


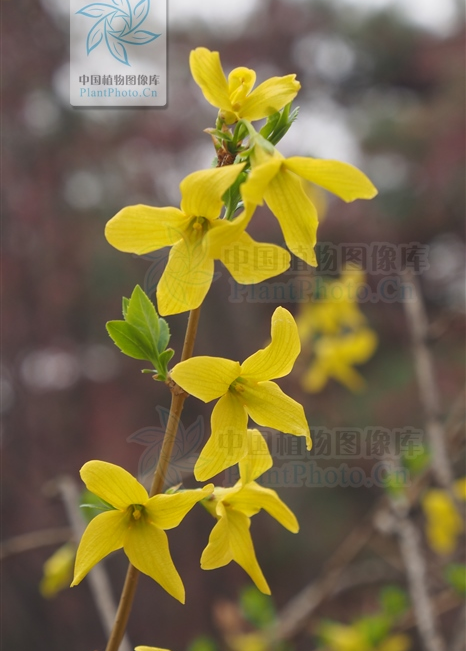
In March, the blooming flowers signal the arrival of spring, and the first to truly convey this feeling is likely the clusters of pale yellow Liánqiáo (Forsythia) swaying in the spring breeze. The name Liánqiáo has been recorded since ancient times in the Éryǎ: “Lián, yìqiáo.” Li Shizhen explained in the Bencao Gangmu: “This is originally called Lián, also known as yìqiáo, and people commonly refer to it as Liánqiáo. Liánqiáo is a plant of the Oleaceae family, and when it blooms, the branches are full of golden yellow flowers, resembling a golden ribbon, hence it is also called Huángshòudài (Yellow Ribbon).
The fruit of Liánqiáo can be used medicinally and has the effect of clearing heat and detoxifying. It is harvested in autumn, with the immature fruit being steamed or briefly boiled, then dried. This is often sold as “Qīngqiáo (Green Forsythia)” due to its greenish color, which is of better quality; the fully ripe fruit is dried after harvesting and referred to as “Lǎoqiáo (Old Forsythia)” or “Huángqiáo (Yellow Forsythia)”; the seeds are used for Liánqiáo heart.
Identifying Medicinal Herbs
1
Plant Characteristics:
Deciduous shrub. The young branches are hollow between the nodes, with solid pith at the nodes.
Flowers—Usually solitary or in clusters of 2 to several in the leaf axils, blooming before the leaves.
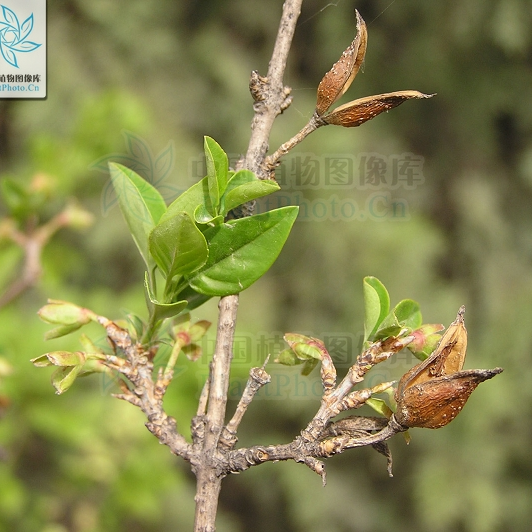
Fruits—Ovoid, oval, or elongated oval, tapering to a beak at the tip.
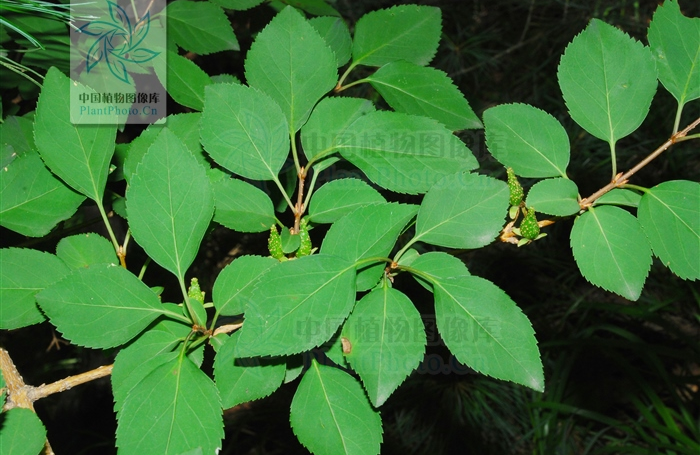



Liánqiáo


2
Characteristics of the Medicinal Material:
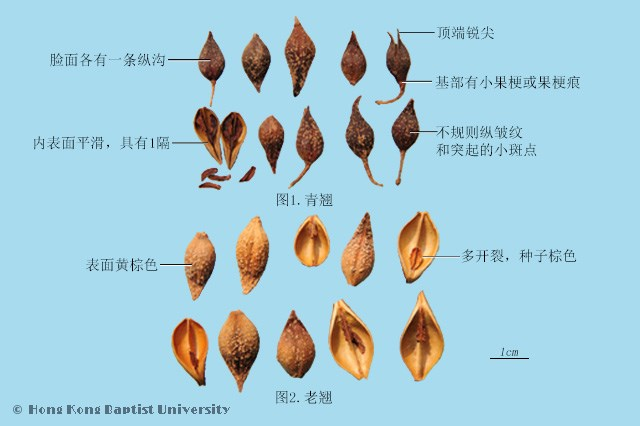
Liánqiáo is long oval to oval, slightly flattened. The surface has irregular longitudinal wrinkles and numerous small raised spots, with a distinct longitudinal groove on each side.
Qīngqiáo is mostly uncracked, with a greenish-brown surface and fewer raised grayish-white spots.
Lǎoqiáo cracks from the top or splits into two lobes, with a yellow-brown or red-brown surface, and the inner surface is mostly light yellow-brown, smooth, with a longitudinal septum.

Medicinal Use

Liánqiáo is bitter and slightly cold. It enters the Lung (肺), Heart (心), and Small Intestine (小肠) meridians. It has the effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, reducing swelling and dispersing nodules, and dispersing wind-heat. It is used for abscesses, scrofula, mastitis, erysipelas, wind-heat colds, initial stages of warm diseases, heat entering the nutritive level, high fever with thirst, delirium with rashes, and painful heat strangury.
Chemical ComponentsContains forsythiaside, volatile oil, triterpenoid saponins, oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, alkaloids, saponins, and a considerable amount of rutin, as well as forsythiaside and geniposide.
Pharmacological EffectsAntimicrobial; inhibits phosphodiesterase and lipoxygenase activity; antipyretic; antiemetic; protects against liver damage; anti-inflammatory; inhibits elastase activity; diuretic; lowers spontaneous hypertension, etc.
Selection of Processed Products
Lǎoqiáo has a strong ability to disperse wind-heat;Qīngqiáo is excellent for clearing heat and detoxifying;Liánqiáo with heart is better at clearing heat evil from the pericardium, effectively treating heat invading the pericardium syndrome.
Contraindications
(1) Disease/Symptom Contraindications: Avoid use in cases of spleen and stomach deficiency-cold, qi deficiency with purulent ulcers; avoid long-term use of single herb in cases of blood-tinged urine, night sweats, low fever, hematemesis, melena, and epistaxis due to yin deficiency with blood-heat; avoid excessive long-term use in chronic enteritis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and chronic diarrhea; patients with low blood pressure should not take it for extended periods.
(2) Compatibility and Combination Contraindications: Should not be used with lactase; should not be used with fluoroquinolone; should not be used with digoxin.
(3) Dietary Contraindications: Avoid spicy and greasy foods.
Differences between Liánqiáo and Yíngchūnhuā (Winter Jasmine)
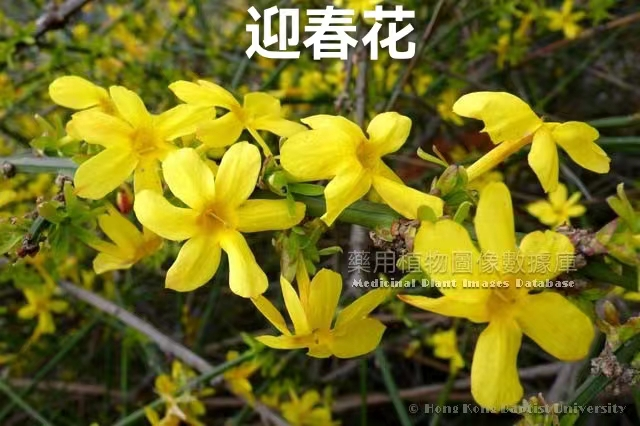
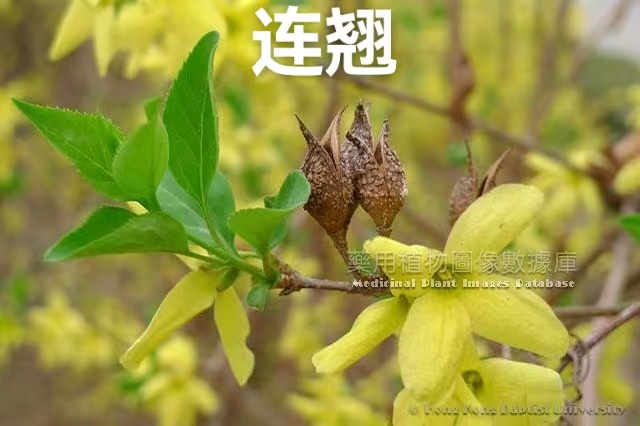



In early spring, the parks or roadsides announce the arrival of spring not only with Liánqiáo flowers but also with the easily confused Yíngchūnhuā (Winter Jasmine). Upon closer observation, there are some differences between the two.
☆ The petals of Liánqiáo are four, while the petals of Yíngchūnhuā are five to six.
☆ Liánqiáo is taller, with branches that do not easily droop; while Yíngchūnhuā is shorter, with drooping branches.
☆ The branches of Liánqiáo are light brown and woody, while Yíngchūnhuā has green and glossy branches.


“Internet News Information Service License”
License No: 14120200027
Source: Beijing First Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital
Editor: Song Xinxin
Coordination: Song Xinxin
Review: Guo Yingge



Special Statement
According to the “Internet News Information Service Management Regulations”, the Lingchuan County Media Center is the only media institution within Lingchuan County with news editing and broadcasting qualifications.
“Internet News Information Service License” License No: 14120200027

