



Introduction: Lethargy and heaviness, prone to obesity. The “phlegm” referred to here is not the secretion produced in the trachea, but rather waste that accumulates due to the body’s fluids not being properly transformed and transported. The most significant symptom of a phlegm-damp constitution is obesity. However, not all obese individuals have a phlegm-damp constitution.

The formation of a phlegm-damp constitution is mainly related to the relative insufficiency of spleen function. About 70% of the human body is water, similar to a river. The upper reaches are managed by the lungs, the middle reaches by the spleen, and the lower reaches by the kidneys. The key point is that “the spleen governs transportation and transformation.” Once the spleen is relatively insufficient for a long time, the so-called phlegm-damp constitution will manifest.
 1. What is a Phlegm-Damp Constitution?
1. What is a Phlegm-Damp Constitution?
Symptoms of Phlegm-Damp Constitution
1. Obesity: Most commonly characterized by a large abdomen, due to the relative insufficiency of the spleen and stomach’s transportation and transformation functions, leading to improper distribution and dispersion of body fluids, resulting in phlegm-damp.
2. Excessive sleepiness: Individuals with phlegm-damp have thicker blood, leading to brain hypoxia and insufficient blood supply to the brain, resulting in poor memory and decreased attention. Especially those with spleen deficiency tend to feel sleepy in the morning.
3. Oily skin: The skin’s pores are also one of the body’s metabolic pathways, and individuals with phlegm-damp often have oily and sticky skin metabolites, making them prone to acne.
4. Slow movements and sluggish reactions: Insufficient blood supply to the brain in phlegm-damp individuals often results in slower reactions.
5. Enlarged tongue (with teeth marks on the sides) and thick coating: The tongue is pale and overall plump, with visible teeth marks on the sides, and the coating is thick, often appearing white and greasy; heat-type phlegm-damp may present with yellow coating; cold-type phlegm-damp may present with white coating.
6. Scanty menstruation, delayed menstruation, or even amenorrhea, and may easily develop polycystic ovarian tumors. If phlegm-damp obesity is accompanied by menstrual irregularities, treatment duration must be extended.
7. Dislike of drinking water: The mouth feels sticky, rarely thirsty, and water is not easily absorbed, leading to abdominal distension. Cloudy and foamy urine: Phlegm-damp individuals often have viscous body fluids, leading to cloudy urine.
2. Diseases Easily Caused by Phlegm-Damp Constitution
Obesity – “Obese individuals often have phlegm-damp, while thin individuals often have internal heat.” Phlegm-damp individuals are prone to obesity.
Hypertension – Generally accompanied by symptoms of chest tightness, nausea, dizziness, and swelling.
Hyperlipidemia – Phlegm-damp increases blood viscosity, easily leading to hyperlipidemia.
Fatty liver – Fatty liver caused by alcohol, greasy diet, and staying up late is often related to phlegm-damp constitution.
Coronary heart disease – Phlegm-damp leads to hyperlipidemia, which can further develop into coronary heart disease.
Cerebrovascular diseases – Hyperlipidemia and hypertension can easily lead to cerebrovascular diseases, such as stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Acne – Individuals with phlegm-damp constitution often have oily skin, making them prone to acne.
Gastric diseases – Individuals with phlegm-damp constitution often suffer from gastrointestinal diseases due to dietary indiscretion over time.
Menstrual irregularities – Easily leads to delayed menstruation, scanty menstruation, or even amenorrhea.
3. Health Management Plan for Phlegm-Damp Constitution Using Common Chinese Herbs
Focus on tonifying the lungs, spleen, and kidneys. Use warming and drying herbs such as Ban Xia (Pinellia), Fu Ling (Poria), Ze Xie (Alisma), Gua Lou (Trichosanthes), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), and Che Qian Zi (Plantago). However, remember to “stop when the condition improves” and do not take them long-term.
Er Chen Tang (Two-Cured Decoction)
For lung failure to descend and disperse, it is used to transform phlegm. It treats phlegm-damp syndrome, with symptoms of excessive phlegm cough, nausea, vomiting, chest tightness, heaviness in limbs, or dizziness and palpitations, with a white and slippery tongue coating.
Shen Ling Bai Zhu San (Ginseng and Poria Powder)
Tonifies qi and strengthens the spleen, drains dampness, and stops diarrhea. It treats spleen deficiency with excessive dampness syndrome. Symptoms include undigested food, chest tightness, intestinal rumbling, diarrhea, fatigue in limbs, pale and white greasy tongue, and weak pulse.
Liu Jun Zi Tang (Six Gentlemen Decoction)
Tonifies qi and strengthens the spleen, dries dampness, and transforms phlegm. It treats spleen and stomach qi deficiency with phlegm-damp syndrome, with symptoms of poor appetite, loose stools, chest tightness, and nausea.
Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang (Aromatic and Sand Six Gentlemen Decoction)
Tonifies qi and strengthens the spleen, moves qi, and transforms phlegm. It treats spleen and stomach qi deficiency with phlegm obstruction and qi stagnation syndrome, with symptoms of vomiting, chest tightness, lack of appetite, abdominal distension, fatigue, or qi deficiency with abdominal fullness.
Chen Xia Liu Jun Wan (Two-Cured Six Gentlemen Pill)
For spleen not functioning well, it is used to strengthen the spleen, transform phlegm, and tonify the spleen and stomach. It treats spleen and stomach deficiency with symptoms of poor appetite, undigested food, abdominal distension, and excessive phlegm.
Ping Wei San (Calm the Stomach Powder)
Dries dampness, strengthens the spleen, and disperses fullness. It treats spleen deficiency with dampness obstructing the middle, with symptoms of chest and abdominal fullness, bland taste, lack of thirst, and lack of appetite.
Healthy Recipes
Eat less sweet, sticky, and greasy foods, drink less alcohol, and avoid overeating. Consume more light foods that strengthen the spleen, drain dampness, transform phlegm, and eliminate dampness, such as white radish, scallions, ginger, ginkgo, and red beans.
-
Stir-fried Leeks with Shrimp
Ingredients: Leeks, fresh shrimp
Method: Wash the fresh leeks, then stir-fry them in oil, add the prepared shrimp, stir-fry, and then add an appropriate amount of salt before serving.
Effects: Enhances yang, strengthens the stomach, transforms stasis, and detoxifies. For patients with qi deficiency and phlegm-damp constitution, this dish can effectively nourish the body.
-
Glutinous Rice and Yam Porridge
Ingredients: Glutinous rice, goji berries, rice, yam
Method: Peel and wash the fresh yam, then cut it into small pieces; soak the goji berries in water until soft; cook the rice and glutinous rice together, adding the yam when it is about 70% cooked, and add goji berries and appropriate seasonings before serving.
Effects: This recipe can effectively tonify the kidneys and benefit the lungs, and is very effective for treating qi deficiency constitution.
Methods to Eliminate Dampness – Moxibustion
For individuals with phlegm-damp, it is essential to strengthen the spleen and tonify spleen yang while eliminating dampness. The most effective method to eliminate dampness is moxibustion.
Learn a few acupoints for dampness elimination, and perform massage and moxibustion on these points to expel dampness, which is very effective.
Acupoints: Shen Que (Shenque), Guan Yuan (Guanyuan), Zhong Wan (Zhongwan), Tian Shu (Tianshu), Zu San Li (Zusanli).
Principle of Dampness Elimination: The acupoints around the navel have the effect of strengthening the spleen and eliminating dampness, while Zu San Li has the effect of warming yang and warming the stomach.
Effects: Warming yang, nurturing the source, tonifying qi, and eliminating dampness.
【Shen Que Point】
Shen Que is the navel, also known as the center of the body, and is a key acupoint on the Ren meridian. It is located at the navel, parallel to the Ming Men point. This area should not be massaged but should be warmed with moxa.
Location: Center of the navel.
Method: Moxibustion, for about 15 minutes.
【Guan Yuan Point】
This point is located three inches below the navel. It is an important acupoint for women to improve gynecological diseases, with functions of nurturing the source and tonifying the lower jiao. It can be used for any deficiency of vital energy.
Method: Use a shaking method, with both hands crossed and placed on the Guan Yuan point, applying slight pressure, then quickly move the hands up and down in a small range. This can be done anytime and anywhere. Do not apply excessive force; you can also use kneading, as long as there is a feeling of soreness and swelling in the local area. Moxibustion is more effective.
【Zhong Wan Point】
Located in the middle of the stomach, hence called Zhong Wan. Zhong Wan can regulate the yin and yang of the stomach’s qi and blood, with functions of harmonizing the stomach, strengthening the spleen, and promoting water metabolism. If the stomach qi is deficient, it can easily lead to stomach and abdominal pain, nausea, acid reflux, diarrhea, and constipation. Massaging Zhong Wan can enhance stomach care.
Location: Upper abdomen, midpoint of the line connecting the xiphoid process and the navel.
Method: Kneading and moxibustion.
【Tian Shu Point】
Tian Shu can treat gastrointestinal diseases and is the gateway for stomach qi. Qi and blood continuously flow into the large intestine from this point. If the stomach is uncomfortable, you can massage Tian Shu.
Location: Located in the middle abdomen, two inches on either side of the navel, one on each side.
Method: Kneading or moxibustion.
【Zu San Li Point】
Sun Simiao once said: “If you want to be healthy, you must not neglect San Li.” This acupoint has the effects of strengthening the spleen, warming the stomach, warming yang, promoting diuresis, and stopping diarrhea, making it a key acupoint for health care. In the past, officials entering Sichuan used moxibustion on Zu San Li to prevent the invasion of dampness and turbid qi.
Location: Located on the outer side of the lower leg, three inches below the outer knee, one finger breadth from the anterior edge of the tibia.
Method: Moxibustion or kneading, for about 10 minutes each time.
In addition to the well-known health acupoints mentioned above, there are several other important points:
【Yin Ling Quan Point】
For individuals with heavy dampness, pressing on Yin Ling Quan will cause soreness; those with spleen deficiency can easily accumulate dampness here, leading to a yellowish complexion over time. Scraping or moxibustion on Yin Ling Quan can eliminate internal dampness, clear damp-heat, strengthen the spleen, and regulate qi.
【Xue Hai Point】
This is a key point for blood generation and promoting blood circulation. The convergence of dampness and turbid qi from the stomach and spleen occurs here. Long-term pressing can eliminate phlegm and turbid substances, making it a weight loss point for individuals with phlegm-damp constitution.
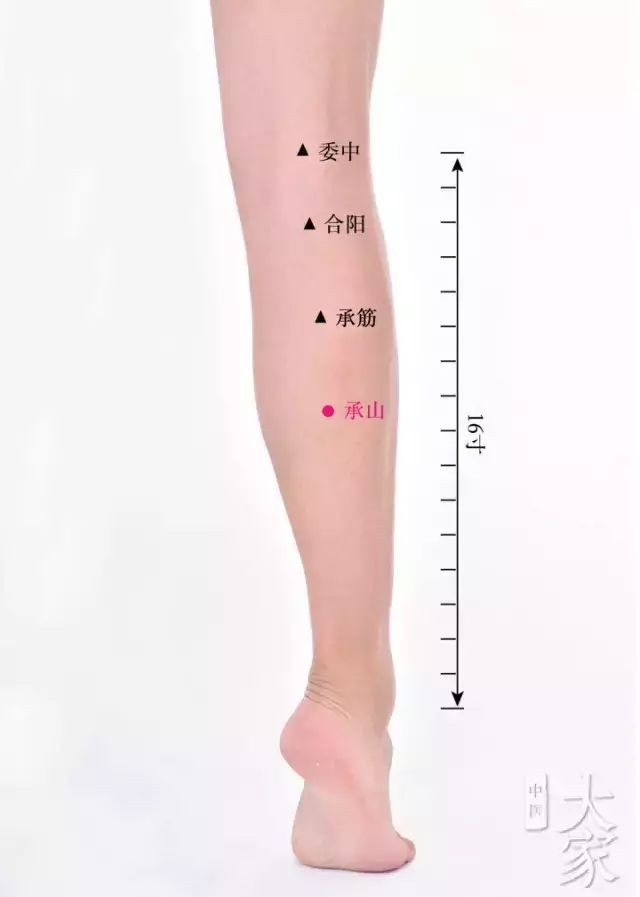
【Cheng Shan Point】
Pressing on Cheng Shan will often cause a noticeable soreness and swelling, which is due to the presence of dampness in the body; after massaging Cheng Shan for a period, you will feel a slight warmth in the body, indicating that the yang energy on the bladder meridian is at work, and the dampness in the body is escaping with the slightly elevated body temperature.
 Physical Exercise
Physical Exercise
In addition to dietary and medicinal approaches, it is also important to maintain a cheerful mood and engage in regular physical exercise. Individuals with a “phlegm-damp constitution” tend to feel heavy and fatigued, so it is essential to persist in exercise. Activities such as walking, jogging, ball games, martial arts, Ba Duan Jin (Eight Pieces of Brocade), and dancing are recommended. Gradually increasing the amount of activity will help to firm and tighten the loose flesh.
Copyright Statement: This article is sourced from:Thinking Tribe. Copyright belongs to the relevant rights holders. Respect knowledge and labor, please retain copyright information when reprinting. Edited and organized by: Zhi Cultural.

◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Guan Yuan Point, a point that cures male infertility
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Moxibustion on four points during the summer solstice, eliminating all diseases!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Four insights from learning TCM with Teacher Feng Shilun
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Rumors stop with the wise; your distortions of TCM only expose your ignorance | Regarding TCM, there is much to say
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Liu Duzhou: Using classical formulas should not be done recklessly, nor should they be inflexible
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Liu Xiyan: The effects of Fu Ling and Bai Zhu
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Liver and kidney deficiency can be discerned by examining the legs
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Uncovering the hidden constitution and fate in “Dream of the Red Chamber”
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Discussing those warming yang herbs that can “reduce fire and anger”
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Curing your pollen allergy! Next year I want to invite you to see the flowers!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Qinglong, Xuanwu, Baihu, why is Zhuque missing in “Treatise on Febrile Diseases”? – The mystery of Zhuque Decoction
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Application of the Five Movements and Six Qi
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Bitter mouth = internal heat? TCM has something to say!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇There are many types of Di Huang Wan, suitable for different populations
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇The journey of moxibustion: I created miracles using TCM!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Tonifying the spleen is the key to treating all diseases, but unfortunately, too few people know this!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Li Keshou: Talking about the past of studying and practicing medicine (sincere and simple)
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Yin Huihe’s organization: A chart showing all treatment methods and formulas for spleen and stomach diseases
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇The common experience of ancient and modern physicians: Without memorizing some texts, there is no skill to speak of!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Common massage techniques in TCM, easy to learn!
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Why is there dryness and heat when the body is clearly cold?
◇Traditional Chinese Medicine◇Dong Hongtao: Clinical application of Huang Qi




