most commonly seen in diabetic patients.20. Red and congested sclera: often caused by bacterial or viral infections. Severe insomnia, heart failure, and high blood pressure can cause conjunctival congestion before cerebral hemorrhage and seizures. If one eye is red, it may indicate a possible sexually transmitted infection.
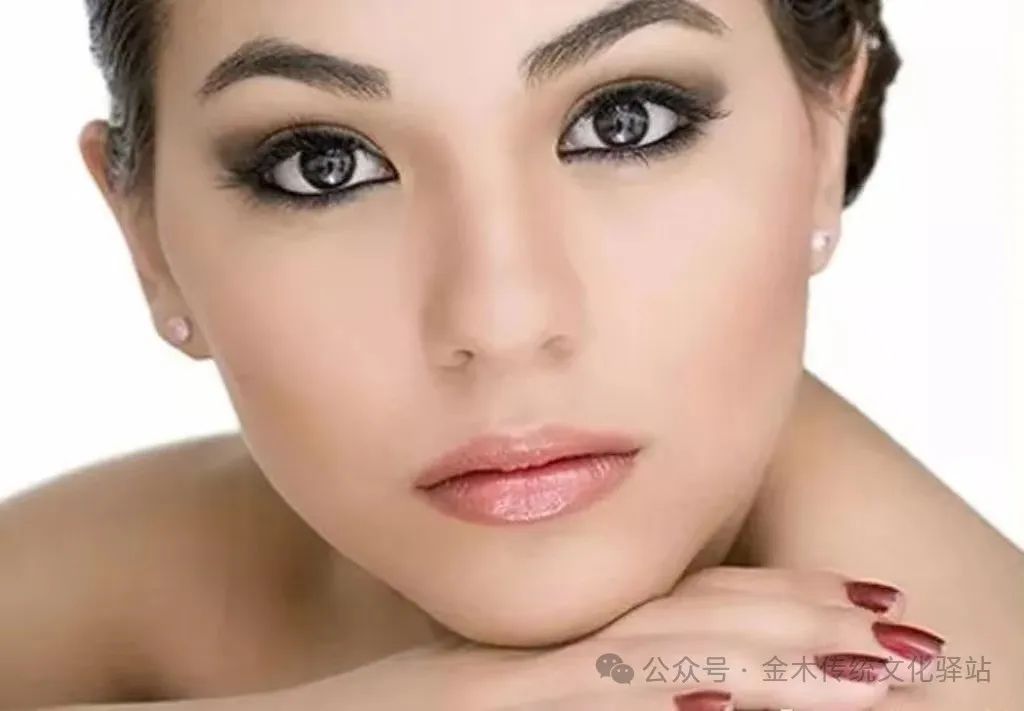

5. Eyebrows
Eyebrows are the faithful companions of the eyes. Normal eyebrows are thick, long, dense, moist, and shiny.1. Sparse and thin eyebrows: indicate weak kidney qi and a frail constitution.2. Overly sparse or fallen eyebrows: commonly seen in mucinous edema, pituitary anterior lobe dysfunction, and hypothyroidism.3. Dry and straight eyebrow tips in women may indicate menstrual irregularities, while in men, it may indicate neurological diseases.4. Especially thick and black eyebrows in women may be related to adrenal cortex hyperfunction.5. Thick skin around the eyebrows, with particularly sparse and fallen eyebrows: should be checked for leprosy to seek medical attention early.6. Eyebrows with a bluish tint: this is a normal color without disease; if they appear pale, it often indicates a heat syndrome.7. Elderly individuals with sparse and fallen eyebrows: often caused by insufficient qi and blood, mostly not a disease.

6. Nose
“The nose is the orifice of the lungs,” serving as the gateway for breathing. Diseases of the internal organs can often be discerned from the nose.1. Pale nose: commonly seen in anemia.2. Black nose: commonly seen in stomach diseases.3. Hard lumps on the nose: may indicate diseases of the pancreas or kidneys.4. Brown or black spots on the skin of the nose bridge: likely caused by sun exposure, black heat disease, or liver disease.5. Red patches on the skin of the nose bridge: often seen in systemic lupus erythematosus.6. Redness and small papules or pustules on the wings and tip of the nose: commonly seen in everyday acne.7. Brown, blue, or black nose: may indicate problems with the spleen and liver.8. Red inner edges of the nostrils, with ulceration of the nasal septum: commonly seen in syphilis.9. Red outer edges of the nostrils: may indicate intestinal diseases.10. Hard nose: may indicate arteriosclerosis or high cholesterol.11. Swollen nose: indicates possible heart problems.12. Sudden redness of the nose: may indicate problems with the heart and blood circulation.
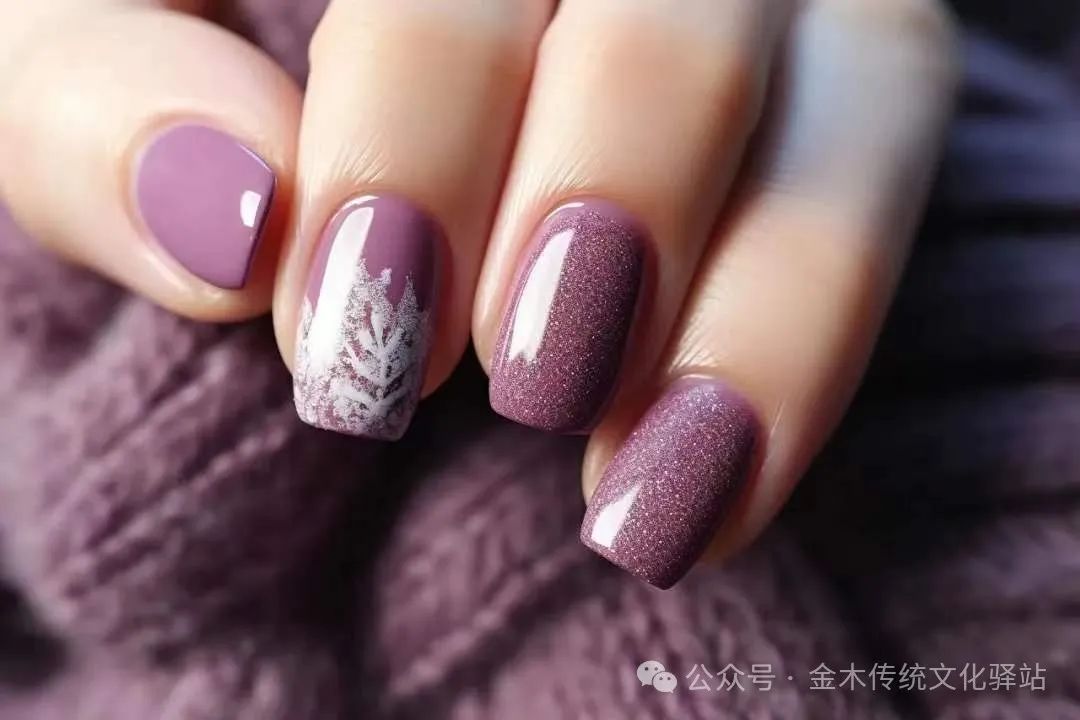

7. Nails
Nails are like small “screens” that reflect the physiological and pathological changes of the body.Healthy nails are semi-transparent, with a light red hue, smooth, shiny, tough, and of appropriate thickness.1. White nails: may indicate kidney or liver disease.2. Blue nails: indicate circulatory disorders.3. Yellow nails: commonly seen in bronchitis.4. Red lines on the nails: indicate hypertension, rheumatism, or heart disease.5. Horizontal grooves on the nails: indicate fatigue, tension, excessive worry, or nutritional deficiencies.6. Glassy nails: indicate liver atrophy or tuberculosis.7. Pale nails: commonly seen in anemic individuals.8. Yellow nails: commonly seen in jaundice.9. Purple nails: often due to bruising and hypoxia, commonly seen in heart disease and blood disorders.10. Blue nails: commonly seen in cold pain and pediatric convulsions.11. Red nails: indicate carbon monoxide poisoning, with both nails and skin turning red.12. White spots: indicate the presence of roundworms or recent viral infections, and calcium deficiency can also lead to white spots.The base of the nails has a white crescent shape, commonly known as the “half-moon.” Its size generally occupies one-fifth of the nail, with the thumb being the largest, followed by the index finger, and the little finger being the smallest. Having this standard shape indicates generally good health. (1) If the “half-moon” is absent on all ten fingers: it often indicates some issues with the circulatory system, and may easily lead to neurasthenia, anemia, or low blood pressure. (2) If the “half-moon” is excessively large, exceeding one-fifth of the nail: it indicates excessive cardiac load, which may lead to cardiovascular diseases. (3) If the “half-moon” is too small: it may lead to asthma, gout, pneumonia, or gastrointestinal diseases. (4) If all four fingers have a “half-moon,” but the thumb does not: it indicates a weak body, prone to illness. (5) If none of the four fingers have a “half-moon,” but the thumb does: it indicates that health is acceptable, and there is no need to worry. (6) If the “half-moon” turns blue: it indicates heart disease. (7) If the “half-moon” suddenly shrinks and becomes barely visible: it indicates a possible serious illness, and immediate medical attention is required.
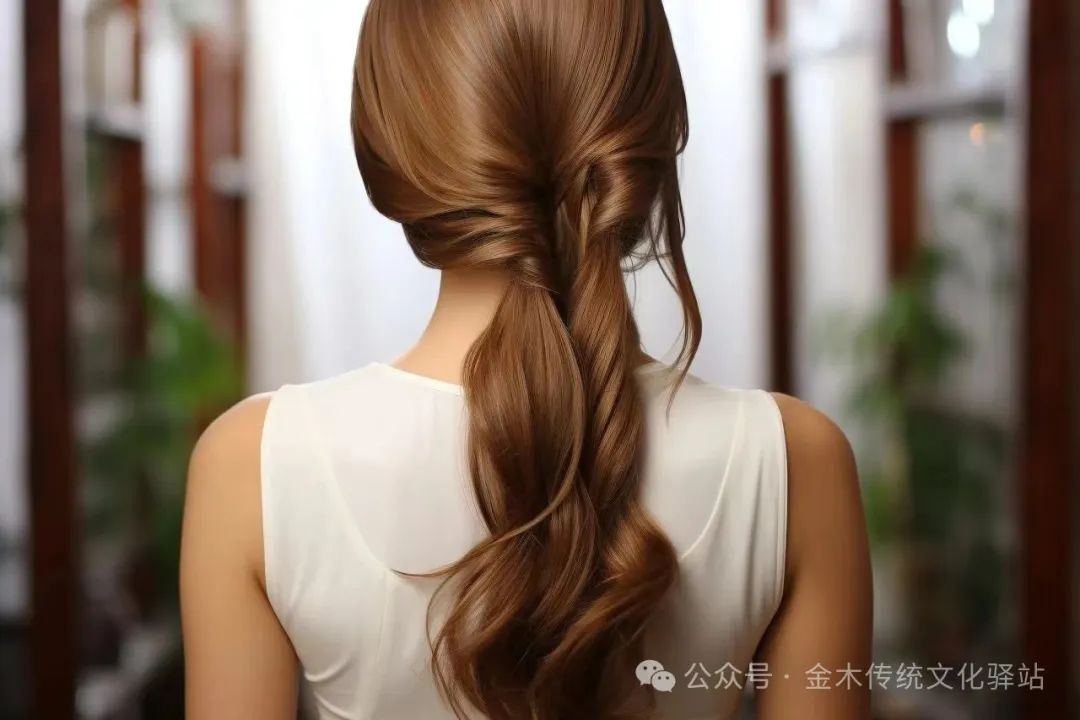

8. Hair
Hair can reflect the journey of life.1. Premature graying: if young individuals have gray hair, it is necessary to check whether it is due to genetic or psychological factors, or if it is caused by disease. Conditions such as tuberculosis, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, and arteriosclerosis can lead to premature graying.2. Gray hair: commonly seen in thyroid dysfunction, premature aging, and vitiligo.3. Gray hair: commonly seen in diabetes, anemia, typhus, and psychological trauma.4. Red hair: often due to lead or arsenic poisoning.5. Yellowish-red hair: indicates dual deficiency of qi and blood, and malnutrition.6. Orange-yellow hair: indicates insufficient kidney qi and loss of essence and blood, commonly seen in liver and gallbladder diseases.7. Androgenetic alopecia: is an autosomal dominant inheritance that can be passed down through generations.8. Early baldness: commonly seen in individuals with mental labor, with genetic influences.9. Patchy alopecia: commonly known as “ghost shaving head,” often due to autoimmune diseases, and is closely related to emotional factors.

9. Skin
The skin is the body’s first line of defense. The skin of a healthy person is slightly translucent and rosy. Certain diseases and many skin conditions can send various signals of disease before and during the course of illness.1. Pale skin: the most common cause is various anemias, due to a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood, leading to pale skin color. Cold, fear, shock, and aortic valve insufficiency can also cause pale skin and mucous membranes.2. Yellow skin: yellowing of the skin, especially the whites of the eyes, is a symptom of jaundice, which can be seen in biliary obstruction, liver cell damage, hemolysis, etc. If the skin is light lemon yellow, it is often seen in hemolytic jaundice; if the skin is golden yellow or orange-yellow, it is often due to jaundice-type viral hepatitis; dark yellow or yellow-green skin is often seen in liver cancer, pancreatic head cancer, obstructive jaundice, etc.3. Red skin: physiological redness can be seen after exercise, drinking, sun exposure, bathing, shyness, or anger. Febrile diseases, such as lobar pneumonia, pulmonary tuberculosis, and scarlet fever, can also cause skin redness. If the entire body is red, it is a signal of rifampicin poisoning, and immediate hospitalization is required.4. Purple skin: purple skin is commonly seen on the tongue, lips, cheeks, ears, and extremities, often due to hypoxia. The appearance of cyanosis, accompanied by difficulty breathing, is often seen in severe heart and lung diseases. Excessive consumption of vegetables containing nitrites, which have deteriorated due to bacterial action, can also cause purple skin.5. Black skin: if the skin suddenly turns black and loses its luster, covering the body with a layer of black veil, this indicates Addison’s disease. Liver cirrhosis and late-stage liver cancer can also cause varying degrees of skin darkening.6. Brown spots: some brown spots that appear on the skin of elderly individuals are called age spots, which are seen as a signal of aging. If an elderly person suddenly develops large age spots in a short period, it may indicate that there is a hidden malignant tumor in the body, and they should immediately go to the hospital for further examination and diagnosis.

10. Itchy Skin
Itching of the skin does not necessarily indicate a skin disease, but it may be a signal of certain diseases that should not be taken lightly.1. Digestive system diseases: such as hemorrhoids, anal fistula, anal fissures, rectal inflammation, intestinal parasitic diseases, etc., often cause anal itching. Obstructive jaundice, due to increased bile salt content in the blood, destroys the body’s lysosomes, releasing proteolytic enzymes and histamine, leading to skin itching.2. Urinary and reproductive system diseases: some chronic nephritis, entering the uremic stage, often cause systemic skin itching due to increased uremic toxins and protein derivatives in the blood.3. Endocrine system diseases: about 1% to 8% of patients with hyperthyroidism experience skin itching.4. Central nervous system diseases: patients with neurasthenia and cerebral arteriosclerosis often experience paroxysmal itching; patients with brain tumors may also experience severe and persistent itching when the lesions invade the bottom of the fourth ventricle, which is limited to the nose area.5. Certain malignant tumors: especially lymphatic system tumors, such as sarcomas, Hodgkin’s disease, and myeloproliferative diseases, often accompany systemic itching.6. Various chemical particles floating in the air: such as glass fibers, furnace ash, mineral powder, pesticides, flour, etc., can cause itching in some individuals.7. Contact with various cosmetics: hair dye, shampoo, paint, coatings, straw, wheat awns, animal fur, etc., can also cause itching in the contact area.
11. Navel
The navel, also known as the umbilicus, is referred to as “Shen Que” in TCM, connecting the twelve meridians and the five internal organs.1. Round shape: a round navel, with a plump upper half facing up, is the best type for men, indicating normal blood pressure and healthy liver, intestines, and stomach.2. Full moon shape: appearing firm and plump, with elasticity in the lower abdomen, is the best type for women, indicating good physical and mental health and good ovarian function.3. Upward triangle shape: if the navel extends upward, almost forming a triangle with the tip facing up, it suggests a tendency to suffer from digestive and urinary system diseases, such as common diseases of the stomach, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys.4. Downward triangle shape: if the navel extends downward, resembling a triangle with the tip facing down, it suggests a tendency to suffer from gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastritis, gastric prolapse, constipation, etc.; women should pay more attention to the occurrence of gynecological diseases.5. Left-leaning shape: a left-leaning navel often indicates a blood deficiency constitution or may be seen in hypertension, right-sided limb paralysis, or gastrointestinal dysfunction.6. Right-leaning shape: a right-leaning navel often indicates a qi deficiency constitution or may be seen in hypertension, left-sided limb paralysis, or gastrointestinal ulcers, hepatitis, etc.7. Shallow and small shape: a shallow navel with a small and non-round navel ring may indicate low reproductive function, low hormone levels, or may be seen in individuals with chronic illness, fatigue, or weak constitutions.8. Sea snake shape: if the area around the navel resembles a sea snake coiling, it is a common sign of liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.9. Protruding shape: if inflammation causes tissue adhesion in the abdomen, it is often seen in adhesive tuberculous peritonitis.

12. Sweat
Sweat is the liquid secreted by the skin’s sweat glands. The body’s sweat glands can secrete 500 to 1000 milliliters of sweat daily. Sweat can regulate body temperature, body fluids, excrete waste from the body, and keep the skin surface acidic to prevent certain bacteria from invading the body.1. No sweat: this condition often occurs in certain skin diseases (such as ichthyosis, psoriasis, scleroderma), and in rare cases, it is due to congenital abnormalities.2. Night sweats: individuals with yin deficiency often experience night sweats; if accompanied by fatigue, cough, chest pain, loss of appetite, menstrual irregularities, fever, or hemoptysis, it is often due to pulmonary tuberculosis.3. Head sweating: sweating only on the head and face. In elderly individuals, excessive head sweating often indicates weak yang qi; in patients with urinary retention, head sweating is often caused by damp heat. However, if sweating occurs during meals or in children during sleep without other symptoms, it is commonly referred to as “steamer head” and is not pathological.4. Spontaneous sweating: in TCM, this is believed to be caused by qi deficiency and unstable defensive yang. Severely ill patients in recovery often experience spontaneous sweating due to extreme weakness, even at rest. Children with rickets and those with hyperthyroidism may also experience spontaneous sweating.5. Profuse sweating: can be seen in summer, due to excessive internal heat or overdose of sweating medications. In such cases, the causes should be identified and addressed, while also replenishing large amounts of saline drinks to prevent collapse. Severe patients with continuous profuse sweating, referred to as “absolute sweating” in TCM, should be closely monitored to prevent accidents.6. Cold sweat: excessive excitement or fright can cause palpitations, pale complexion, and cold extremities, often leading to “cold sweat.” Cold sweat can also be seen in acute heart failure, myocardial infarction, and critically ill patients experiencing shock.7. Hot sweat: often caused by external wind-heat or internal heat.8. Forehead sweating: if a patient suddenly experiences continuous forehead sweating, it often indicates a worsening condition, and caution should be exercised.9. Chest sweating: often caused by worry, thinking, fright, or fear, excessively damaging the heart and spleen, leading to insufficient heart control over blood and spleen control over blood. Chest sweating can also be seen in patients with abnormal heart and lung function.10. Hand sweating: caused by spleen and stomach heat deficiency, or due to excessive nervousness.11. Unilateral sweating: also known as left or right half-body sweating or upper and lower half-body sweating, refers to sudden sweating. This peculiar sweating phenomenon often indicates a precursor to a stroke.12. Yellow sweat: if the sweat is yellow and has a special fishy odor, it is often seen in liver cirrhosis.13. Foul-smelling sweat: foul-smelling sweat refers to sweat with an unpleasant odor. Sweating in the thighs, chest, armpits, and under the breasts with an odor is normal; however, if the sweat has a fox-like odor, is milky white, and viscous, it indicates axillary osmidrosis. Axillary osmidrosis is caused by abnormal secretion of apocrine glands in areas such as the armpits. If the sweat has a urine-like odor and crystals form on the skin, it is one of the manifestations of uremia.

13. Phlegm
Phlegm is the mucus secreted by the respiratory tract mucosa. Under normal circumstances, healthy individuals do not cough up phlegm; if they do, it is usually only a small amount in the morning after waking up. If the phlegm is clear and transparent, it indicates normal metabolism of lung tissue and bronchial mucosa, without disease. The color of the phlegm can help identify diseases.1. White phlegm: can be seen in bronchitis or pneumonia, often caused by Candida albicans.2. Yellow or green phlegm: indicates infection.3. Green phlegm: commonly seen in jaundice, dry cough pneumonia, and lung infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.4. Brownish-red phlegm: indicates the presence of blood or hemoglobin in the phlegm.5. Pink phlegm: commonly seen in acute pulmonary edema.6. Rust-colored phlegm: commonly seen in lobar pneumonia.7. Brown phlegm: may indicate chronic congestion in the lungs or pulmonary bleeding in heart disease patients.8. Chocolate-colored phlegm: may indicate amoebic dysentery.9. Black or gray phlegm: indicates a high level of dust in the trachea, with phlegm containing dust, coal dust, or smoke, commonly seen in coal miners, boiler workers, or those living in heavily polluted areas and heavy smokers. These individuals should enhance self-protection in their work and life.

14. Urine
Normal urine is generally colorless and transparent or light yellow; in hot weather, with little drinking or excessive sweating, it may appear dark yellow. If the urine appears in various colors, it often indicates a certain disease.1. Colorless urine: commonly seen in psychogenic polydipsia, diabetes insipidus, and diabetes mellitus.2. Red urine: urine that is light red like meat washing water, or bright red, indicates the presence of blood in the urine, often associated with acute nephritis, kidney stones, bladder stones, urethral stones, and tumors. Women with uterine, ovarian, or fallopian tube diseases may also have red urine; sometimes inflammation of the appendix, colon, or rectum can also cause red urine.3. Milky white urine: fresh urine that is turbid like rice soup, commonly seen in filariasis, purulent urinary tract infections, or gonorrhea.4. Yellow urine: indicates biliary obstruction, with bile not being smoothly excreted and refluxing into the blood, causing the urine to be yellow due to a large amount of bilirubin. Common liver and gallbladder diseases (such as acute hepatitis, cholecystitis, and cholelithiasis), total bile duct stones, and pancreatic head cancer can also lead to obstructive jaundice.5. Blue urine: blue urine can be seen in cholera, typhus, especially when the urine is decomposed.6. Black urine: black urine like soy sauce, or brown like wine, is commonly seen in incompatible blood transfusions, favism, etc. Black urine often indicates a serious condition, requiring urgent rescue measures to save lives.7. Foamy urine: if there are many large bubbles in the urine, or if bubbles continue to rise from the urine after the surface bubbles disappear, this is medically termed “foamy urine.” This may indicate cystitis, diabetes, colitis, bladder cancer, rectal cancer, etc. For persistent foamy urine, especially if the bubbles are large and numerous, immediate hospital examination is necessary, as this is crucial for early detection of subtle pathological changes.8. Normal urine often has a special aromatic smell due to the presence of volatile acids.(1) Foul smell: fresh urine with a foul smell is often due to bacterial infections in the urinary tract, such as cystitis, pyelonephritis with abscesses, etc.(2) Apple smell: in diabetic ketoacidosis or starvation, urine may contain acetone, giving it an apple-like smell.(3) Ammonia smell: fresh urine with an ammonia smell is commonly seen in uremic patients.(4) Fecal smell: when E. coli proliferates, urine may have a fecal odor.(5) Foul smell: urine with a foul smell is often seen in malignant tumors, necrosis, and ulceration. Additionally, the frequency of urination can also indicate health status. Healthy individuals urinate 6 to 10 times a day; urinating dozens of times a day is abnormal.
15. Nasal Mucus
Under normal circumstances, nasal mucus is colorless, transparent, and slightly viscous.1. Clear, watery nasal mucus: thin, transparent secretions, like clear water, are often seen in patients with wind-cold colds or acute rhinitis or allergic rhinitis. If clear nasal mucus drips out at a uniform speed, it may indicate the possibility of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea, and timely consultation with a neurosurgeon is necessary.2. Yellow purulent nasal mucus: commonly seen in wind-heat colds, chronic rhinitis, and sinusitis. This yellow purulent nasal mucus is not only abundant but also viscous and difficult to expel.3. Yellow-green nasal mucus or crusts: this is a characteristic of atrophic rhinitis. The main manifestations are: dryness in the nasopharynx, reduced secretion from mucous glands, and difficulty in expelling secretions, leading to the accumulation of a large amount of yellow-green purulent secretions, forming crusts that block the nasal passages, causing nasal congestion. A significant reduction in smell is often accompanied by headaches and nasal bleeding. Yellow-green nasal mucus or crusts are often expelled from the nose, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.4. White, mucous nasal mucus: commonly seen in chronic rhinitis. The main manifestations are nasal congestion and increased nasal mucus. Nasal congestion is often intermittent on both sides or alternates between left and right, sometimes persistent, worsening when lying down, and heavier on the lower side when lying on one side. Severe nasal congestion may be accompanied by nasal voice, reduced sense of smell, dizziness, and dry pain in the throat.5. Blood-stained nasal mucus: nasal trauma, surgery, inflammatory infections, foreign bodies, and systemic diseases (such as hypertension, arteriosclerosis, blood disorders, etc.) can all lead to blood-stained nasal mucus. It is particularly important to be vigilant, as blood-stained nasal mucus is also one of the early symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer, and one should not be complacent.

16. Stool
Healthy stool is brownish-yellow, and changes in stool color are closely related to diseases.1. White or grayish-white stool: indicates biliary obstruction, with possible gallstones, biliary tumors, or pancreatic head cancer. Additionally, grayish-white stool can also be seen after barium meal imaging, which is not caused by disease but is physiological stool.2. White rice-water-like stool: this stool resembles the white liquid of rice washing, is abundant, and is commonly seen in cholera.3. White, greasy stool: abundant and foul-smelling, commonly seen in pancreatic diarrhea or malabsorption syndrome.4. White, mucous stool: indicates possible chronic enteritis, intestinal polyps, and tumors.5. Dark yellow stool: may be caused by congenital defects in red blood cells, hemolytic bacterial infections, malignant malaria, mismatched blood transfusions, certain chemical drug or toxin poisoning, and various immune reactions (including autoimmune diseases).6. Green stool: watery or pasty, with a sour odor and many bubbles, commonly seen in digestive disorders and intestinal dysfunction. If green stool contains pus, it indicates acute enteritis or dysentery. Additionally, consuming large amounts of chlorophyll-containing foods or excessive acidity in the intestines can also turn stool green.7. Light red stool: this stool resembles the washing water of meat, most commonly seen in summer due to consumption of certain pickled foods contaminated by halophilic bacteria; commonly seen in diarrhea caused by salmonella infection.8. Bright red stool: commonly seen in lower gastrointestinal bleeding. The outer layer is covered with fresh blood, with a small amount, and accompanied by severe pain, pain disappears after defecation, indicating anal fissures; if the blood is bright red, varying in amount or in clots, and is on the outer layer of the stool, it may indicate hemorrhoidal bleeding. If the bright red blood is mixed with the stool, it may indicate intestinal polyps or rectal cancer, colon cancer.9. Dark red stool: if the blood and stool are evenly dark red, it is also known as “jam-colored” stool, commonly seen in amoebic dysentery, intestinal polyps, and colon tumors. Another situation is that normal individuals consuming excessive amounts of coffee, chocolate, cocoa, cherries, mulberries, etc., may also have dark red stool, which should be distinguished from the above diseases.10. Black stool: resembling the color of asphalt, also known as tarry stool, is a common type of upper gastrointestinal bleeding stool. This includes duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, gastric antrum inflammation, mucosal prolapse, and esophageal varices bleeding during liver cirrhosis. However, excessive consumption of meat, animal blood, liver, spinach, oral iron supplements, bismuth, activated charcoal, etc., can also cause black stool, which should be distinguished. If black stool disperses in water and shows blood color, it indicates gastrointestinal bleeding. It is often said: “Nine out of ten men have hemorrhoids.” When people experience blood in their stool, they often think of hemorrhoids, neglecting the possibility of colon cancer. Blood in the stool should first raise suspicion of cancer, especially important for the elderly.

17. Flatulence
In medicine, flatulence is often used as a “test balloon” to measure the function of the gastrointestinal tract. No flatulence or abnormal flatulence indicates the presence of disease in the body.1. No flatulence: if there is no flatulence, it means that the anus has stopped expelling gas, and there are subjective symptoms and signs, such as abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting, constipation, increased or absent bowel sounds, or metallic sounds, which may indicate intestinal obstruction. After abdominal surgery, if the patient does not pass gas for several days, it indicates that the patient’s intestinal motility has not recovered well, and the patient cannot eat, requiring appropriate treatment. If the patient can frequently pass gas, it indicates that gastrointestinal function has returned to normal, suggesting that the patient can eat.2. Excessive flatulence: excessive flatulence can be seen in various causes of digestive disorders. Additionally, excessive flatulence may also be caused by excessive intake of starchy and protein-rich foods (such as beans, potatoes, eggs, etc.), or eating too quickly, swallowing too much air, or habitual swallowing of saliva. These do not indicate disease and do not require treatment.3. Foul-smelling flatulence: under normal circumstances, flatulence should not be particularly foul. If flatulence is extremely foul, it is often the result of digestive disorders or excessive consumption of meat, requiring dietary adjustments and digestive aids. Additionally, foul-smelling flatulence can also be caused by consuming foods with strong odors, such as garlic, onions, and leeks, which is not pathological and should not be a cause for concern.

18. Odor
Odor diagnosis has a long history, and the “smell” in the four examinations of traditional Chinese medicine includes smelling odors.When individuals have certain diseases, they emit specific odors, which mostly come from excretions and the respiratory, digestive, urinary, oral, and nasal cavities. Different diseases produce different odors.1. Toast smell: can be seen in patients with typhoid fever.2. Chicken feather smell (like freshly plucked chicken feathers): can be seen in patients with measles.3. Old beer smell: can be seen in patients with lymphatic tuberculosis.4. Raw meat shop smell: can be seen in patients with yellow fever.5. Bitter almond smell: indicates possible cyanide poisoning.6. Peanut smell: indicates possible ingestion of certain rodenticides.7. Metallic smell: long-term exposure to some toxic heavy metals can cause a metallic taste in the mouth.8. Rotten apple smell: can be seen in diabetic patients. When diabetes worsens, a large amount of ketone bodies is produced, leading to a rotten apple smell in the mouth.9. Musty cellar smell: can be seen in patients with infected wounds.10. Sour smell (referring to acidic sweat): can be seen in rheumatic diseases.11. Sour and rotten smell: can be seen in digestive disorders, as the accumulation of food in the stomach often leads to sour and rotten odors.12. Ammonia smell (referring to urine smell): can be seen in patients with nephritis.13. Moldy smell: indicates possible liver disease.14. Foul smell: often caused by poor oral hygiene.15. Pus smell: commonly seen in purulent rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal foreign bodies, or lung abscesses, where ulcers, erosions, and pus formation occur.16. Fecal smell (referring to vomit with a fecal odor): can be seen in acute peritonitis and intestinal obstruction, requiring immediate hospitalization for rescue.17. Foul smell (referring to the foul odor of pus): can be seen in gas gangrene.18. Fox odor: can be seen in osmidrosis (fox odor). If one passes by someone and smells a fox-like odor, it indicates that the person has excessive secretion from the apocrine glands in the armpits, suffering from osmidrosis. This condition does not affect health, is non-contagious, but is often related to family history.

19. Shortness of Breath
Some individuals often experience shortness of breath but do not pay attention to it. In fact, shortness of breath is often a signal of many diseases.1. Left heart failure: commonly seen in hypertension, coronary heart disease, and valvular heart disease. The initial symptoms include a preference for gradually elevating the pillow while sleeping, often being disturbed by chest tightness and shortness of breath. Sudden onset of dyspnea at night is a typical symptom of left heart failure.2. Pulmonary emphysema: when chronic respiratory diseases obstruct ventilation, leading to the expansion of alveoli and loss of elasticity, commonly seen in chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, asthma, and tuberculosis. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, worsening with slight activity, weak cough, and difficulty expectorating phlegm. Early detection and timely control of infection are necessary to avoid respiratory failure.3. Coronary heart disease: when coronary artery blood supply is insufficient, there is often a feeling of chest tightness and difficulty breathing, and it is best to have an electrocardiogram examination promptly.4. Spontaneous pneumothorax: is a common serious complication of pulmonary bullae, pulmonary emphysema, and tuberculosis. When sudden severe chest pain and difficulty breathing occur, careful observation may reveal bulging of the affected side of the chest and widening of the intercostal spaces, with a drum-like sound upon percussion. At this time, avoid vigorous coughing and seek timely examination.5. Pulmonary embolism: commonly seen in valvular heart disease, deep vein thrombosis, cerebrovascular disease, and post-surgical embolism of the pulmonary artery. If symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, cough, or hemoptysis occur, caution is warranted. Additionally, lung cancer, late-stage tuberculosis, silicosis, bronchial asthma, and various pneumonias may also present with shortness of breath. Therefore, one should not take shortness of breath lightly.

20. Dreams
Recurring nightmares are often a sign of disease. They have irreplaceable reference value in diagnosing diseases. These dreams, where the same scenario repeatedly occurs, are medically referred to as “premonitory dreams.”1. Frequently dreaming of someone or a monster knocking on your head or pouring something into your orifices: suggests possible brain tumors or neurological diseases.2. Frequently dreaming of loud horns near your ears or bullets or arrows passing through your head: suggests possible lesions in the head.3. Frequently dreaming of someone choking your throat or feeling as if a fishbone is stuck in your throat, or feeling as if a fork is inserted into your throat: suggests possible lesions in the throat.4. Frequently dreaming of being chased from behind, wanting to call out but unable to: suggests possible insufficient blood supply to the coronary arteries.5. Frequently dreaming of your body being twisted and feeling suffocated, then suddenly waking up: is a sign of angina pectoris.6. Frequently dreaming of falling from a height but waking up before hitting the ground: suggests possible hidden heart disease.7. Frequently dreaming of being trapped in a dark room, feeling difficulty breathing, or dreaming of pressure on the chest, feeling as if carrying a heavy load while walking: suggests possible lung or respiratory tract lesions.8. Frequently dreaming of dealing with fire, such as a raging fire: suggests possible hypertension.9. Frequently dreaming of dealing with water, such as floods: suggests possible liver and gallbladder issues.10. Frequently dreaming of riding clouds with a terrifying appearance: suggests possible lesions in the circulatory and digestive systems.11. Frequently dreaming of being kicked from behind or stabbed, waking up with pain in the waist: suggests possible latent lesions in the waist and kidneys.12. Frequently dreaming of eating rotten food, waking up with a bitter taste in the mouth, or feeling very hungry or experiencing abdominal bloating: suggests possible gastrointestinal diseases.13. Frequently dreaming of needing to urinate but unable to find a toilet, or dreaming of sexual activity: suggests possible endocrine system diseases.14. Frequently dreaming of your legs or one leg feeling heavy as a stone, unable to move: suggests possible lesions in the legs.15. If you remember your dreams clearly upon waking in the morning: indicates neurasthenia or weakened constitution.

21. Signals of Cancer in the Body
Cancer is terrifying, but it does not come suddenly; there are always signs to follow. If your body exhibits the following conditions, it is a reminder to be vigilant, even though this does not necessarily mean cancer, these bodily signals should not be taken lightly, as they are often precursors to cancer.1. Hair: texture and appearance suddenly become poor, becoming brittle and easy to break, with a dry and sparse appearance.2. Chest: lumps of varying sizes appear, usually without pain, with some only painful upon touch.3. Tongue: when eating, all foods taste the same, with no distinction between sour, sweet, bitter, or spicy.4. Eyes: rapid deterioration, with a dull and blurred gaze.5. Stomach: discomfort after eating, with a loss of appetite for previously loved foods.6. Intestines: abnormal bowel habits, such as frequent constipation and blood in the stool.7. Testicles: the most common occurrence in men is the appearance of lumps.8. Uterus or Ovaries: uterine cancer is the most common malignant tumor of the female reproductive system, with frequent contact bleeding, increased vaginal discharge, irregular vaginal bleeding, pain, urgency in urination, constipation, or blood in the stool requiring vigilance.9. Fingers: frequently cold and lacking warmth, with nails appearing grayish and colorless, breaking and peeling.

Spread TCM health knowledge, promote Chinese traditional culture, share health concepts, and convey care, passing health knowledge and traditional culture to more friends…
People are great because they have dreams; we are different because we have love.
Liu Ling Ning: 182 7127 1941 or (WeChat ID)
Yang Shun Song: 138 7171 7447 or (WeChat ID)