Cupping therapy is a method that uses cups as tools, employing techniques such as fire and suction to create negative pressure, which adheres to the body surface, causing local stasis to achieve effects such as promoting circulation, invigorating blood flow, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. This includes techniques such as stationary cupping, moving cupping, flash cupping, and needling cupping.

Cupping therapy has a long history in China, with records dating back to the Western Han Dynasty in the “Fifty-Two Disease Formulas,” where it was referred to as “Jiao Fa”. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, it quickly became popular among the people.
Today, the clinical applications of cupping are very broad, involving internal and external medicine, gynecology, pediatrics, orthopedics, dermatology, and otorhinolaryngology diseases.
1
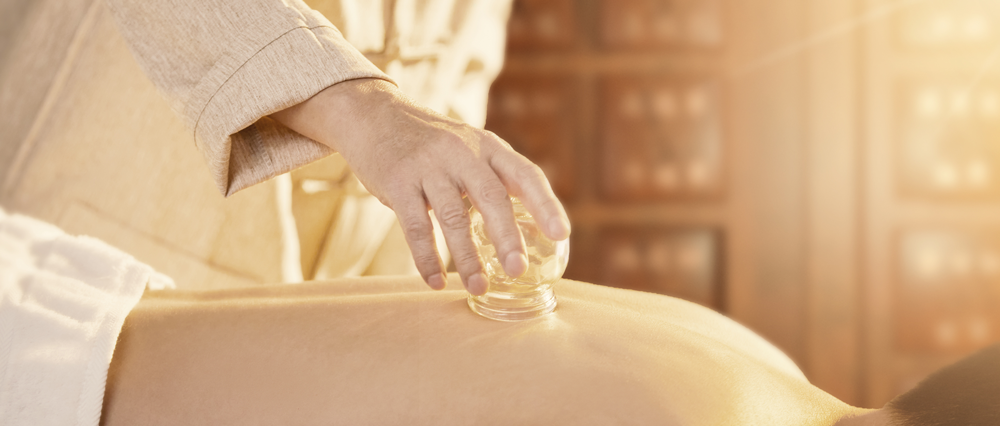
Effects of Cupping
◎ Invigorating Blood and Alleviating Pain
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) holds that “where there is flow, there is no pain; where there is no flow, there is pain”. When the muscles, ligaments, or bones of the body are injured, local stasis occurs, and the flow of qi and blood becomes obstructed. If the stasis does not dissipate, pain will persist.
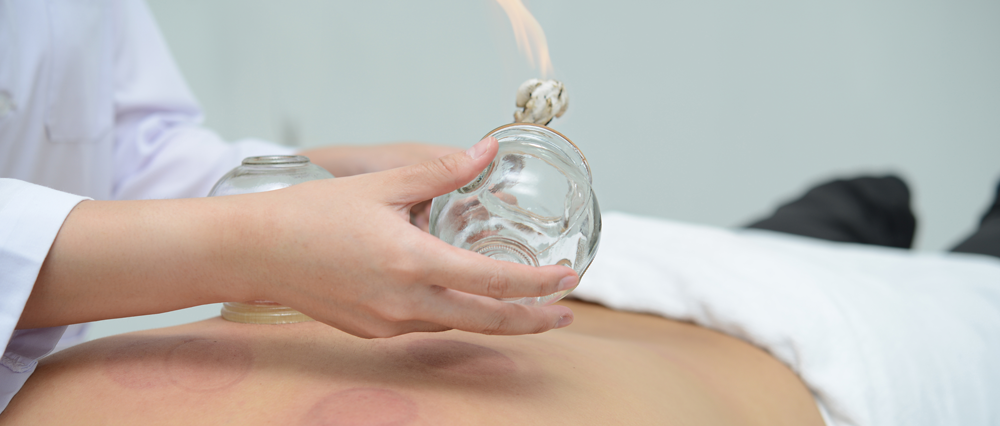
The negative pressure effect inside the cup (the suction generated) can cause blood vessels to dilate, improve local blood circulation, and enhance metabolism, thereby relieving muscle tension, eliminating stasis, and unblocking the meridians to achieve the goal of “where there is flow, there is no pain”.
◎ Clearing Heat and Reducing Swelling
According to the TCM principle of “treating heat with heat”, the stimulation from fire cupping can expel pathogenic heat, achieving the goal of clearing heat by allowing internal yang heat to reach the surface of the body and ultimately be expelled.
◎ Regulating Internal Diseases
TCM believes that the back acupoints are connected to each organ. Cupping at specific acupoints can provide continuous stimulation to the acupoints, stimulating various organs and enhancing the body’s resistance, thus playing a role in regulating and treating specific internal diseases.

2
Indications for Cupping Therapy
The indications for cupping therapy are extensive and can treat:
❶ Common internal diseases such as colds, coughs, stomach pain, and indigestion;
❷ Orthopedic diseases such as cervical spondylosis, stiff neck, lumbar disc herniation, lumbar muscle strain, shoulder periarthritis, and rheumatic pain;
❸ Gynecological diseases such as menstrual disorders, dysmenorrhea, and mastitis;
❹ Dermatological diseases such as shingles and eczema;
❺ Otorhinolaryngological diseases such as toothache, temporomandibular joint disorder, and throat swelling and pain.。
3
Is a Deeper Cupping Mark Better?
The marks left by cupping are not “toxins”; therefore, deeper cupping marks do not necessarily indicate better results.
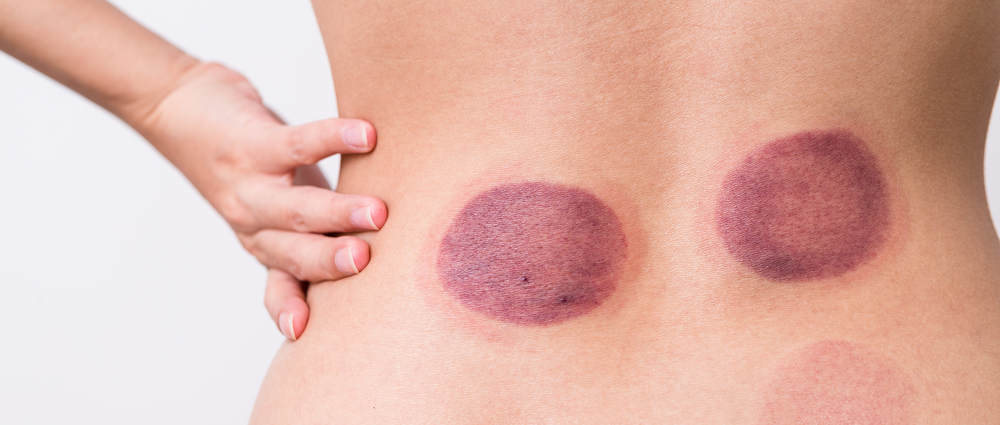
The color and shape of the cupping marks do not have strict classifications; they merely reflect certain conditions of the body to some extent:
|
Color |
Cause |
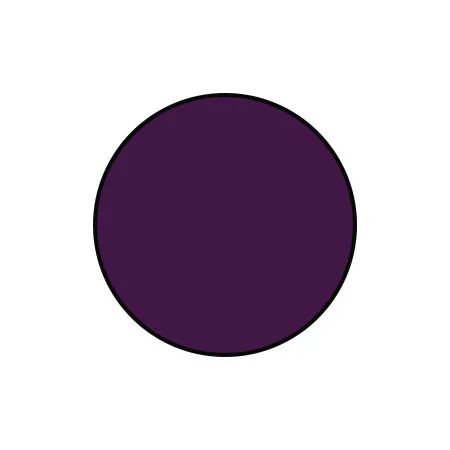
Purple-black |
Insufficient blood supply, accumulation of cold in the body |
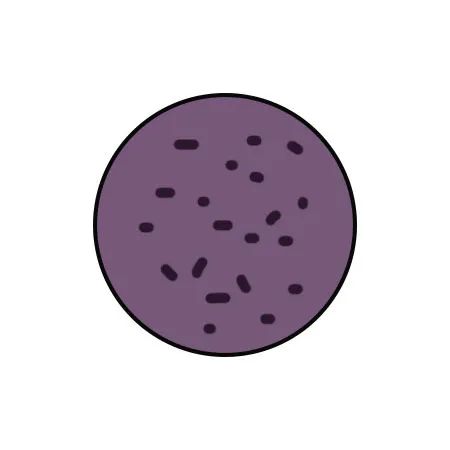
Purple with black spots |
Insufficient qi and blood flow in the body |
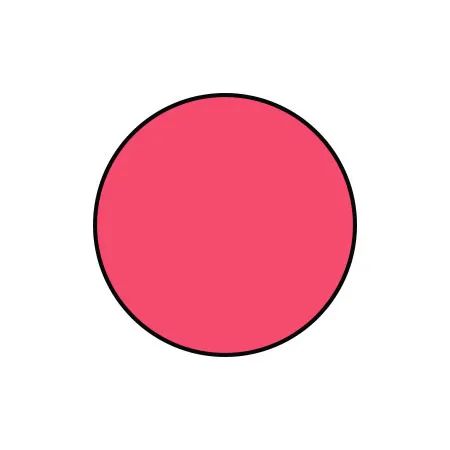
Bright red |
Presence of heat or a constitution of yin deficiency with excess fire |
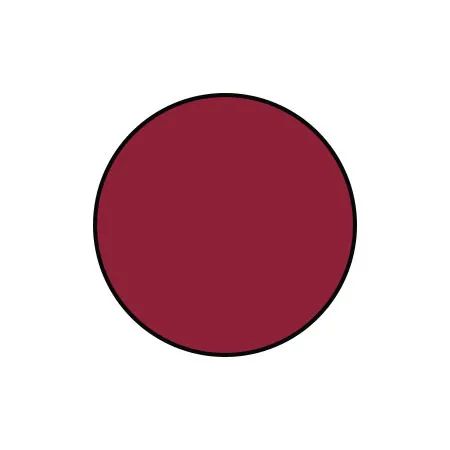
Dark red |
Presence of heat and insufficient blood supply |
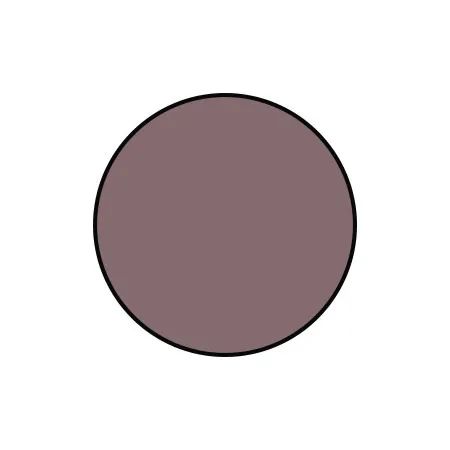
Gray |
Deficient colddampness in the body |
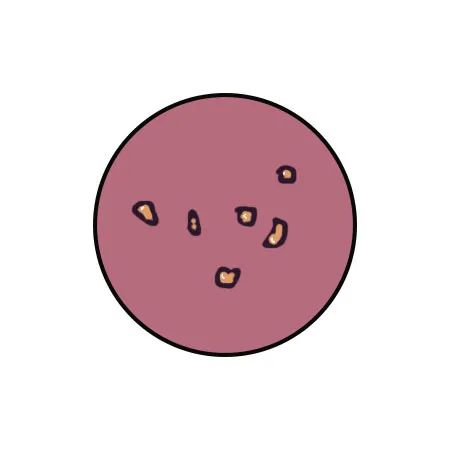
Blisters or edema |
Presence of cold and dampness in the body |
Note: The color of the cupping marks is also influenced by factors such as cupping technique, duration, and alcohol concentration used. It is not advisable to rely solely on cupping marks to diagnose conditions; a comprehensive assessment by a physician is necessary.
4
Locations for Cupping Techniques
The selection of cupping sites is closely related to the meridians and acupoints. Different diseases require different cupping sites. For example:
Shoulder and Neck Pain
Cupping can be performed at Dazhui (大椎), Jianjing (肩井), and Fengmen (风门) acupoints.
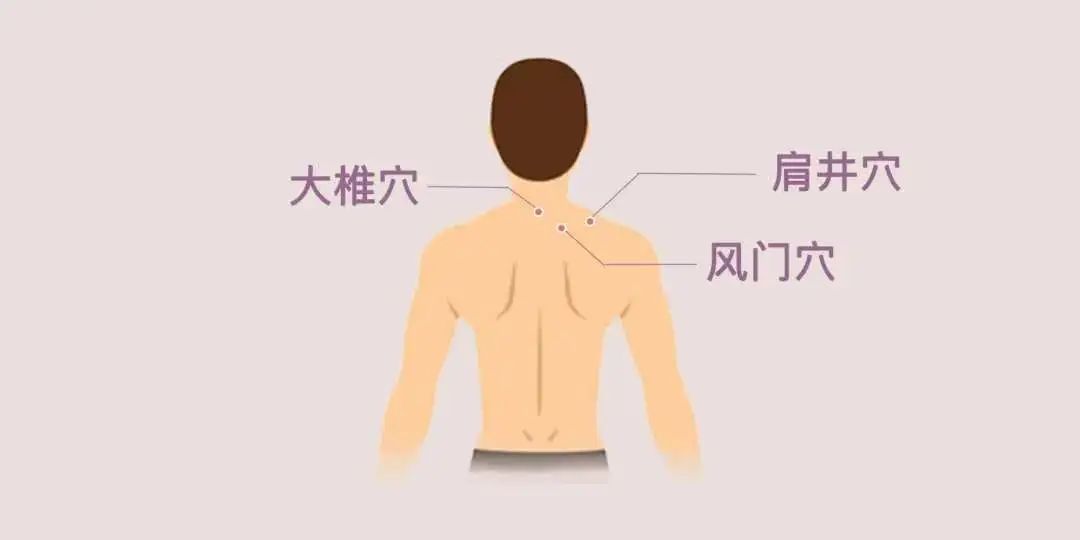
Low Back Pain
Cupping can be performed at Shenshu (肾俞), Dachangshu (大肠俞), and Yaoyangguan (腰阳关) acupoints.
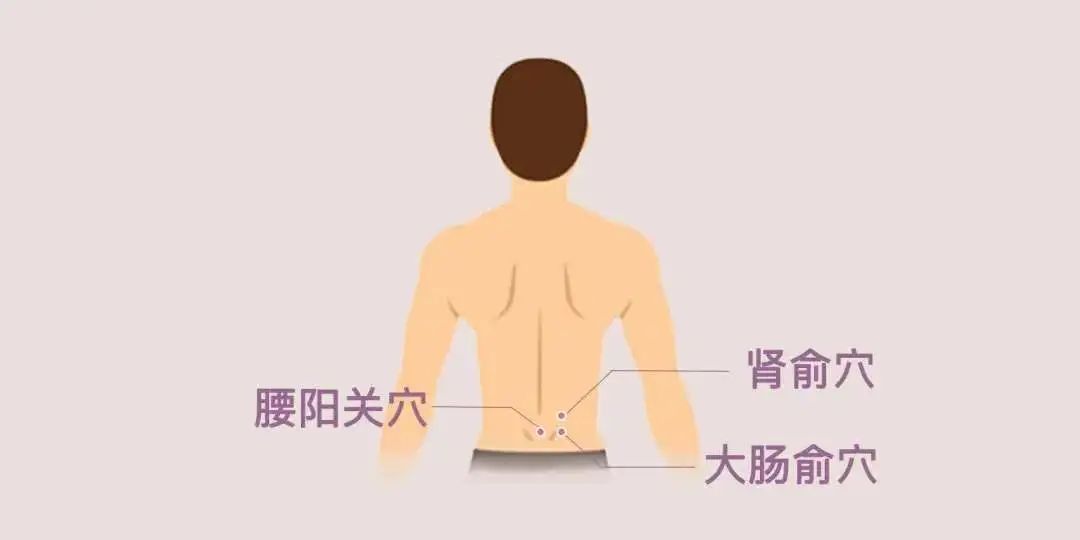
Cold, Cough, and Asthma
Cupping can be performed at Dazhui (大椎) and Feishu (肺俞) acupoints.
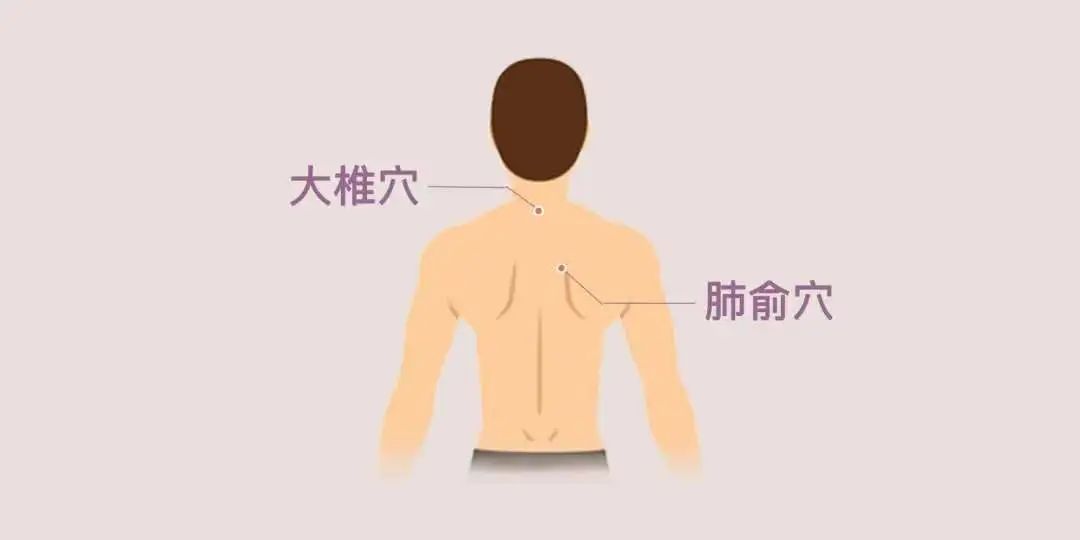
Spleen Deficiency Edema
Cupping can be performed at Pishu (脾俞) and Ganshu (肝俞) acupoints.
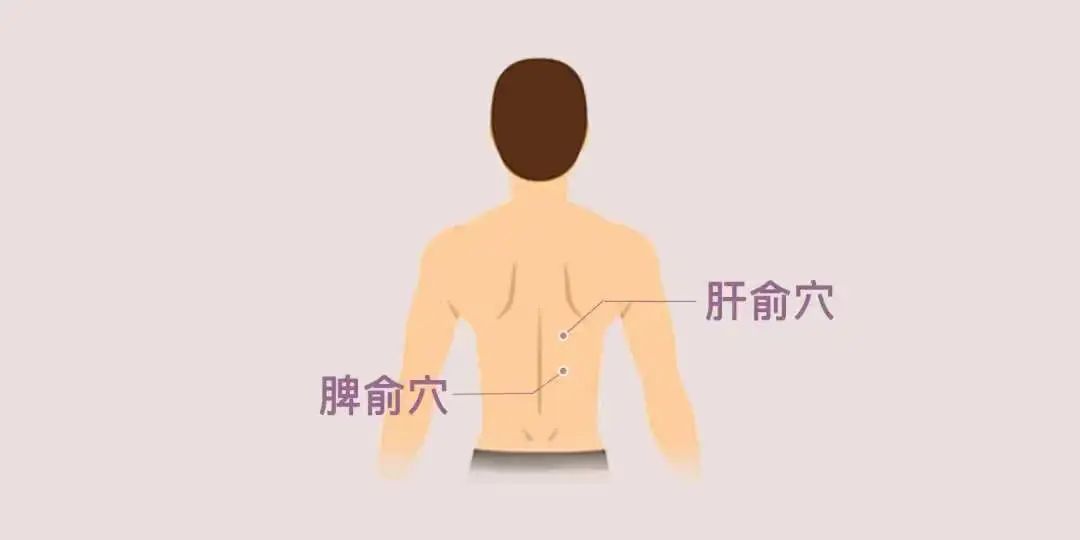
Chronic Fatigue
Cupping can be performed along the Dazhu (大杼) to the Pishu (脾俞) along the Bladder meridian.
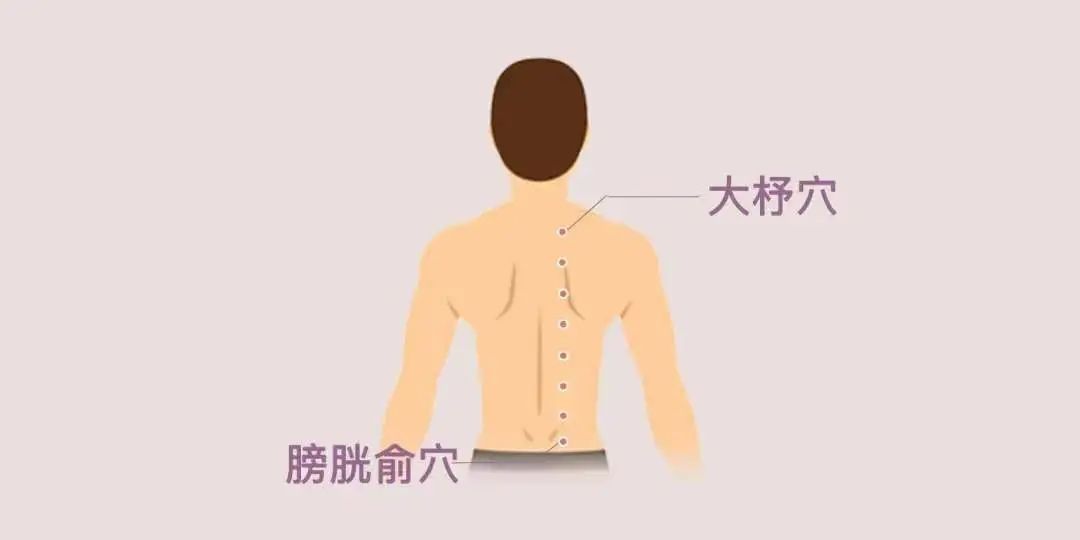
Therefore, the selection of cupping sites is a specialized task, and it is recommended to consult a physician for guidance.
5
Six Misconceptions About Cupping
Misconception1Anyone Can Do Cupping
Not everyone can undergo cupping therapy. The following individuals should avoid cupping:
① Those with severe spinal diseases, such as spondylolisthesis;
② Those with severe heart, liver, lung, or kidney diseases;
③ Those with high fever, convulsions, or spasms;
④ Children, elderly individuals, those with weak constitutions, and pregnant women should avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back;
⑤ Those with acute traumatic fractures or severe edema;
⑥ Patients with certain skin allergies or skin diseases;
⑦ Patients with bleeding disorders, such as thrombocytopenia, leukemia, or allergic purpura;
⑧ Those who are intoxicated, overly hungry, overly full, or excessively fatigued.
If you have any medical conditions, you should inform your doctor before cupping to avoid further harm.
Misconception2Any Body Part Can Be Cupped
Cupping should not be performed on the navel, precordial area, facial features, the front and back of the lower body, areas with delicate skin, or areas with burns, ulcers, infections, tumors, nipples, lower back, or bony protrusions.
Pregnant women should avoid cupping on the lower back and abdomen, as it can easily lead to miscarriage.
Misconception3Repeated Cupping on the Same Spot
Performing cupping multiple times on the same area in a short period can easily cause skin damage. Cupping marks should not be cupped again until they have faded.
Generally, it is advisable to limit cupping to no more than twice a week.
Misconception4Showering Immediately After Cupping
The skin is temporarily vulnerable after cupping, and showering immediately may cause damage and infection. It is recommended to wait 12 hours before showering to avoid friction on the cupping area.

Additionally, during cupping, the body’s capillaries dilate and pores open. If exposed to cold air or air conditioning, it can easily allow cold to enter the body, leading to other diseases. After cupping, avoid wind and cold, and pay attention to warmth.
Misconception5Longer Cupping Time is Better
Some people leave the cups on for an hour, which is dangerous and can lead to skin damage, blisters, and burns.
Generally, in clinical practice, cupping is left on for 20-30 minutes to create blisters, but under normal circumstances, 10-15 minutes is appropriate.
Misconception6Cupping Can Cure All Diseases
Some people think that cupping can treat any illness, which is incorrect. While cupping has a wide range of therapeutic applications, it does not mean it can cure all diseases.
For pain-related conditions, it is essential to first identify the underlying cause of the pain. If the pain is due to chronic diseases or muscle tension, such as lumbar muscle strain, cupping will not be effective.
END








Disclaimer:
The content reproduced from the WeChat public platform of the Comprehensive Internal Medicine Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University maintains a neutral stance on the viewpoints and judgments expressed in the text and does not provide any express or implied guarantees regarding the accuracy, reliability, or completeness of the content. Readers are advised to use it for reference only and assume corresponding responsibilities. Since many articles are sourced from the internet, we will delete any content that infringes copyright within 24 hours.
Contributor/Yu Sihua
Proofreader/Chen Lin
Reviewer/Dai Zhimin

