

In Guangdong, it is truly hard to escape from “dampness”.
The current weather is hot and humid, causing many people to suffer from internal dampness, leading to a series of symptoms such as fatigue, decreased appetite, excessive sweating, weakness, and greasy breath. Aside from regional and climatic reasons, many people actually have worsening dampness due to poor dietary habits.

However, dampness is not a one-size-fits-all issue; Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) emphasizes differentiation and treatment based on patterns. In simple terms, dampness can be categorized into cold dampness, phlegm dampness, and damp-heat. In this article, we will focus on understanding phlegm dampness.
01
What is Phlegm Dampness?
Phlegm and dampness are two different concepts. We have discussed “dampness” above. So what about “phlegm”? “Phlegm” can be understood in both broad and narrow senses. In a narrow sense, phlegm refers to the mucus expelled from the respiratory tract. However, in a broader sense, phlegm refers to waste produced when the metabolism of fluids is obstructed, circulating throughout the body with qi and blood, causing various diseases, hence the saying “All diseases are caused by phlegm, and stubborn phlegm leads to strange symptoms”. Both phlegm and dampness are pathological products formed by the accumulation of fluids in the body, making it difficult to distinguish them clearly, and they can transform into each other; dampness can become phlegm, and phlegm can become dampness, thus they often coexist clinically.
02
What is Phlegm Dampness Constitution?
TCM classifies human constitution into nine types, and phlegm dampness constitution is one of them.This refers to a condition where the functions of the organs are disordered, leading to the dysfunction of qi, blood, and body fluids, resulting in the accumulation of dampness and phlegm. The emergence of phlegm dampness constitution is mainly related to the lungs, spleen, and kidneys, with the spleen being the most closely related.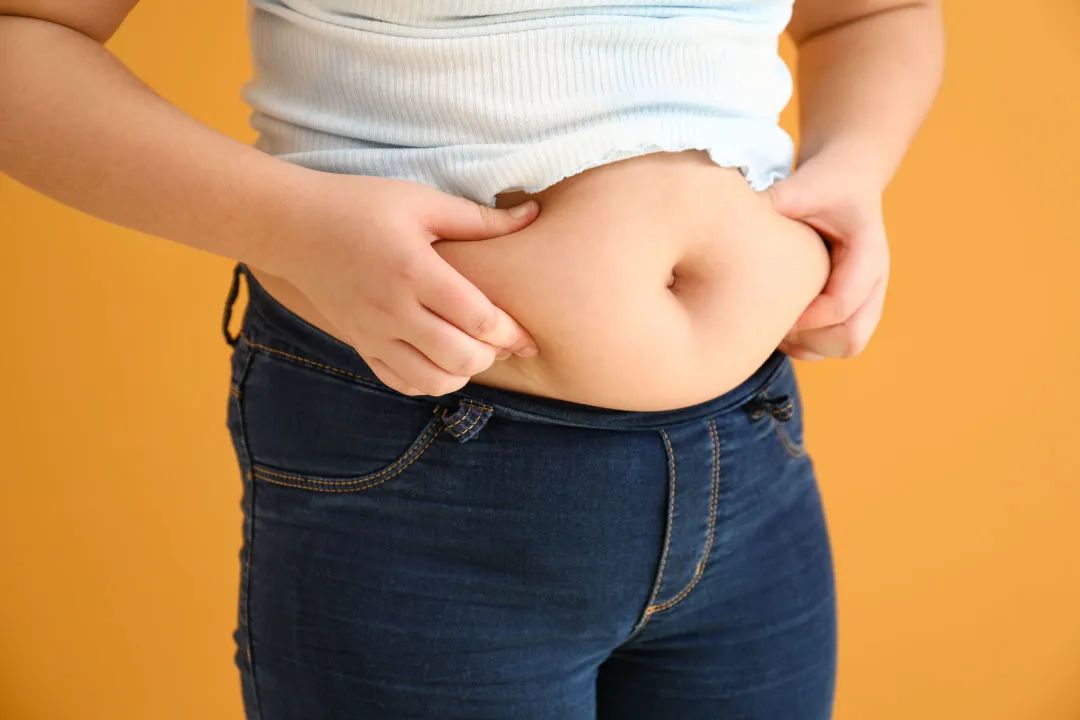 The spleen governs the transformation and transportation of fluids, including the metabolism of water and fluids. The absorption of nutrients from food is primarily in liquid form, and the function of transforming and transporting fluids means that excess moisture from the absorbed nutrients can be promptly transported to the lungs and kidneys, where it is transformed into sweat and urine for excretion. Therefore, when the spleen’s function of transforming and transporting fluids is strong, the metabolism of fluids in the body is normal, which naturally prevents the generation of pathological products such as dampness, phlegm, and fluids. Conversely, when the spleen’s function is weakened, it inevitably leads to the stagnation of fluids in the body, resulting in the production of dampness, phlegm, and fluids, which can even lead to edema. Thus, the Suwen: The Great Treatise on True Essentials states: “All swellings and fullness due to dampness belong to the spleen,” indicating that spleen deficiency leads to dampness, and the spleen is the source of phlegm and the mechanism of edema.
The spleen governs the transformation and transportation of fluids, including the metabolism of water and fluids. The absorption of nutrients from food is primarily in liquid form, and the function of transforming and transporting fluids means that excess moisture from the absorbed nutrients can be promptly transported to the lungs and kidneys, where it is transformed into sweat and urine for excretion. Therefore, when the spleen’s function of transforming and transporting fluids is strong, the metabolism of fluids in the body is normal, which naturally prevents the generation of pathological products such as dampness, phlegm, and fluids. Conversely, when the spleen’s function is weakened, it inevitably leads to the stagnation of fluids in the body, resulting in the production of dampness, phlegm, and fluids, which can even lead to edema. Thus, the Suwen: The Great Treatise on True Essentials states: “All swellings and fullness due to dampness belong to the spleen,” indicating that spleen deficiency leads to dampness, and the spleen is the source of phlegm and the mechanism of edema.
03
What are the Characteristics of Phlegm Dampness Constitution?
1. Physical Characteristics The body type is overweight, with soft and loose flesh, which is different from a solid and muscular type of fat.2. Psychological Characteristics The personality is mild, steady in handling matters, respectful and humble, and good at enduring.3. Common Manifestations The face appears oily, prone to sweating, often feeling chest tightness and excessive phlegm, with a preference for greasy or overly sweet foods. They often feel drowsy, experience heaviness in the limbs, slight puffiness around the eyes. The mouth feels sticky, with a slight sensation of thirst but a reluctance to drink water. Bowel movements show no obvious abnormalities, while urine may be slightly turbid.
04
How to Maintain Health with Phlegm Dampness Constitution?
Phlegm dampness constitution is not a pathological state, nor is it a healthy state; it is in a sub-health state between pathological and non-pathological. However, this does not mean that no intervention is needed. Due to the inherent phlegm dampness, it is more likely to trigger diseases related to phlegm dampness, such as diabetes, hypertension, cough, asthma, gout, coronary heart disease, etc. Phlegm dampness constitution can be caused by congenital factors or acquired factors. Some unhealthy lifestyle habits can make one more prone to phlegm dampness constitution, such as irregular eating (frequently consuming cold, high-fat, high-protein, high-calorie foods), exposure to cold and damp weather, lack of exercise, and staying up late. Therefore, for individuals with phlegm dampness constitution, maintaining health involves not staying up late, exercising regularly, keeping the indoor environment dry, wearing breathable clothing, and getting plenty of sunlight. In addition, TCM conditioning can also be a primary choice. The focus is on tonifying the physiological functions of the lungs, spleen, and kidneys, applying methods such as dispersing lung phlegm, strengthening the spleen, and warming yang to transform phlegm, with formulas like Six Gentlemen Decoction (Liu Jun Zi Tang) and Er Chen Decoction (Er Chen Tang) being commonly used.1Gua Sha (Scraping Therapy) Gua Sha can invigorate yang qi, strengthen the spleen, promote metabolism, eliminate dampness and phlegm, and improve symptoms caused by the accumulation of water and dampness. Common acupoints include Zhongwan (中脘), Qihai (气海), Feiyu (肺俞), Piyu (脾俞), Shenyu (肾俞), Pangguangyu (膀胱俞), and Zusanli (足三里).2Acupuncture For individuals with phlegm dampness constitution, meridian regulation focuses on dispersing lung qi and eliminating dampness and phlegm. Acupuncture points such as Taiyuan (太渊), Zhongfu (中府), Chize (尺泽), Lieque (列缺), Taibai (太白), Sanyinjiao (三阴交), Fenglong (丰隆), Zusanli (足三里), Feiyu (肺俞), Piyu (脾俞), and Yinlingquan (阴陵泉) can be used for treatment.Acupuncture is an invasive procedure and should be performed by professionals.3Dietary Therapy
Therefore, for individuals with phlegm dampness constitution, maintaining health involves not staying up late, exercising regularly, keeping the indoor environment dry, wearing breathable clothing, and getting plenty of sunlight. In addition, TCM conditioning can also be a primary choice. The focus is on tonifying the physiological functions of the lungs, spleen, and kidneys, applying methods such as dispersing lung phlegm, strengthening the spleen, and warming yang to transform phlegm, with formulas like Six Gentlemen Decoction (Liu Jun Zi Tang) and Er Chen Decoction (Er Chen Tang) being commonly used.1Gua Sha (Scraping Therapy) Gua Sha can invigorate yang qi, strengthen the spleen, promote metabolism, eliminate dampness and phlegm, and improve symptoms caused by the accumulation of water and dampness. Common acupoints include Zhongwan (中脘), Qihai (气海), Feiyu (肺俞), Piyu (脾俞), Shenyu (肾俞), Pangguangyu (膀胱俞), and Zusanli (足三里).2Acupuncture For individuals with phlegm dampness constitution, meridian regulation focuses on dispersing lung qi and eliminating dampness and phlegm. Acupuncture points such as Taiyuan (太渊), Zhongfu (中府), Chize (尺泽), Lieque (列缺), Taibai (太白), Sanyinjiao (三阴交), Fenglong (丰隆), Zusanli (足三里), Feiyu (肺俞), Piyu (脾俞), and Yinlingquan (阴陵泉) can be used for treatment.Acupuncture is an invasive procedure and should be performed by professionals.3Dietary Therapy
Individuals with phlegm dampness constitution should avoid sweet, sticky, and greasy foods, and limit alcohol consumption.
The diet should include light foods that strengthen the spleen, eliminate dampness, and transform phlegm, such as white radish, scallions, ginger, ginkgo, red beans, kelp, winter melon, loofah, and carp.
Here are some dietary recipes that not only taste good but also help improve constitution:
Seaweed and Radish Soup
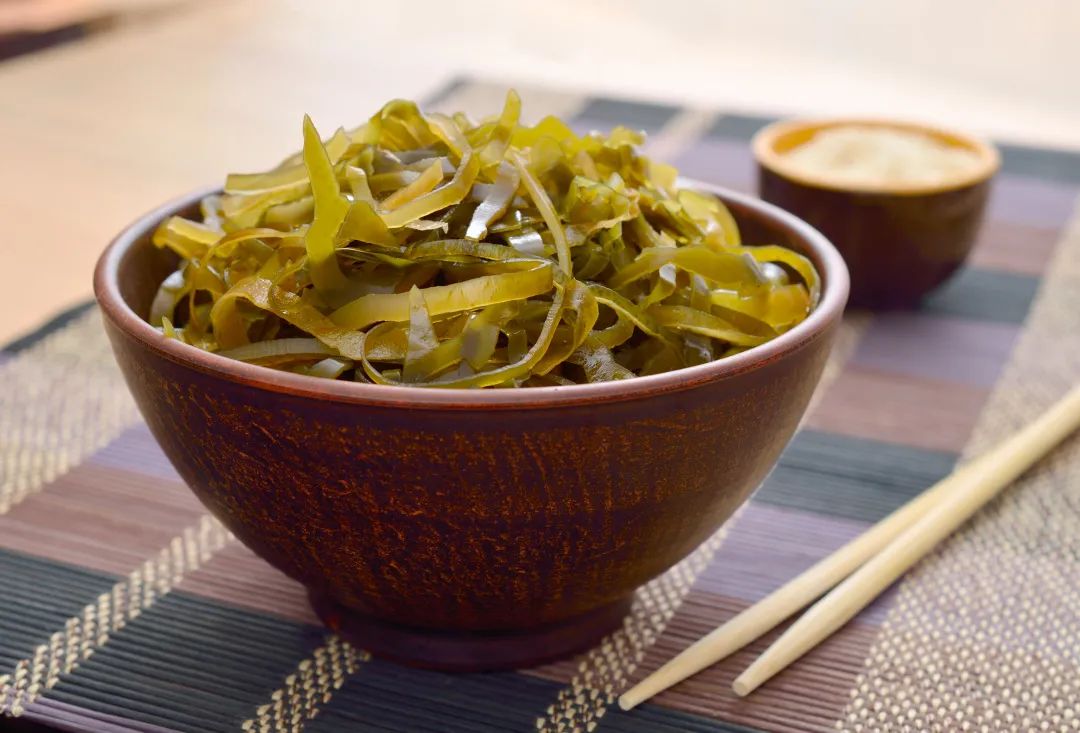

Ingredients: 150g of seaweed, 300g of white radish, appropriate amount of shredded chicken, half a large head of cabbage, a little salt, pepper, soy sauce, and vinegar.
Method: Peel and slice the white radish. Peel and cut the cabbage into chunks. Cut the seaweed into thin slices. Place the white radish, cabbage, and seaweed in a pot, add salt, and cook the soup. Add a little vinegar, then add shredded chicken, pepper, and soy sauce to finish. Drink the soup.
Job’s Tears Porridge
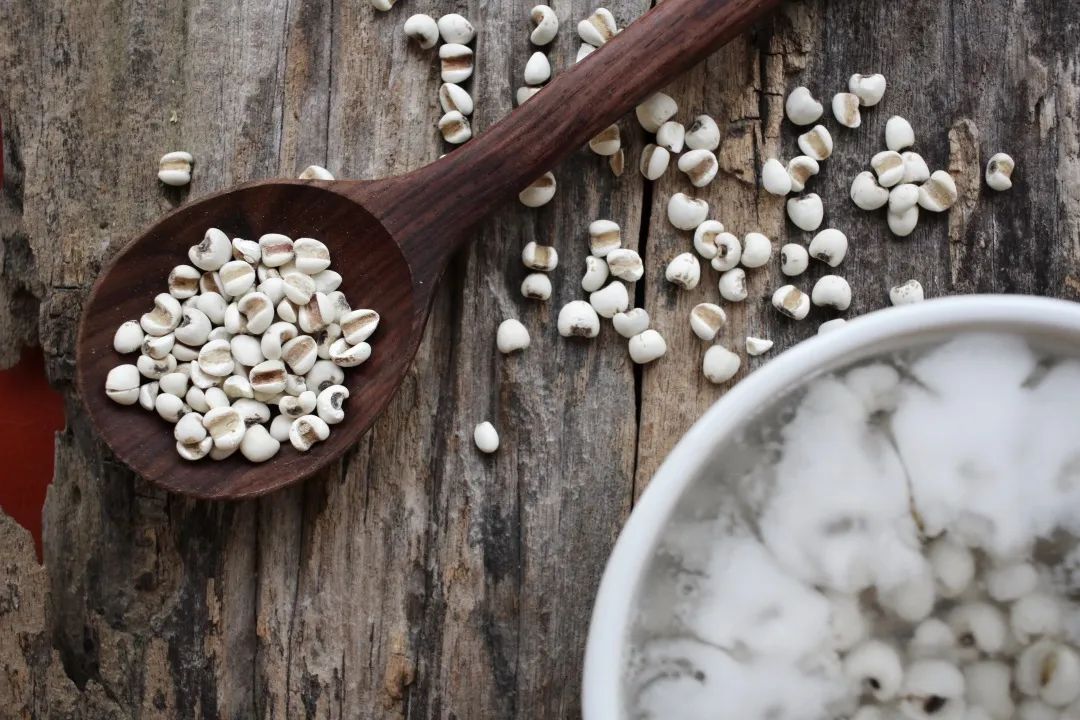

Ingredients: 30g of Job’s tears and an appropriate amount of white sugar.
Method: Wash the Job’s tears, place them in a clay pot, add an appropriate amount of water, bring to a boil over high heat, then simmer on low heat. Once the Job’s tears are cooked, add white sugar to finish, and eat as desired.
Effects: Strengthens the spleen, eliminates dampness, aids in weight loss, and reduces swelling.
Poria Cake
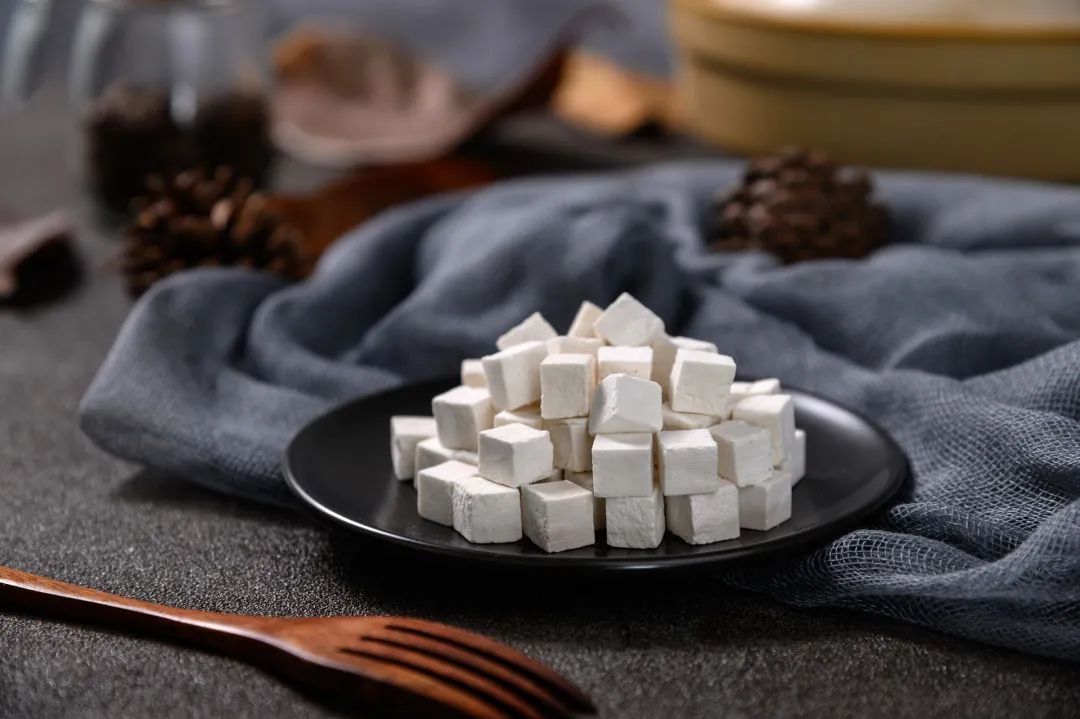

Ingredients: Poria powder, rice flour, and white sugar.
Method: Grind the poria into fine powder, mix with rice flour and white sugar, add an appropriate amount of water to form a paste, and cook in a pan over low heat to make thin cakes.
Effects: Nourishes yin, tonifies yang, calms the mind, benefits the spleen, promotes urination, and drains dampness.
Having read this, I believe you have gained some understanding of phlegm dampness constitution. While dampness is hard to escape, active conditioning after its appearance will not have too much impact~Long press to identify the QR codefor medicinal recipes + limited-time free consultations + occasional benefits~Welcome to join the group↓↓↓
 Lu GuanglingAssociate Chief Physician, TCM Internal Medicine
Lu GuanglingAssociate Chief Physician, TCM Internal Medicine (Long press the image to make an appointment with the doctor) Associate Chief Physician, comes from a family of TCM practitioners, with a father who was a famous TCM doctor during the Republic of China. Having inherited family teachings, he has been engaged in TCM for over 40 years, a member of the Gynecology Professional Committee of the Nanjing TCM Association, a special invited lecturer on provincial and municipal radio stations, a general practitioner, and a member of the Nanjing TCM Association.Specializes in: Clinical treatment of various difficult and complicated diseases, using the theory of “turbid toxins” to regulate chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia, gastric ulcers, reflux gastritis, and esophagitis, ulcerative colitis, chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and ascites. He has rich experience in post-operative and post-chemotherapy conditioning for various tumors (gastric cancer, rectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, uterine cancer, etc.). He has effective treatments for lung nodules, thyroid nodules, breast nodules, and gallbladder polyps. He has stable conditioning effects for children with low immune function leading to allergic bronchitis, asthma, developmental delays, excessive sweating, hyperactivity, stunted growth, and bedwetting, as well as gynecological disorders, various menstrual irregularities, infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, adenomyosis, and conditions characterized by a pale face and sensitivity to cold. He also has certain therapeutic effects on various stubborn skin diseases, chronic urticaria, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, and acne.Consultation Hours: Wednesday and Sunday mornings at the Gu Shengtang Nanjing Ningxi TCM Clinic
(Long press the image to make an appointment with the doctor) Associate Chief Physician, comes from a family of TCM practitioners, with a father who was a famous TCM doctor during the Republic of China. Having inherited family teachings, he has been engaged in TCM for over 40 years, a member of the Gynecology Professional Committee of the Nanjing TCM Association, a special invited lecturer on provincial and municipal radio stations, a general practitioner, and a member of the Nanjing TCM Association.Specializes in: Clinical treatment of various difficult and complicated diseases, using the theory of “turbid toxins” to regulate chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia, gastric ulcers, reflux gastritis, and esophagitis, ulcerative colitis, chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and ascites. He has rich experience in post-operative and post-chemotherapy conditioning for various tumors (gastric cancer, rectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, uterine cancer, etc.). He has effective treatments for lung nodules, thyroid nodules, breast nodules, and gallbladder polyps. He has stable conditioning effects for children with low immune function leading to allergic bronchitis, asthma, developmental delays, excessive sweating, hyperactivity, stunted growth, and bedwetting, as well as gynecological disorders, various menstrual irregularities, infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, adenomyosis, and conditions characterized by a pale face and sensitivity to cold. He also has certain therapeutic effects on various stubborn skin diseases, chronic urticaria, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, and acne.Consultation Hours: Wednesday and Sunday mornings at the Gu Shengtang Nanjing Ningxi TCM Clinic
Reminder: This article is for medical popularization and reference for readers. TCM diagnosis and treatment require pattern differentiation; if you have any discomfort, please seek medical attention promptly.
Note: The images in this article are sourced from the legitimate image library 123rf.com.cn and QianKu.com
More Exciting Recommendations
1
Poor stomach health leads to a shorter lifespan! Seize the “golden time” for stomach care and do these 5 things to ensure good stomach qi and eating well~
2
Is it too late when discovered? Women should be cautious! Regulate qi and blood to prevent premature aging, eat these 3 items well~
3
How to treat lung nodules without surgery? Understand the 6 major misconceptions about lung nodules and see how many pitfalls you have fallen into?
Follow Gu Shengtang TCM for more information

 Share
Share Save
Save  View
View Like
Like

