
Fu Ling (Poria), a key herb for promoting urination and resolving dampness
Promotes urination, resolves dampness, strengthens the spleen, and calms the heart
This issue introduces the herb for young TCM practitioners
The herb is——Fu Ling (Poria)










 1. Source and Prescription Names
1. Source and Prescription Names
【Source】
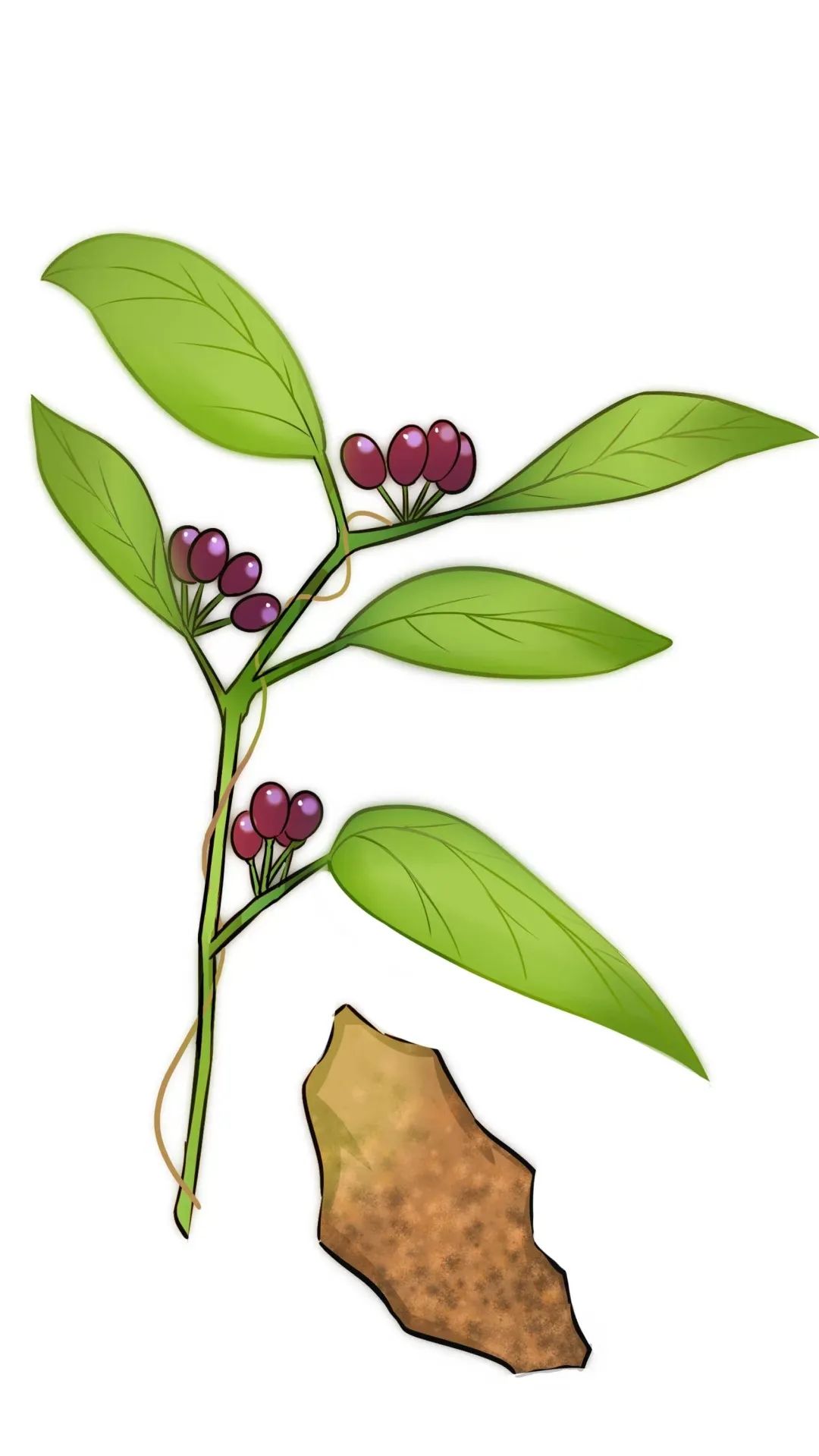
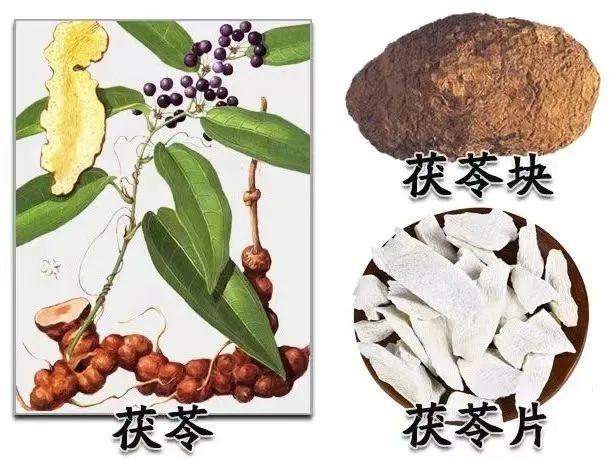
It is the dried sclerotium of the fungus Poria cocos, belonging to the family Polyporaceae. It is mainly produced in Anhui, Yunnan, and Hubei provinces. Harvested mainly from July to September, it is dried in the shade and used raw.

【Prescription Names】
Fu Ling (Poria), Yun Ling, Bai Fu Ling (White Poria), Chi Fu Ling (Red Poria).

 2. Properties and Effects
2. Properties and Effects
【Properties】
Sweet, bland, neutral; enters the Heart, Lung, Spleen, and Kidney meridians.
【Effects】
Promotes urination, resolves dampness, strengthens the spleen, calms the heart.

 3. Clinical Applications
3. Clinical Applications 【Edema, Urinary Difficulty】
【Edema, Urinary Difficulty】

This herb has both diuretic and tonifying properties, being neutral and gentle. It can dispel pathogenic factors while supporting the body’s vital energy, promoting urination without harming the vital qi, making it a key herb for resolving dampness. It can be used for all types of edema, whether due to cold, heat, deficiency, or excess. It treats edema due to internal dampness and urinary difficulty, often combined with Ze Xie (Alisma), Zhu Ling (Polyporus), and Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), as in the Wu Ling San (Five-Ingredient Powder). It is also used for edema due to Spleen and Kidney Yang deficiency, often combined with Fu Zi (Aconite) and Sheng Jiang (Ginger), as in the Zhen Wu Tang (True Warrior Decoction); for water-heat accumulation, it is often combined with Hua Shi (Talc), E Jiao (Donkey-hide Gelatin), and Ze Xie, as in the Zhu Ling Tang (Polyporus Decoction).
 【Spleen Deficiency Symptoms】
【Spleen Deficiency Symptoms】
This herb can strengthen the spleen and resolve dampness, treating diarrhea due to Spleen deficiency with excess dampness, often combined with Shan Yao (Chinese Yam), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), and Yi Yi Ren (Job’s Tears), as in the Shen Ling Bai Zhu San (Ginseng and Atractylodes Powder); it treats Spleen and Stomach deficiency with fatigue, poor appetite, and loose stools, often combined with Ren Shen (Ginseng), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), and Gan Cao (Licorice), as in the Si Jun Zi Tang (Four Gentlemen Decoction); it treats dizziness and palpitations due to phlegm-dampness affecting the heart, often combined with Gui Zhi (Cinnamon Twig), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), and Gan Cao (Licorice), as in the Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang (Poria, Cinnamon, and Licorice Decoction).
 【Palpitations, Insomnia】
【Palpitations, Insomnia】
This herb strengthens the spleen, benefits the heart, and calms the spirit. It treats palpitations and insomnia due to both Heart and Spleen deficiency, often combined with Huang Qi (Astragalus), Dang Gui (Angelica), and Yuan Zhi (Polygala), as in the Gui Pi Tang (Restore the Spleen Decoction); it treats palpitations due to water qi disturbing the heart, often combined with Gui Zhi (Cinnamon Twig) and Bai Zhu (Atractylodes), as in the Fu Ling Gan Cao Tang (Poria and Licorice Decoction).
 4. Dosage and Preparation Methods
4. Dosage and Preparation Methods
【Dosage】
Decocted for oral use, 10-15g.
【Preparation Method】
Dried in the shade, used raw.

 5. Precautions
5. Precautions
1. Caution is advised for patients with Yin deficiency without damp-heat, deficiency-cold, or spermatorrhea. This is because Fu Ling has diuretic properties, and if consumed by these groups, it may damage the kidney’s vital energy and worsen kidney deficiency, thus exacerbating the condition.
2. It should not be taken on an empty stomach to avoid increased gastric acid, leading to gastrointestinal discomfort. Therefore, those with gastric ulcers and excessive gastric acid should also use it with caution.
3. Generally, Fu Ling has few side effects, but if patients do not follow medical advice, it may lead to damage to Yin energy. If used excessively, it may also increase urine output.
4. Individuals with sensitive constitutions may experience allergic reactions, such as skin itching, rashes, and in rare cases, severe allergic reactions.
5. Special populations such as pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a physician before use.

 6. Associated Herbs
6. Associated Herbs
1. Fu Ling Pi (Poria Skin)
It is the dried outer skin of the sclerotium of Poria cocos. Properties: Sweet, bland, neutral; enters the Heart, Lung, Spleen, and Kidney meridians. Effects: Promotes urination and reduces swelling. Suitable for edema and urinary difficulty. Dosage: 15-30g for decoction.
2. Chi Fu Ling (Red Poria)
It is the dried sclerotium of Poria cocos, near the outer skin, with a light red color. Properties: Sweet, bland, neutral; enters the Heart, Spleen, and Bladder meridians. Effects: Promotes urination and resolves damp-heat. Suitable for urinary difficulty, edema, cloudy urine, and diarrhea. Dosage: 6-12g for decoction or in pills and powders.
3. Fu Shen (Poria Spirit)
It is the part of the dried sclerotium of Poria cocos that contains pine roots. Properties: Sweet, bland, neutral; enters the Heart, Lung, Spleen, and Kidney meridians. Effects: Calms the heart and spirit. Suitable for anxiety, palpitations, forgetfulness, and insomnia. Dosage: 10-15g for decoction.
⊙Copyright Statement: This article is sourced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact the 【Ai Jiang】 public account for deletion. Thank you.


