Dear friends, we meet again!
Today, I will introduce to you the multifunctional uses of
Lianqiao (Forsythia)
Qingqiao and Laoqiao
LIANQIAO
Qingqiao and Laoqiao
连翘 (Lianqiao, Fructus Forsythiae) is a commonly used clinical herbal medicine, first recorded in the Shennong Bencao Jing. It is the dried fruit of the plant Forsythia suspense (Thunb.) Vahl, belonging to the Oleaceae family. Depending on the harvest time, it can be divided into “Qingqiao” (green forsythia) and “Laoqiao” (ripe forsythia). Qingqiao refers to the nearly mature fruit, while Laoqiao refers to the fully mature fruit.


+ ✦ +
Morphological Characteristics
Qingqiao: Generally does not crack open, with a green-brown surface and fewer raised grayish-white spots; it is hard, with many seeds that are yellow-green and elongated, having one wing that is protruding.
Laoqiao: Cracks open from the top or splits into two lobes, with a yellow-brown surface and a smooth inner surface that is mostly light yellow-brown, featuring a longitudinal septum. It is brittle, with brown seeds that have mostly fallen off.
+ ✦ +
Harvest Time
Qingqiao: Harvested from mid-August to mid-September when the fruit is initially ripe and still green, impurities are removed, steamed, and then dried.
Laoqiao: Harvested from late October to early December when the fruit is fully ripe, dried, and impurities are removed.
+ ✦ +
Properties and Channels
It has a slightly fragrant aroma, is cold in nature, has a bitter taste, and enters the Lung (Fei), Heart (Xin), and Small Intestine (Xiao Chang) meridians.
+ ✦ +
Functions
It has the effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, dissipating nodules and reducing swelling, and dispersing wind-heat. It is used for conditions such as carbuncles, scrofula, mastitis, erysipelas, wind-heat colds, initial stages of warm diseases, heat entering the nutritive level, high fever with thirst, delirium with rashes, and painful urinary dribbling.
Qingqiao is initially green and has a stronger ability to clear heat and detoxify;
Laoqiao is light and disperses heat to the surface, effectively dispersing wind-heat.
+ ✦ +
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of Lianqiao is complex, mainly containing lignans, phenylethanoid glycosides, flavonoids, terpenes, volatile oils, and phenolic acids, among which lignans and phenylethanoid glycosides are the main active components.
Qingqiao: The total amino acid content and Lianqiao glycoside levels are higher than those in Laoqiao.
Laoqiao: The trace element content and Lianqiao glycoside levels are higher than those in Qingqiao; R, S-ampelopsin and ampelopsin methyl ether are present in higher amounts.
The content of Lianqiao glycosides in Qingqiao is higher than in Laoqiao, but Lianqiao glycosides are unstable. Therefore, in traditional Chinese medicine formulations containing Lianqiao, such as Yin Qiao Jie Du Pian, Lianhua Qingwen Jiao Nang, Shuang Huang Lian Zhusheye, and antiviral oral liquids, Lianqiao glycoside is often used as a quality control standard.



The content of Lianqiao glycosides in Laoqiao is higher than in Qingqiao. Research has reported that the anticancer activity of Lianqiao is based on Lianqiao glycosides. Therefore, in cancer treatment, Laoqiao is more effective than Qingqiao.
+ ✦ +
Modern Pharmacological Research
1. Antibacterial Effects
Li Zhongxing and others compared the antibacterial activity of Qingqiao and Laoqiao using the agar dilution method. The results showed that there are differences in the antibacterial activity of Laoqiao and Qingqiao against different bacteria. Laoqiao exhibited better inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis, while Qingqiao showed better inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Ma Xuemei and others studied the antibacterial activity of Lianqiao extracts using the paper disc diffusion method (K-B method), and the results were consistent with Li Zhongxing’s conclusions. Compared to Laoqiao, Qingqiao had better inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus, while its inhibitory activity against Candida albicans was inferior to that of Laoqiao.
2. Anti-inflammatory, Anti-endotoxin, Sweating, and Hepatoprotective Effects
Sun Yingna’s research on the anti-inflammatory, anti-endotoxin, and sweating activities of Qingqiao and Laoqiao indicated that both have good effects in these areas, but Qingqiao acts faster and is more effective than Laoqiao. In terms of hepatoprotective effects, Laoqiao is more effective than Qingqiao in reducing alanine aminotransferase activity.
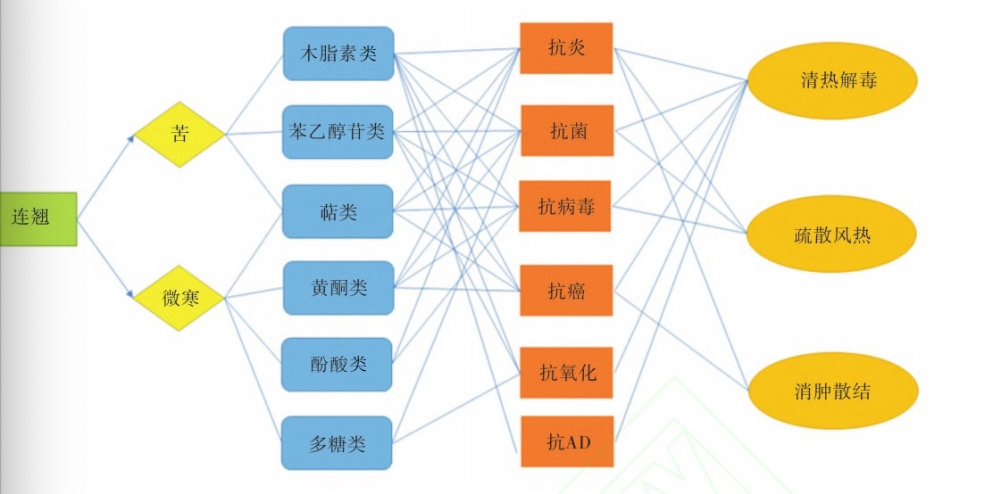
“Pharmacological Activity – Components – Efficacy” correlation diagram
References
[1] Jing Fengtang, Li Feng, Zhang Tianyi, et al. Recent research progress on the chemical composition and biological activity of Lianqiao [J/OL]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2023(01):243-252.
[2] Niu Qun. Research on the harvesting period of Lianqiao fruit [J]. Hebei Forestry Science and Technology, 2021, No.231(04):24-27.
[3] Li Shifei, Zhang Liwei, Zhan Zhilai. The herbal basis of Lianqiao in classic famous prescriptions [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2022, 28(10):111-122.
[4] Yuan Xin. Preliminary study on the quality control standards of Laoqiao [D]. Shanxi University, 2021.
That concludes today’s sharing.
See you next time!
Previous Review
The multifunctional uses of mulberry leaves, mulberry branches, mulberry bark, and mulberries
Text and Images | Network
Design | Liu Meirong
Editors | Ma Baolian, Zhu Yairui