1. Plant Characteristics and Medicinal Form
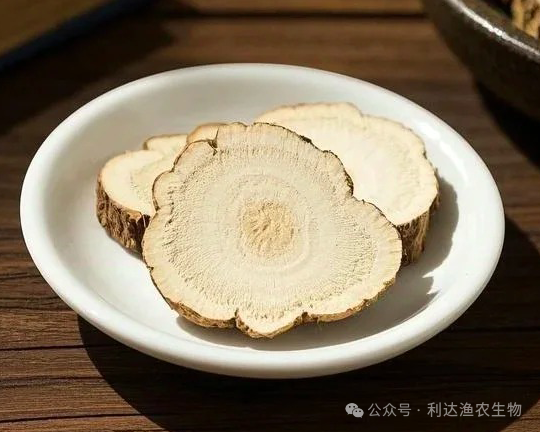
Bai Shao is a perennial herbaceous plant of the Ranunculaceae family and Paeonia genus, primarily used for its dried root. The plant grows to a height of 40-80 cm, with a thick, cylindrical or spindle-shaped root, the surface being dark brown or whitish, firm in texture, and with distinct ring formations on the cross-section. The stem is erect, with the lower leaves being twice pinnate, and the leaflets are narrow-ovate or lanceolate, with edges densely covered with small, bony, white tubercles. It flowers in spring, with petals typically white or pink, and double-flowered cultivated varieties are common. The medicinal characteristics are cylindrical, with flat ends and a smooth surface, having a slightly bitter and sour taste. The three main production areas are Bozhou, Anhui (Bo Bai Shao, accounting for 70% of national production), Zhejiang (Hang Bai Shao, of the highest quality), and Sichuan (Chuan Bai Shao). In recent years, cultivation has increased in Henan, Shanxi, and Hunan, but the quality is inferior to traditional production areas.

2. TCM Efficacy and Modern Pharmacological Effects
1. TCM Efficacy Bai Shao is slightly cold in nature, with a bitter and sour taste, and enters the liver and spleen meridians. It has the effects of nourishing blood, regulating menstruation, astringing yin to stop sweating, softening the liver to relieve pain, and calming liver yang, improving conditions such as blood deficiency, irregular menstruation, and excessive bleeding, treating spontaneous sweating and night sweats, alleviating flank pain, abdominal pain, and limb spasms, and is used for headaches and dizziness caused by excessive liver yang. Bai Shao emphasizes nourishing yin and blood.
2. Modern Pharmacological Effects
Anti-inflammatory and Immune Regulation: Inhibits inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α, IL-6) and regulates T cell activity.
Liver Protection: Reduces liver damage by enhancing SOD and GSH-Px activity and lowering MDA levels.
Analgesic and Neuroprotective: Paeoniflorin alleviates visceral pain and cancer pain by inhibiting the release of P substance.
Anti-tumor and Antioxidant: Terpenoid components induce apoptosis in tumor cells and scavenge free radicals to delay aging.
3. Active Ingredients in Bai Shao Bai Shao contains over 140 compounds, including:
Monoterpenes: Such as paeoniflorin, oxypaeoniflorin, benzoylpaeoniflorin, etc. These compounds are the most important active ingredients in Bai Shao, accounting for over 90% of the total glycosides, dominating the active components with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Triterpenes: Such as paeonolide and hydroxypaeoniflorin, which have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor effects.
Flavonoids: Such as paeoniflorin and danshen phenol, which have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-regulating effects.
Polysaccharide-protein complexes: Containing D-glucose, which regulates immunity.
Tannins and Volatile Oils: Such as gallic acid, which has antioxidant and antibacterial effects; benzoic acid has antibacterial and analgesic effects.
4. Efficacy in Aquaculture
1. Immune Regulation The compounds rich in Bai Shao can promote blood cell production, enhance hematopoietic function in aquatic animals, improve their tolerance to low oxygen, and enhance the activity of phagocytes and T lymphocytes, thereby increasing the non-specific immunity and disease resistance of aquatic animals.
2. Growth Promotion The compounds rich in Bai Shao can enhance digestive enzyme activity, regulate intestinal flora structure, reduce fat deposition in the liver and muscles of aquatic animals, accelerate metabolism, improve feed utilization, and increase the growth rate of aquatic animals.
3. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant The compounds rich in Bai Shao can reduce the release of inflammatory factors (such as leukotriene B4), scavenge free radicals, inhibit lipid peroxidation reactions, protect cell membrane integrity, and delay oxidative damage in aquatic animals caused by environmental stress.
Liver Benefit, composed of Bai Shao powder, bile acids, liver repair factors, biological enzymes, and composite multivitamins, promotes liver cell development, enhances enzyme activity, accelerates liver cell repair, improves and strengthens liver function, enhances detoxification ability, emulsifies fats, increases lipid absorption and transport, reduces fat accumulation in the liver, and prevents liver and gallbladder syndromes such as liver enlargement, white liver, green liver, and fatty liver.


Official WeChat, scan to follow Jiuding Biological