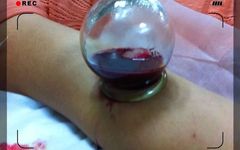
Bloodletting therapy, commonly known as “bloodletting” or “phlebotomy,” is an ancient and unique treatment method in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Due to its lesser-known status compared to acupuncture, its complexity compared to tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage), and its simplicity compared to moxibustion, public understanding of this therapy is generally shallow, leading to a common aversion to the concept of bloodletting. Many people’s knowledge of bloodletting therapy is limited to instances like “letting blood from a child’s finger to treat malnutrition” or “quickly pinching the philtrum or pricking the middle finger to let blood in case of a stroke in the elderly.”
(Attached: A shocking image)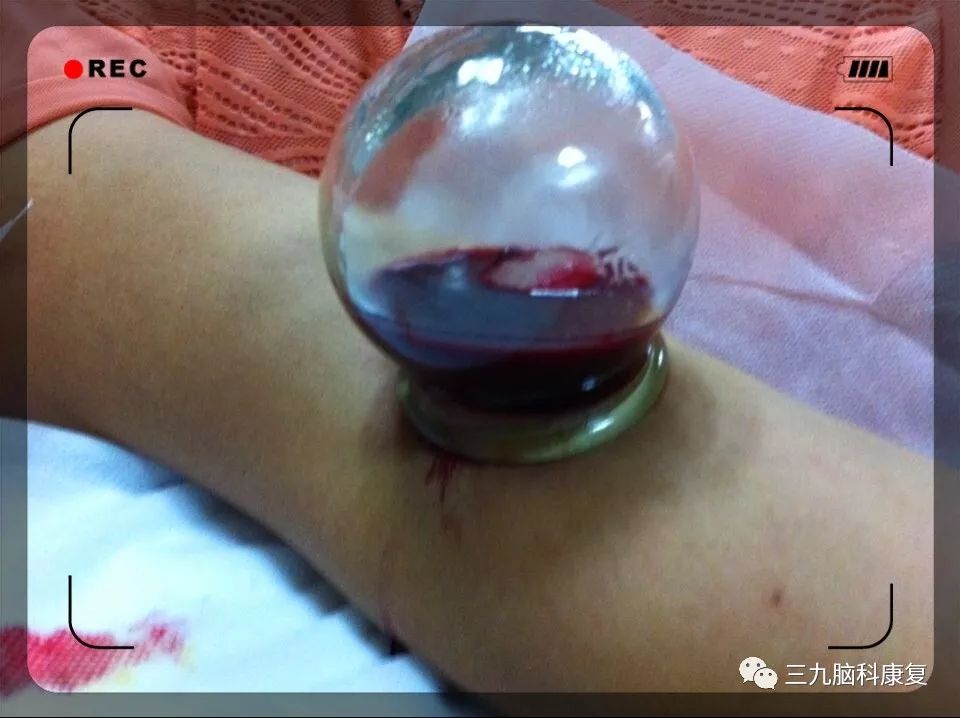
What is Bloodletting Therapy? Bloodletting therapy is simply defined as a treatment method that involves puncturing specific acupuncture points or superficial meridians on the body with specialized needles to release a small amount of blood. As early as in the “Huangdi Neijing” (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon), there are detailed records regarding the mechanisms, treatment principles, and techniques of bloodletting. The “Lingshu: Xiaozhenjie” states: “To remove stagnation, one must clear the meridians.” The “Suwen: Qixue Lun” states: “If there is excess blood, drain the excess from the meridian…” “How to let blood? Qi Bo said: Observe the blood vessels, let out the blood, and ensure that no stagnant blood enters the meridians, causing disease.” From this, we can understand that the mechanism of bloodletting therapy is to unblock the meridians, invigorate blood circulation, and expel pathogens and toxins. By letting out stagnant blood, it clears the meridians and improves the function of the organs and blood, thus achieving the goal of treating diseases.What Diseases Can Bloodletting Therapy Treat?
Bloodletting therapy is simply defined as a treatment method that involves puncturing specific acupuncture points or superficial meridians on the body with specialized needles to release a small amount of blood. As early as in the “Huangdi Neijing” (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon), there are detailed records regarding the mechanisms, treatment principles, and techniques of bloodletting. The “Lingshu: Xiaozhenjie” states: “To remove stagnation, one must clear the meridians.” The “Suwen: Qixue Lun” states: “If there is excess blood, drain the excess from the meridian…” “How to let blood? Qi Bo said: Observe the blood vessels, let out the blood, and ensure that no stagnant blood enters the meridians, causing disease.” From this, we can understand that the mechanism of bloodletting therapy is to unblock the meridians, invigorate blood circulation, and expel pathogens and toxins. By letting out stagnant blood, it clears the meridians and improves the function of the organs and blood, thus achieving the goal of treating diseases.What Diseases Can Bloodletting Therapy Treat? Bloodletting therapy has a wide range of indications, applicable to various conditions of yin and yang, deficiency and excess, exterior and interior, cold and heat, including internal diseases such as organ disorders, mental disorders, pain syndromes, and malaria, as well as external diseases like sores, carbuncles, and herpes. It is also used for gynecological conditions such as irregular menstruation, mastopathy (breast hyperplasia), infertility, and menopausal syndrome, as well as pediatric diseases like fever, cough, food accumulation, night crying, and childhood convulsions.
Bloodletting therapy has a wide range of indications, applicable to various conditions of yin and yang, deficiency and excess, exterior and interior, cold and heat, including internal diseases such as organ disorders, mental disorders, pain syndromes, and malaria, as well as external diseases like sores, carbuncles, and herpes. It is also used for gynecological conditions such as irregular menstruation, mastopathy (breast hyperplasia), infertility, and menopausal syndrome, as well as pediatric diseases like fever, cough, food accumulation, night crying, and childhood convulsions.
Here are a few common examples:
1
Cold, fever, sore throat, hoarseness
Puncturing the Shaoshang point (LU-11, Jing-Well point of the Lung meridian) to let blood, or performing bloodletting and cupping at the Dazhui point (GV-14, meeting point of the Yang meridians and the Governing Vessel), can disperse wind, clear heat, and open the lung orifices, significantly improving sore throat symptoms.
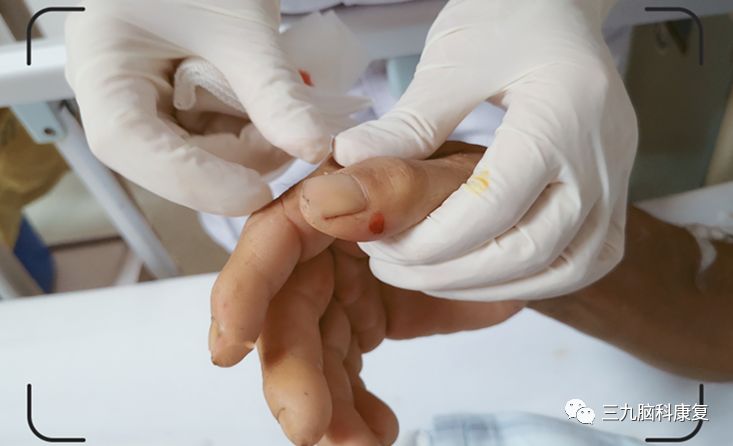
2
After eating spicy food, swollen throat, mouth ulcers
Puncturing the Shangyang point (LI-1, Jing-Well point of the Large Intestine meridian) and the Lidui point (ST-45, Jing-Well point of the Stomach meridian) to let blood can clear the heat from the Large Intestine and Stomach meridians.
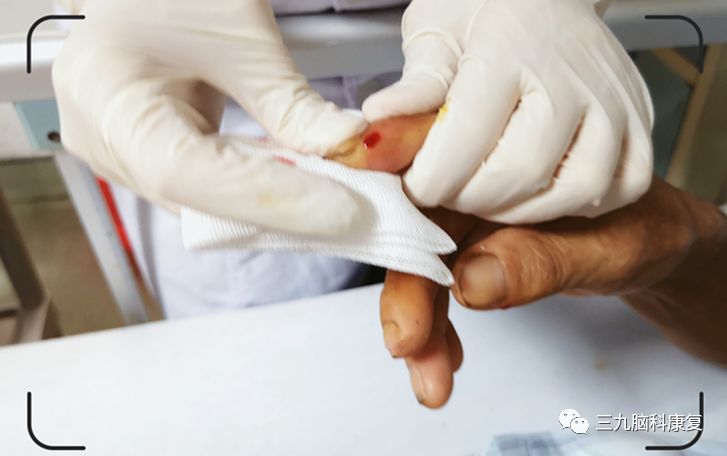
3
Excessive worry, insomnia with vivid dreams, anxiety
Puncturing the Zhongchong point (PC-9, Jing-Well point of the Pericardium meridian) to let blood, or performing bloodletting and cupping at the Xinshu (BL-15) and Gan Shu (BL-18) points can soothe the liver, relieve depression, and calm the heart and spirit.
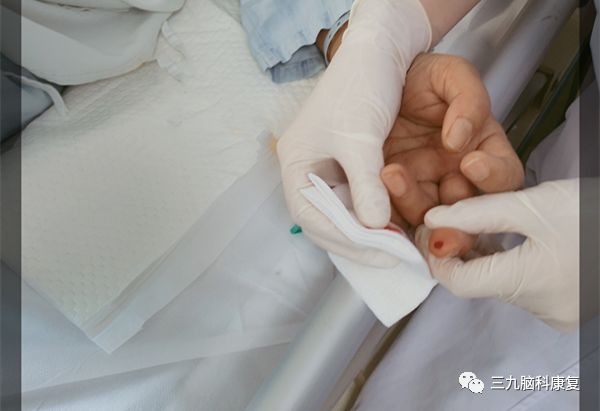
4
Acute lumbar sprain, unable to move
Puncturing the Weizhong point (BL-40, He-Sea point of the Bladder meridian) with bloodletting and cupping can help you stand up again in just one minute.
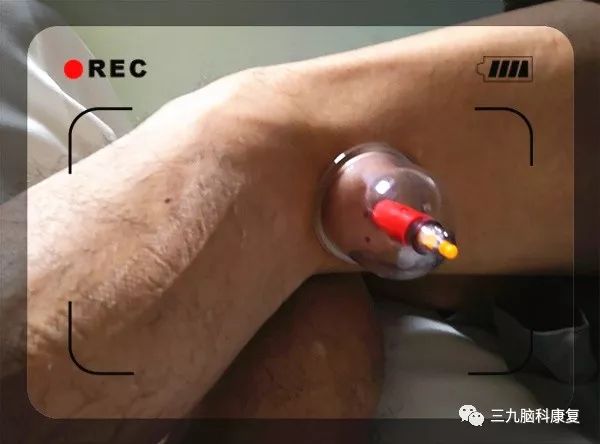
5
High stress causing qi stagnation and blood stasis, or postpartum qi and blood deficiency in young mothers,
leading to hair loss, resulting in alopecia areata or receding hairlines
Local plum blossom needle tapping, causing slight bleeding, can stimulate local qi and blood flow, invigorate circulation, and nourish the hair, allowing it to regain vitality!
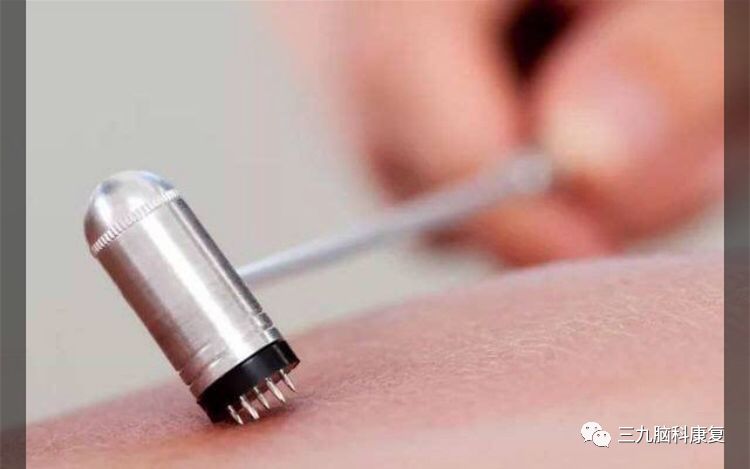
Precautions
Bloodletting therapy is remarkably effective, but it is not suitable for everyone at any time! The following precautions must be observed:
1. Bloodletting therapy must be performed in a legitimate medical institution, after diagnosis by a TCM physician, and carried out by qualified medical personnel;
2. The treatment process must strictly adhere to aseptic techniques;
3. Individuals who are overly hungry, overly full, intoxicated, fatigued, or those suffering from severe anemia, hypoglycemia, bleeding disorders, severe liver or kidney diseases, or serious heart conditions should avoid this method;
4. Pregnant women and the elderly or frail individuals should use this method with caution;
5. If during the treatment, symptoms such as dizziness, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or even pale complexion, cold sweat, weak pulse, or decreased blood pressure occur, the bloodletting treatment should be immediately stopped. For mild cases, have the patient lie down, elevate their legs, ensure good air circulation, and drink warm water; for severe cases, moxibustion at the Baihui point (GV-20) or acupuncture at the Ren Zhong point (GV-26) or Yongquan point (KD-1) may be necessary, and emergency measures should be taken if needed.
Source: Sanjiu Brain Rehabilitation
Recommended Reading
Join Group:Various specialized nursing WeChat groups, join quickly
Submissions: Original articles related to nursing are welcome for submission
Follow:WeChat public account categorized by nursing departments
Buy Books:Nursing books, click “Read the original text” below to purchase