 Bloodletting Therapy is a unique acupuncture treatment method in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It is one of the most commonly used treatment methods since the era of the Huangdi Neijing (Inner Canon of Huangdi), which even considers bloodletting as the first choice for treating diseases and alleviating suffering. Depending on the patient’s specific condition, a three-edged needle or a thick, sharp needle is used to puncture specific acupuncture points or superficial blood vessels on the patient, allowing a certain amount of blood to be released as a form of external treatment.
Bloodletting Therapy is a unique acupuncture treatment method in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It is one of the most commonly used treatment methods since the era of the Huangdi Neijing (Inner Canon of Huangdi), which even considers bloodletting as the first choice for treating diseases and alleviating suffering. Depending on the patient’s specific condition, a three-edged needle or a thick, sharp needle is used to puncture specific acupuncture points or superficial blood vessels on the patient, allowing a certain amount of blood to be released as a form of external treatment.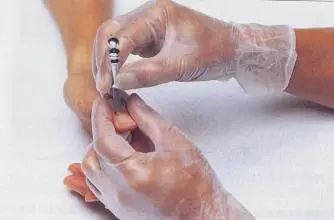 Effects of Bloodletting Therapy:Good bidirectional regulation of the blood systemResearch shows that bloodletting therapy can promote metabolism, stimulate bone marrow hematopoiesis, accelerate metabolism, improve microcirculation and vascular function, facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the blood, and ensure beneficial substances are timely replenished into the bloodstream, helping the body re-establish homeostasis and restore normal physiological functions. By improving microcirculation, it can also prevent excessive inflammatory responses and promote recovery from inflammation.Understanding Your Health Status Through Blood Color:Which type do you belong to?1. Dark black blood, resembling ink, indicates a long-standing illness, suggesting blood stasis. 2. Blood mixed with water indicates rheumatism or liver disease. 3. Blood containing jelly-like mucus indicates damp-heat accumulation. 4. Light blood indicates inflammation or an early-stage illness. Purple-red blood indicates a new injury. 5. Blood resembling wash water indicates severe chronic injury. 6. Clear watery fluid indicates edema. 7. Presence of blisters indicates heavy dampness. 8. Foamy fluid indicates wind pathogen. 9. Large volume of blood indicates a long illness duration. 10. Small volume of blood indicates a short illness duration or deep-seated condition. 11. If cupping is performed and a sudden heat sensation is felt when the cup is removed, it indicates heavy damp-heat. 12. Slow bleeding after multiple punctures suggests qi deficiency and blood deficiency. 13. Light bleeding that does not coagulate easily indicates blood deficiency. 14. Blood that settles quickly and coagulates easily indicates qi deficiency.Bloodletting from the Fingers, also known asMinor Bloodletting, is generally performed near the Jing points or at various extremities where small red or purple blood vessels resembling fine hair are found, puncturing to release dark blood to treat diseases.Clinical Validation:Minor Bloodletting can resolve various difficult diseases. For example:
Effects of Bloodletting Therapy:Good bidirectional regulation of the blood systemResearch shows that bloodletting therapy can promote metabolism, stimulate bone marrow hematopoiesis, accelerate metabolism, improve microcirculation and vascular function, facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the blood, and ensure beneficial substances are timely replenished into the bloodstream, helping the body re-establish homeostasis and restore normal physiological functions. By improving microcirculation, it can also prevent excessive inflammatory responses and promote recovery from inflammation.Understanding Your Health Status Through Blood Color:Which type do you belong to?1. Dark black blood, resembling ink, indicates a long-standing illness, suggesting blood stasis. 2. Blood mixed with water indicates rheumatism or liver disease. 3. Blood containing jelly-like mucus indicates damp-heat accumulation. 4. Light blood indicates inflammation or an early-stage illness. Purple-red blood indicates a new injury. 5. Blood resembling wash water indicates severe chronic injury. 6. Clear watery fluid indicates edema. 7. Presence of blisters indicates heavy dampness. 8. Foamy fluid indicates wind pathogen. 9. Large volume of blood indicates a long illness duration. 10. Small volume of blood indicates a short illness duration or deep-seated condition. 11. If cupping is performed and a sudden heat sensation is felt when the cup is removed, it indicates heavy damp-heat. 12. Slow bleeding after multiple punctures suggests qi deficiency and blood deficiency. 13. Light bleeding that does not coagulate easily indicates blood deficiency. 14. Blood that settles quickly and coagulates easily indicates qi deficiency.Bloodletting from the Fingers, also known asMinor Bloodletting, is generally performed near the Jing points or at various extremities where small red or purple blood vessels resembling fine hair are found, puncturing to release dark blood to treat diseases.Clinical Validation:Minor Bloodletting can resolve various difficult diseases. For example: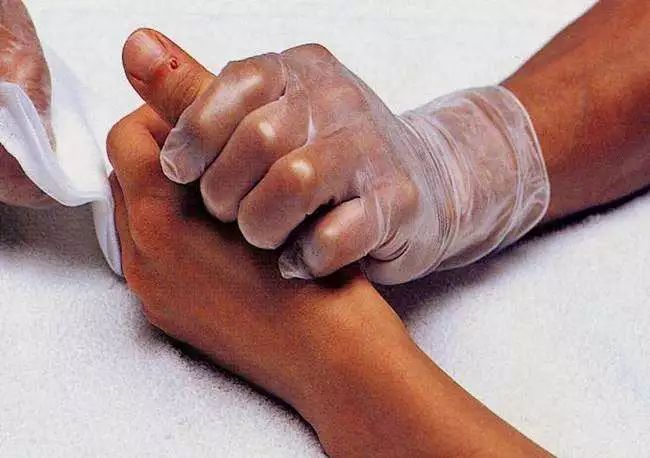 Case 1: AnxietyMr. Li, 33 years old, overweight, under immense work pressure, anxious and restless, nearly on the verge of collapse. Upon meridian observation, stagnation was found near the Zhongchong (中冲) point on the dorsal side of the middle finger, with small blue veins bulging. After puncturing, a large amount of dark blood was released, resulting in a significant improvement in his mental state. A disposable blood collection needle can be used instead of a three-edged needle.
Case 1: AnxietyMr. Li, 33 years old, overweight, under immense work pressure, anxious and restless, nearly on the verge of collapse. Upon meridian observation, stagnation was found near the Zhongchong (中冲) point on the dorsal side of the middle finger, with small blue veins bulging. After puncturing, a large amount of dark blood was released, resulting in a significant improvement in his mental state. A disposable blood collection needle can be used instead of a three-edged needle.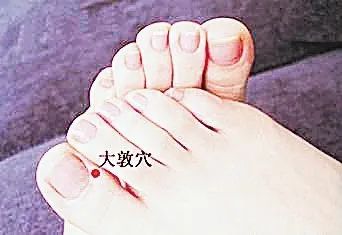 Case 2: Nasal UlcerationMr. Ji, 36 years old, has a small ulcer in the right nostril that worsens every winter, causing unbearable pain for many years, and has not been cured despite multiple treatments. Upon meridian examination, several small red blood vessels were found at the Dazhu (大敦) and Yinbai (隐白) points on the right big toe. After puncturing, dozens of drops of dark blood were released, and the ulcer healed the next day, with no recurrence for two years. Case 3: Oral UlcersMr. Zhao, 50 years old, robust physique, busy with work and socializing, prone to heat, prefers cold and fears heat, suffers from recurrent oral ulcers and hoarseness every summer. Upon meridian examination, small red blood vessels were found near the Jing points of the big toe. After several punctures, significant improvement was noted. He has not experienced significant heat-related ulcers in recent years. Additionally, after puncturing on the back, his hoarseness also improved.Case 4: Increased Vaginal DischargeMs. Gou has abnormal vaginal discharge that has not been cured despite various treatments. Upon meridian examination, several prominent red blood vessels were found around the Liyin (厉兑) point on the second toe. After a small amount of blood was released through puncturing, symptoms improved, and after another puncture a week later, she was clinically cured.Case 5: Sensitivity and SuspicionMr. Qian, 26 years old, suffers from nervous sensitivity and suspicion, often suspecting others of having malicious intentions or plotting against him. His eyes appeared overly bright and exposed. Upon examination, a segment of a bulging blood vessel was found near the Shenmen (神门) point on the upper ear. After puncturing, a large amount of stagnant blood was released, resulting in a calmer demeanor and significant improvement in his suspicion.
Case 2: Nasal UlcerationMr. Ji, 36 years old, has a small ulcer in the right nostril that worsens every winter, causing unbearable pain for many years, and has not been cured despite multiple treatments. Upon meridian examination, several small red blood vessels were found at the Dazhu (大敦) and Yinbai (隐白) points on the right big toe. After puncturing, dozens of drops of dark blood were released, and the ulcer healed the next day, with no recurrence for two years. Case 3: Oral UlcersMr. Zhao, 50 years old, robust physique, busy with work and socializing, prone to heat, prefers cold and fears heat, suffers from recurrent oral ulcers and hoarseness every summer. Upon meridian examination, small red blood vessels were found near the Jing points of the big toe. After several punctures, significant improvement was noted. He has not experienced significant heat-related ulcers in recent years. Additionally, after puncturing on the back, his hoarseness also improved.Case 4: Increased Vaginal DischargeMs. Gou has abnormal vaginal discharge that has not been cured despite various treatments. Upon meridian examination, several prominent red blood vessels were found around the Liyin (厉兑) point on the second toe. After a small amount of blood was released through puncturing, symptoms improved, and after another puncture a week later, she was clinically cured.Case 5: Sensitivity and SuspicionMr. Qian, 26 years old, suffers from nervous sensitivity and suspicion, often suspecting others of having malicious intentions or plotting against him. His eyes appeared overly bright and exposed. Upon examination, a segment of a bulging blood vessel was found near the Shenmen (神门) point on the upper ear. After puncturing, a large amount of stagnant blood was released, resulting in a calmer demeanor and significant improvement in his suspicion.
It is said that when the disease comes, the corresponding acupuncture point should be treated; when the disease goes, the corresponding blood stasis will gradually disappear. If the disease does not resolve, puncturing can be done every three days until recovery, with each puncture stopping when fresh blood is released, as excessive bleeding is not beneficial.
Precautions for Bloodletting:1. Bloodletting Technique1. After identifying the blood point, quickly puncture with wrist strength, aiming for 6-9 punctures in one second.2. For bulging blood vessels, one puncture should yield blood, which will usually spurt out, so be prepared to avoid splattering.2. Reactions After Bloodletting1. 80% of patients feel relaxed and comfortable after bloodletting, while 20% may experience increased pain. Those who feel increased pain tend to heal faster than those who feel immediate relief.2. If there is no sensation after 5-10 punctures, further bloodletting is not advisable.3. Timing of Bloodletting1. For inflammation or acute pain, bloodletting can be done once a day, and after symptoms improve, every 3-5 days. 2. For chronic patients, every other day, and once every 5-7 days after improvement. Cupping can be performed after puncturing for 15-20 minutes.4. Contraindications for Bloodletting1. Patients with significant bleeding or those prone to subcutaneous bleeding.2. Severe heart disease.3. Patients with sexually transmitted diseases, skin diseases, or skin ulcers.4. Pregnant women or those on their menstrual cycle, and patients with leukemia should not undergo bloodletting.5. Patients who are overly hungry or full, frightened, or excessively tense should not be treated.6. For liver disease patients, bloodletting should be done with caution (as with any other treatment), and blood should not come into contact with oneself or open wounds to avoid transmission.5. Treatment for “Needle Fainting”1. Immediately warm the patient’s Dazhui (大椎) point with your palm.2. Pinch the Renzhong (人中) and Hegu (合谷) points simultaneously.3. Then press Neiguan (内关), Yongquan (涌泉), and Taichong (太冲). If conditions allow, have the patient drink a cup of warm sugar water or glucose immediately.4. Immediately have the patient lie down (head lower than feet).6. Diagnosing Through Blood Appearance1. Light blood indicates inflammation or an early-stage illness. Blood mixed with water indicates rheumatism or liver disease, while dark blood indicates a long-standing illness with blood stasis.2. If pain decreases during the day but worsens at night, it indicates blood stasis, and another puncture is necessary until relief is achieved.
The above is for reference only; non-professionals should not perform these procedures.
 Appendix: Bloodletting Therapy for 24 Difficult Diseases1. Cerebral Hemorrhage (Stroke):This refers to non-traumatic bleeding caused by the rupture of blood vessels within the brain, accounting for 20%-30% of all strokes, with an acute mortality rate of 30%-40%. The causes are mainly related to cerebrovascular diseases: hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, vascular aging, smoking, etc. Patients who bleed will often be comatose; puncturing the Yintang (印堂), Taiyang (太阳), Taichong (太冲), and all ten fingers to release 1-5 drops of blood can help them regain consciousness sooner and reduce the severity of hemiplegia. If a patient is comatose for more than 24 hours, the rate of hemiplegia is over 90%. If it exceeds 72 hours, there is a 100% chance of hemiplegic sequelae, making it extremely difficult to treat. Therefore, early awakening is a priceless secret technique; once the patient awakens, puncturing Dazhui, Quchi, and Weizhong can lead to recovery.2. Neuralgia:For pain along the Gallbladder meridian (outer thigh and calf), check for bulging blood vessels around the Yanglingquan (阳陵泉) and Fenglong (丰隆) points. If present, bloodletting can lead to recovery.
Appendix: Bloodletting Therapy for 24 Difficult Diseases1. Cerebral Hemorrhage (Stroke):This refers to non-traumatic bleeding caused by the rupture of blood vessels within the brain, accounting for 20%-30% of all strokes, with an acute mortality rate of 30%-40%. The causes are mainly related to cerebrovascular diseases: hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, vascular aging, smoking, etc. Patients who bleed will often be comatose; puncturing the Yintang (印堂), Taiyang (太阳), Taichong (太冲), and all ten fingers to release 1-5 drops of blood can help them regain consciousness sooner and reduce the severity of hemiplegia. If a patient is comatose for more than 24 hours, the rate of hemiplegia is over 90%. If it exceeds 72 hours, there is a 100% chance of hemiplegic sequelae, making it extremely difficult to treat. Therefore, early awakening is a priceless secret technique; once the patient awakens, puncturing Dazhui, Quchi, and Weizhong can lead to recovery.2. Neuralgia:For pain along the Gallbladder meridian (outer thigh and calf), check for bulging blood vessels around the Yanglingquan (阳陵泉) and Fenglong (丰隆) points. If present, bloodletting can lead to recovery. 3. Long-standing Boils and Abscesses:Boils: Red, swollen, hot, and painful, shallow and large, easy to resolve if not yet pus-filled, but difficult to heal if pus has formed. Caused by heat toxins and qi-blood stagnation. Abscesses: Diffuse swelling without a head, unchanged skin color, unclear boundaries, little pain, difficult to resolve if not yet pus-filled. Caused by cold evil stagnating qi and blood. Carbuncles: Initially like millet, deep-rooted and small, needle-like in shape, white at the top and painful. Caused by evil toxins invading and qi-blood stagnation. Furuncles: Superficial, localized, small and round, mildly red, swollen, and painful, easy to resolve. Caused by damp-heat accumulation. Boils, abscesses, carbuncles, and furuncles are four types of surgical conditions occurring on the body surface. Bloodletting is performed at the Xin heart point.4. Initial Stage of Conjunctivitis, Stye Not Yet Pus-Filled:Puncture the Taiyang (太阳) point to release 7-9 drops of blood, and puncture the tips of the middle toes to release 3-5 drops of blood; this can lead to recovery by the next day.5. Severe Rheumatism in the Legs:This is a group of diseases affecting joints, bones, muscles, blood vessels, and related soft or connective tissues, most of which are autoimmune diseases. The onset is often insidious and slow, with a long course and a genetic tendency. Diagnosis and treatment can be challenging. Puncturing 3 inches beside the third, fourth, and fifth thoracic vertebrae can yield significant effects; many severe cases can be cured in 1-2 sessions.6. Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers:These are very common diseases characterized by localized round or oval defects in the gastric and duodenal walls. Patients experience periodic upper abdominal pain, acid reflux, and belching. This condition is prone to recurrence and has a chronic course. Puncturing the blue veins from the Neiting (内庭) to the Jiexi (解溪) points and near the outer ankle can release blood. For gastric ulcers, blood vessels should be sought within 0.5 inches above and 2.5 inches below the Tiaokou (条口) point.7. Chronic Nephritis:This refers to a group of glomerular diseases characterized by proteinuria, hematuria, hypertension, and edema, with varying onset patterns and slow progression, potentially leading to chronic renal failure. (1) Bloodletting at the Yaoyang (臑俞) point can resolve yellow fluid. (2) Around the kidneys. (3) Bloodletting around the navel (do not puncture the center of the navel).8. Hepatitis Bloodletting:This usually refers to liver cell damage caused by various pathogenic factors such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, chemical toxins, drugs, alcohol, and autoimmune factors, leading to a series of discomfort symptoms and abnormal liver function indicators. Puncturing Yangjiao (阳交), Zusanli (足三里), Quze (曲泽), Yanglingquan (阳陵泉), and Sanyinjiao (三阴交).9. Cirrhosis with Ascites:This is a common chronic progressive liver disease caused by one or more long-term or recurrent factors leading to diffuse liver damage. In China, most cases are post-hepatitis cirrhosis, with a small number being alcoholic or schistosomiasis-related cirrhosis. Late-stage complications often include upper gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, secondary infections, splenomegaly, ascites, and cancer. Use hepatitis acupuncture points plus: Shenshu (肾俞), Yaoyang (腰俞) points, Tiaokou (条口) (0.5 inches above and outside), and Gan Shu (肝俞).10. Effective Points for Hemorrhoids:This is a common disease located at the anal area, which can occur at any age, but the incidence increases with age. (1) Chaojiao (龊交) point (located at the junction of the upper gum and upper lip) can be found at the white granule point, and can be cured in 1-3 sessions. (2) For red, swollen, and ulcerated anal areas, puncturing Weizhong (委中) can relieve pain.11. Insomnia:This refers to the inability to fall asleep or maintain sleep, leading to insufficient sleep. Also known as sleep onset and maintenance disorders, it is caused by various factors leading to difficulty falling asleep, shallow sleep, frequent awakenings, and poor sleep quality, making it a common condition. Insomnia often causes significant suffering and psychological burden for patients, and the misuse of sleeping pills can harm other aspects of health. (1) Shenmen (神门), Xingjian (行间), and Zusanli (足三里). (2) Dazhui, Shendao (神道), Zhongwan (中脘), puncturing followed by cupping.12. Cervical Spondylosis:Pain points, Tianzong (天宗), Jianzheng (肩贞), and Chize (尺泽) points.13. Chest Internal Injuries:Dazhui, Jianjing (肩井), and then the injured area.2. Puncturing joint points.14. Shoulder Periarthritis:Kidney point (1.5 inches below Yinlingquan (阴陵泉)), Chize point, effective in one session.15. Acute and Chronic Throat Diseases:Dazhui, Ear apex, ear back vein, Shaoshang (少商), Quchi, Taiyang, bloodletting reduces pain.16. Impotence:(1) Puncturing Shenshu, Fuliu (复溜) for bloodletting, Guanyuan (关元), and cupping at Shenshu for 15 minutes. (2) Bloodletting at Sanyinjiao, Mingmen (命门), and cupping at Shenshu and Xuehai (血海).
3. Long-standing Boils and Abscesses:Boils: Red, swollen, hot, and painful, shallow and large, easy to resolve if not yet pus-filled, but difficult to heal if pus has formed. Caused by heat toxins and qi-blood stagnation. Abscesses: Diffuse swelling without a head, unchanged skin color, unclear boundaries, little pain, difficult to resolve if not yet pus-filled. Caused by cold evil stagnating qi and blood. Carbuncles: Initially like millet, deep-rooted and small, needle-like in shape, white at the top and painful. Caused by evil toxins invading and qi-blood stagnation. Furuncles: Superficial, localized, small and round, mildly red, swollen, and painful, easy to resolve. Caused by damp-heat accumulation. Boils, abscesses, carbuncles, and furuncles are four types of surgical conditions occurring on the body surface. Bloodletting is performed at the Xin heart point.4. Initial Stage of Conjunctivitis, Stye Not Yet Pus-Filled:Puncture the Taiyang (太阳) point to release 7-9 drops of blood, and puncture the tips of the middle toes to release 3-5 drops of blood; this can lead to recovery by the next day.5. Severe Rheumatism in the Legs:This is a group of diseases affecting joints, bones, muscles, blood vessels, and related soft or connective tissues, most of which are autoimmune diseases. The onset is often insidious and slow, with a long course and a genetic tendency. Diagnosis and treatment can be challenging. Puncturing 3 inches beside the third, fourth, and fifth thoracic vertebrae can yield significant effects; many severe cases can be cured in 1-2 sessions.6. Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers:These are very common diseases characterized by localized round or oval defects in the gastric and duodenal walls. Patients experience periodic upper abdominal pain, acid reflux, and belching. This condition is prone to recurrence and has a chronic course. Puncturing the blue veins from the Neiting (内庭) to the Jiexi (解溪) points and near the outer ankle can release blood. For gastric ulcers, blood vessels should be sought within 0.5 inches above and 2.5 inches below the Tiaokou (条口) point.7. Chronic Nephritis:This refers to a group of glomerular diseases characterized by proteinuria, hematuria, hypertension, and edema, with varying onset patterns and slow progression, potentially leading to chronic renal failure. (1) Bloodletting at the Yaoyang (臑俞) point can resolve yellow fluid. (2) Around the kidneys. (3) Bloodletting around the navel (do not puncture the center of the navel).8. Hepatitis Bloodletting:This usually refers to liver cell damage caused by various pathogenic factors such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, chemical toxins, drugs, alcohol, and autoimmune factors, leading to a series of discomfort symptoms and abnormal liver function indicators. Puncturing Yangjiao (阳交), Zusanli (足三里), Quze (曲泽), Yanglingquan (阳陵泉), and Sanyinjiao (三阴交).9. Cirrhosis with Ascites:This is a common chronic progressive liver disease caused by one or more long-term or recurrent factors leading to diffuse liver damage. In China, most cases are post-hepatitis cirrhosis, with a small number being alcoholic or schistosomiasis-related cirrhosis. Late-stage complications often include upper gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, secondary infections, splenomegaly, ascites, and cancer. Use hepatitis acupuncture points plus: Shenshu (肾俞), Yaoyang (腰俞) points, Tiaokou (条口) (0.5 inches above and outside), and Gan Shu (肝俞).10. Effective Points for Hemorrhoids:This is a common disease located at the anal area, which can occur at any age, but the incidence increases with age. (1) Chaojiao (龊交) point (located at the junction of the upper gum and upper lip) can be found at the white granule point, and can be cured in 1-3 sessions. (2) For red, swollen, and ulcerated anal areas, puncturing Weizhong (委中) can relieve pain.11. Insomnia:This refers to the inability to fall asleep or maintain sleep, leading to insufficient sleep. Also known as sleep onset and maintenance disorders, it is caused by various factors leading to difficulty falling asleep, shallow sleep, frequent awakenings, and poor sleep quality, making it a common condition. Insomnia often causes significant suffering and psychological burden for patients, and the misuse of sleeping pills can harm other aspects of health. (1) Shenmen (神门), Xingjian (行间), and Zusanli (足三里). (2) Dazhui, Shendao (神道), Zhongwan (中脘), puncturing followed by cupping.12. Cervical Spondylosis:Pain points, Tianzong (天宗), Jianzheng (肩贞), and Chize (尺泽) points.13. Chest Internal Injuries:Dazhui, Jianjing (肩井), and then the injured area.2. Puncturing joint points.14. Shoulder Periarthritis:Kidney point (1.5 inches below Yinlingquan (阴陵泉)), Chize point, effective in one session.15. Acute and Chronic Throat Diseases:Dazhui, Ear apex, ear back vein, Shaoshang (少商), Quchi, Taiyang, bloodletting reduces pain.16. Impotence:(1) Puncturing Shenshu, Fuliu (复溜) for bloodletting, Guanyuan (关元), and cupping at Shenshu for 15 minutes. (2) Bloodletting at Sanyinjiao, Mingmen (命门), and cupping at Shenshu and Xuehai (血海).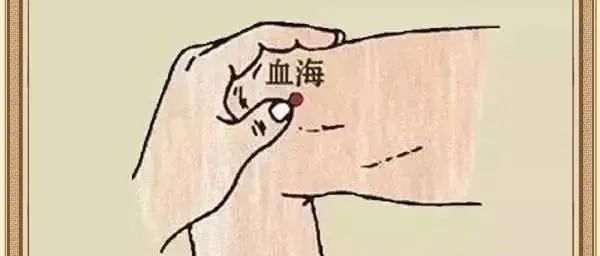 17. Hypertension:Puncturing Taiyang, Dazhui, ear apex, ear back vein, and Quchi can lower blood pressure immediately; note: do not drink water within one hour after bloodletting, as it may reduce effectiveness.18. Asthma:(1) Puncturing Dazhui, Shenyu (肺俞), Fengmen (风门), Gaomang (膏盲), and Lieque (列缺). Cupping at Zhongfu (中府) and Dazhui for 15 minutes.19. Hyperlipidemia:Puncturing Dazhui, Taiyang, Yaoyang, Weizhong, and Quchi.20. Rheumatic Heart Disease:Puncturing Yangjiao, Chize, and Taiyang.21. Eyelid Pterygium:Puncturing Shaoze (少泽), Zhiyin (至阴), ear apex, and Dazhui every other day for a ten-day course.22. Otitis Media:Puncturing the outer ankle joint.23. Epilepsy:(1) Puncturing Taiyang, Quze, Weizhong, and Yangjiao. (2) Puncturing Shaoshang and Renzhong. Cupping at Gan Shu and Dazhui for 15 minutes. (3) Finding pain points at the lower part of the back of the neck and Neiguan, using a plum blossom needle to puncture and release blood.24. Mental Illness:Puncturing Taiyang, Quze, Weizhong, Taichong, Yangjiao, Fenglong, and Xinshu, followed by cupping.The Secret of Bloodletting For diseases that have not been cured for a long time and have not responded to any treatment, bloodletting can be performed on the bulging blood vessels at the ankles, elbows, wrists, and knees, which may yield unexpected results.Bloodletting should generally not be performed at night; it is best done around noon.Among all forms of giving, the giving of knowledge is the highest. Sharing an article filled with wisdom and positive energy can save many people and change their confused lives, guiding them towards the light. Thank you for sharing, allowing more people to benefit.
17. Hypertension:Puncturing Taiyang, Dazhui, ear apex, ear back vein, and Quchi can lower blood pressure immediately; note: do not drink water within one hour after bloodletting, as it may reduce effectiveness.18. Asthma:(1) Puncturing Dazhui, Shenyu (肺俞), Fengmen (风门), Gaomang (膏盲), and Lieque (列缺). Cupping at Zhongfu (中府) and Dazhui for 15 minutes.19. Hyperlipidemia:Puncturing Dazhui, Taiyang, Yaoyang, Weizhong, and Quchi.20. Rheumatic Heart Disease:Puncturing Yangjiao, Chize, and Taiyang.21. Eyelid Pterygium:Puncturing Shaoze (少泽), Zhiyin (至阴), ear apex, and Dazhui every other day for a ten-day course.22. Otitis Media:Puncturing the outer ankle joint.23. Epilepsy:(1) Puncturing Taiyang, Quze, Weizhong, and Yangjiao. (2) Puncturing Shaoshang and Renzhong. Cupping at Gan Shu and Dazhui for 15 minutes. (3) Finding pain points at the lower part of the back of the neck and Neiguan, using a plum blossom needle to puncture and release blood.24. Mental Illness:Puncturing Taiyang, Quze, Weizhong, Taichong, Yangjiao, Fenglong, and Xinshu, followed by cupping.The Secret of Bloodletting For diseases that have not been cured for a long time and have not responded to any treatment, bloodletting can be performed on the bulging blood vessels at the ankles, elbows, wrists, and knees, which may yield unexpected results.Bloodletting should generally not be performed at night; it is best done around noon.Among all forms of giving, the giving of knowledge is the highest. Sharing an article filled with wisdom and positive energy can save many people and change their confused lives, guiding them towards the light. Thank you for sharing, allowing more people to benefit.
There are no advertisements or rumors here; long press the QR code to follow for more positive health knowledge!
⊙This article is reproduced from the internet, and the original author cannot be verified. The content is for public sharing only; please follow medical advice for specific treatment and medication!Copyright belongs to the original author; if there are any objections, please contact [email protected] for timely deletion.


