Dampness is the root of many ailments; when dampness enters the body, it can lead to various diseases. Many people know they need to eliminate dampness, but the dampness in the body can be categorized as ‘cold’ or ‘heat’! The methods for eliminating dampness differ based on its properties. Let’s explore which methods are more suitable for you!

 Dampness easily ‘permeates’
Dampness easily ‘permeates’ 01 Dampness + Cold = Cold Damp
01 Dampness + Cold = Cold Damp
When dampness encounters cold, it becomes cold damp: this is similar to winter; if the climate is dry, people can tolerate the cold, but if the dampness is heavy, it becomes uncomfortable. The winter in the south is more unbearable than in the north due to the heavier dampness.
02 Dampness + Heat = Damp Heat
When dampness encounters heat, it becomes damp heat: this is like a sauna in summer, hot and humid, making it hard to breathe, which is clearly less pleasant than dry, sunny weather.
03 Dampness + Wind = Wind Damp
When dampness encounters wind, it becomes wind damp: driving away wind is easy, but once it becomes wind damp, it often leads to chronic diseases that are difficult to treat quickly.
 How to determine which type of ‘damp’?
How to determine which type of ‘damp’?
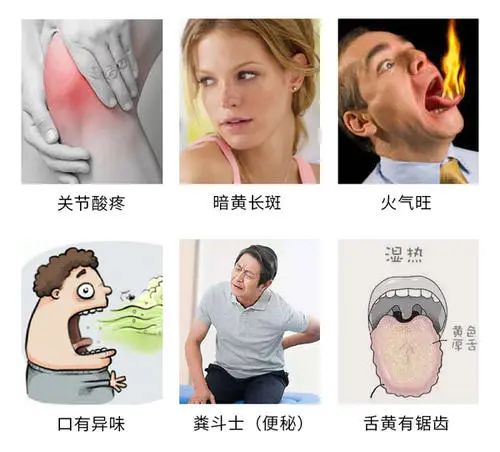
What to do about ‘Cold Damp’?
Cold damp, also known in TCM as phlegm damp or damp cold. ‘Phlegm’ refers to a type of constitution formed by the stagnation of water and fluids in the body.
People with a phlegm damp constitution tend to gain weight due to the stagnation caused by phlegm damp, which affects metabolism. Heavy cold damp in the body can also harm the kidneys, leading to kidney yang deficiency, kidney qi deficiency, blood deficiency, and blockage of meridians, resulting in acne, spots, and even body pain.
Cold damp is most afraid of cold! First, to eliminate cold damp, one must ensure warmth, especially for women, who should not sacrifice health for beauty. In terms of diet, it is important to avoid raw and cold foods, especially in summer when the weather is hot; do not indulge in cold foods! Additionally, drinking water with herbal teas to eliminate dampness is also quite effective.
01Osmanthus and Dried Tangerine Peel Tea: Osmanthus + Dried Tangerine Peel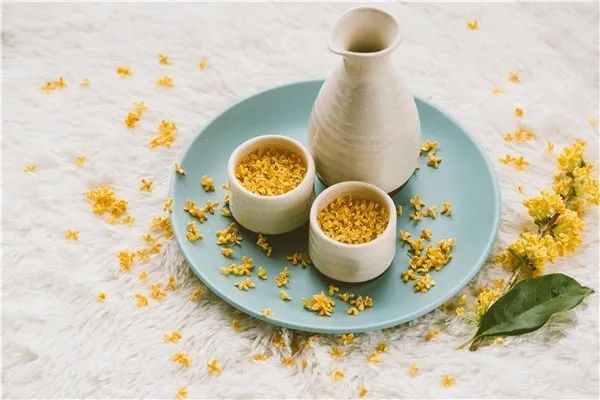
Osmanthus and Dried Tangerine Peel Tea
Osmanthus is a rare warm flower tea that not only has a fragrant and sweet aroma, uplifting the mood and refreshing the breath, but also has effects of warming the lungs, dispelling cold, warming the stomach, transforming phlegm, and nourishing the complexion. Dried tangerine peel is a commonly used herb for regulating qi, strengthening the spleen, and drying dampness to transform phlegm; especially aged dried tangerine peel is milder and more effective.
02Double Ginseng Tea: Dongyang Ginseng + Codonopsis
Double Ginseng Tea
Dongyang ginseng, also known as burdock, has effects of eliminating dampness, strengthening the spleen, nourishing yin, promoting bowel movements, and benefiting qi. It can also promote blood circulation and detoxify the intestines. Codonopsis is a superior type of codonopsis, known for its ability to strengthen the spleen without causing dryness, nourish stomach yin without causing dampness, moisten the lungs without being cold, and nourish blood without being greasy. Together, they can achieve the effects of dispelling cold and dampness, strengthening the spleen and stomach, and nourishing qi and blood.
Tip:
Mugwort used externally also has effects of dispelling cold and dampness. Soaking feet regularly with dried ginger and safflower can also promote blood circulation, unblock meridians, and relieve pain.
What to do about ‘Heat Damp’?
Heat damp, also known in TCM as damp heat. When damp heat accumulates in the body, it obstructs the functioning of the organs and meridians, leading to pathological changes associated with damp heat symptoms.
Damp heat injures yin; those with damp heat constitution may suffer from chronic gastritis, ulcers, liver cirrhosis, or gallbladder polyps, so it should not be taken lightly. Conversely, various disease factors can easily lead to dysfunction of the spleen and stomach, resulting in damp heat.
People with damp heat constitution should eat a light diet, avoiding greasy and sweet foods to prevent damp heat. They should quit smoking and drinking, and reduce spicy foods that promote heat (as smoking and drinking have warming effects). For those with damp heat constitution, tea therapy should focus on soothing the liver, benefiting the gallbladder, clearing heat, and eliminating dampness.
01Lotus Leaf and Jasmine Tea: Lotus Leaf + Jasmine Flower
Lotus Leaf and Jasmine Tea
Lotus leaf has a refreshing and slightly bitter taste, clearing the heart and relieving summer heat. Many people know that lotus leaves can aid in weight loss, which mainly relies on their ability to eliminate dampness and promote diuresis. Jasmine flowers are fragrant and elegant, with effects of soothing the liver, relieving depression, and clearing heat and eliminating dampness. Together, they can eliminate phlegm and dampness, clear heat and reduce turbidity, making it a great drink for summer.
02Dried Tangerine Peel and Chrysanthemum Tea: Dried Tangerine Peel + Chrysanthemum + Licorice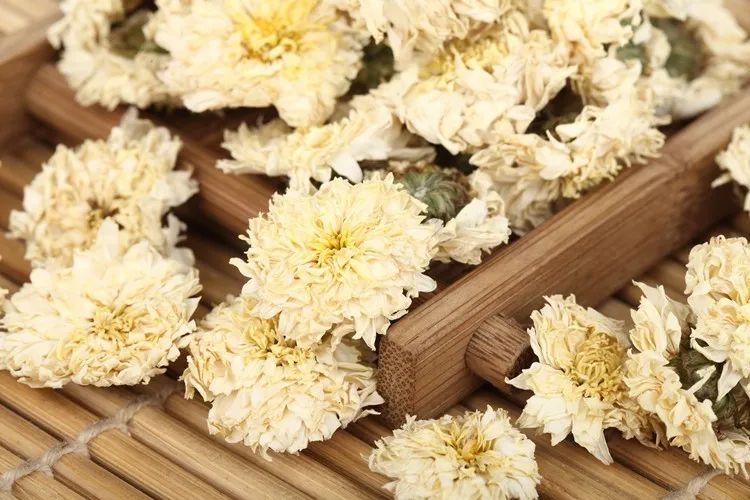
Dried Tangerine Peel and Chrysanthemum Tea
Chrysanthemum can clear the liver and brighten the eyes, cool and reduce fire; when drunk hot, it can induce sweating and dissipate heat, making the body feel relaxed. Licorice also has certain effects of tonifying the spleen, eliminating phlegm, and clearing heat and detoxifying. Together with dried tangerine peel, they are more beneficial for clearing liver fire and tonifying the spleen to eliminate dampness.
Tip:
Cold damp and heat damp can sometimes coexist, making it difficult to identify one’s symptoms. For those who cannot discern their body’s dampness symptoms, regular exercise and careful body care will gradually help both ‘cold’ and ‘heat’ dampness to dissipate.
[Source: Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Editor: Huang Yongxin, Correspondent: Li Zhao]


