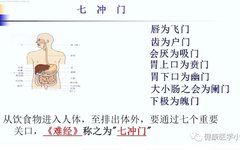
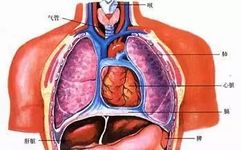
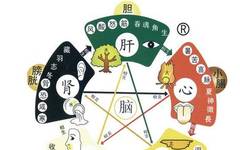
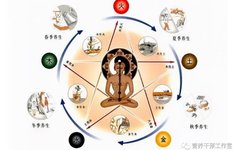
Introduction to TCM Health Preservation: What Are the Six Fu Organs? The Functions of the Stomach, Gallbladder, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Bladder, and San Jiao in the Human Body
The term “Zangfu” refers to the internal organs as a whole. According to their physiological functions, the “Huangdi Neijing” classifies the internal organs into three categories: the Five Zang, the Six Fu, and the Extraordinary Organs. As stated in the “Lüshi Chunqiu”: “There are three hundred sixty joints in a person, nine orifices, five Zang, … Read more