Angelica Sinensis (Dang Gui)
Angelica Sinensis, the dried root of the plant from the Apiaceae family, is a perennial herb that grows to a height of 0.4-1 meter. The flowering period is from June to July, and the fruiting period is from July to September. It is primarily produced in the southeastern part of Gansu Province, particularly in Min County, which is known for its high yield and quality, followed by Yunnan and Sichuan provinces. Its root is used in medicine and is one of the most commonly used traditional Chinese medicines (TCM). It has the effects of nourishing blood, invigorating blood circulation, regulating menstruation, alleviating pain, and moistening the intestines to relieve constipation.
Image of Angelica Sinensis
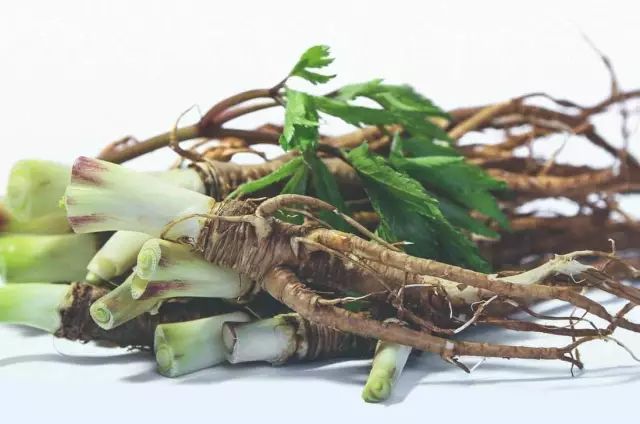

Image of Angelica Sinensis Rhizome

Image of Angelica Sinensis in TCM
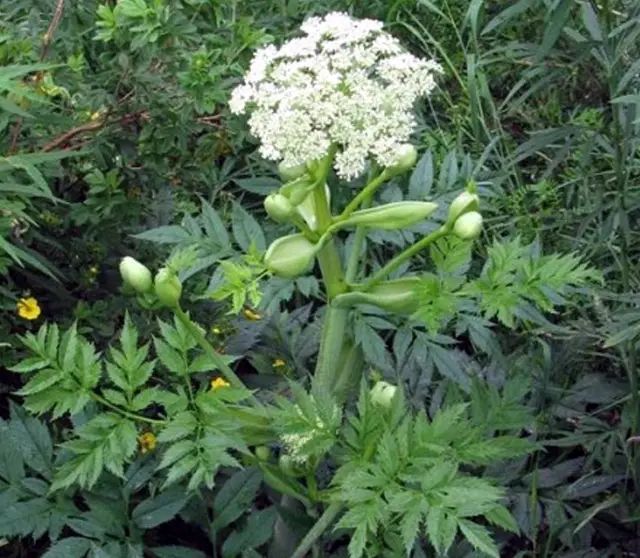

Image of Angelica Sinensis Plant
Introduction to Angelica Sinensis
Herb Name: Angelica Sinensis (Dang Gui)
Pinyin: Dānɡ Guī
Alias: Dang Gui, Xidanggui, Mindanggui, Jindanggui, Dangguishen, Hanguwei, Dangguiqu, Tudanggui, Maweidanggui, Qingu, Maweigui, Yungui.
Source: The dried root of the plant Angelica Sinensis from the Apiaceae family. Harvested in late autumn, the fibrous roots and soil are removed, and after some moisture evaporates, they are bundled into small bunches, placed on racks, and slowly dried with smoke. Impurities are removed, cleaned, moistened, and slightly dried until the internal and external moisture is suitable, then sliced and sun-dried.
Characteristics: The product is slightly cylindrical, with 3-5 or more lateral roots at the lower part, measuring 15-25 cm in length. The surface is yellow-brown to brown, with longitudinal wrinkles and horizontal lenticels. The root head has a diameter of 1.5-4 cm, with annular markings, the upper end is rounded and blunt, with remnants of purple or yellow-green stems and leaf sheaths; the main root surface is uneven; the lateral roots have a diameter of 0.3-1 cm, thicker at the top and thinner at the bottom, often twisted, with a few fibrous root marks.
Chemical Composition: The root contains volatile oil, with samples from Min County in Gansu containing 0.4%, and those from Wenchuan in Sichuan containing 0.7%. The main components of the volatile oil include: phthalide, o-carboxyphenyl pentanone, and Δ2,4-dihydrophthalic anhydride.
Taste and Properties: Sweet, pungent, warm.
Meridian Affinity: Liver, Heart, Spleen meridians.
Storage: Store in a cool, dry place, protect from moisture and pests.
Contraindications:
1. Excessive dosage, such as with Angelica Sinensis tincture, may cause fatigue and drowsiness after administration; these effects can disappear after stopping the medication, but excessive dosage should be avoided.
2. Allergic reactions; some injections of Angelica Sinensis may cause anaphylactic shock, requiring special attention.
3. Improper use; as Angelica Sinensis is a sweet, warm, and moistening tonic, it should not be used in cases of excessive heat and bleeding. Caution is advised in cases of fullness and loose stools.
4. The essential oil of Angelica Sinensis should not be consumed due to the presence of small amounts of carcinogenic substances.
5. Patients with chronic diarrhea or abdominal distension should avoid Angelica Sinensis.
6. Pregnant women should not use Angelica Sinensis.
7. Children should not use Angelica Sinensis.
Efficacy of Angelica Sinensis
Nourishes blood and invigorates blood circulation, regulates menstruation and alleviates pain, moistens dryness and lubricates the intestines. It is used to treat irregular menstruation, amenorrhea with abdominal pain, masses and accumulations, and excessive bleeding; blood deficiency headaches, dizziness, and atrophy; dry intestines and constipation, post-dysentery fatigue; abscesses and sores, and injuries from falls.
Functions of Angelica Sinensis
1. Effect on uterine smooth muscle
Studies by Fu Hua et al. in 1954 reported that Angelica Sinensis from Min County, Gansu, contains two components that stimulate and inhibit uterine smooth muscle, exhibiting a bidirectional effect.
2. Effect on the heart
Experiments on isolated frog hearts showed that the decoction of Angelica Sinensis or the volatile oil contained in its roots and leaves significantly inhibited the contraction frequency of the myocardium.
3. Effect on the blood system
Angelica Sinensis has long been regarded in TCM as a key herb for nourishing blood, used in the treatment of anemia. It has been suggested that its blood-nourishing effect may be related to its vitamin B12 content. However, some studies indicate that Angelica Sinensis alone does not significantly promote the recovery of red blood cells and hemoglobin in animals with hemorrhagic anemia.
4. Effect on the immune system
In an experiment where protein extracted from pig roundworms was used as an antigen along with a whooping cough vaccine to immunize white rats, it was found that Angelica Sinensis significantly inhibited antibody production, with its water extract at a daily dose of 100 mg/kg having effects comparable to the immunosuppressant azathioprine at 5-10 mg/kg.
5. Hepatoprotective effect
Angelica Sinensis has protective effects against liver damage caused by acute carbon tetrachloride poisoning in mice.
6. Antitumor effect
In 1986, five polysaccharide samples from Angelica Sinensis in Min County were screened for antitumor activity in mice, showing that these polysaccharide samples had a certain degree of inhibitory effect on transplanted tumors such as EC and Hep, with tumor growth inhibition rates reaching 39%, minimal side effects, and suitability for long-term use.
7. Radioprotective effect
Mei Qibing et al. observed the protective effects of Angelica Sinensis polysaccharides against acute radiation sickness in mice.
Dosage of Angelica Sinensis
Internal use: 6-12 g. — “Chinese Pharmacopoeia”
Internal use: decoction, 1.5-3 qian; tincture, syrup, or in pills or powders. — “Dictionary of Chinese Medicine”
Internal use: decoction, 6-12 g; or in pills, powders; or tincture; or as a plaster. — “Compendium of Materia Medica”
Formulas with Angelica Sinensis
Note: The following formulas should be used under the guidance of a physician.
1. For treating menstrual obstruction in young women
Angelica Sinensis (sliced and roasted) 1 liang, dry lacquer (stir-fried until smoky) and Chuanxiong each 0.5 liang. Grind the three ingredients into a powder, mix with honey, and form into pills the size of a wutong seed. Take twenty pills with warm wine. — “Sheng Ji Zong Lu”
2. For treating retrograde menstruation from the mouth and nose
First, use ink from Beijing to stop it, then use Angelica Sinensis tail and safflower each 3 qian, with 1.5 cups of water, decoct to 8 parts, and take warm. — “Simple Prescriptions”
3. For treating excessive bleeding
Angelica Sinensis 1 liang, dragon bone 2 liang (stir-fried until red), and fragrant cyperus 3 qian (stir-fried). Grind into a powder, mix with rice wine, and take 3-4 qian on an empty stomach. — “Rumen Shiqin”
4. For treating blood stasis pain and distension with a rough pulse
Angelica Sinensis 3 liang, cinnamon heart 1.5 liang, white peony 1.5 liang (stir-fried with wine), and cattail pollen 2 liang (stir-fried), with blood-resolving agent 3 liang, and Yanhusuo 1.5 liang. Grind into a powder, decoct 3 qian with wine, and take warm after straining. — “Medical Notes”
5. For treating abdominal pain during pregnancy
Angelica Sinensis 3 liang, white peony 1 jin, poria 4 liang, white atractylodes 4 liang, and ze xie 0.5 jin, and Chuanxiong 0.5 jin (0.5 jin can also be 3 liang). Grind into a powder, take a small spoonful mixed with wine, three times a day. — “Jin Kui Yao Lue”
6. For treating urinary difficulty during pregnancy, with normal appetite
Angelica Sinensis, Fritillaria, and Sophora flavescens each 4 liang. Grind the three ingredients into a powder, mix with honey, and form into pills the size of a small bean, taking three pills, increasing to ten pills. — “Jin Kui Yao Lue”
7. For treating fetal movement instability during pregnancy, with abdominal pain
Angelica Sinensis 0.5 liang (chopped), and scallion white 1 fen (finely chopped). Combine the two, first boil with three cups of water until reduced to two cups, add good wine 1 cup, and boil a few more times, strain, and divide into three doses. — “Sheng Ji Zong Lu”

Long press the QR code to follow
Share

Save
Like
View

