Cupping Therapy Techniques and Proper Procedures
Based on the severity of the patient’s condition, cupping therapy can be divided into four techniques: flash cupping, sliding cupping, retained cupping, and bloodletting cupping.
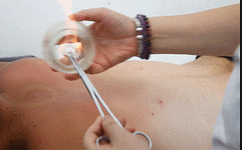
● Flash Cupping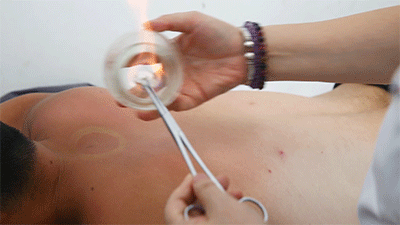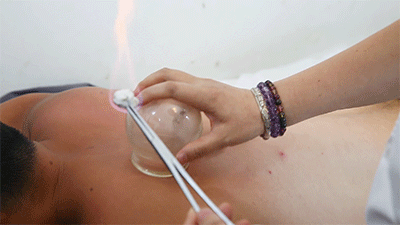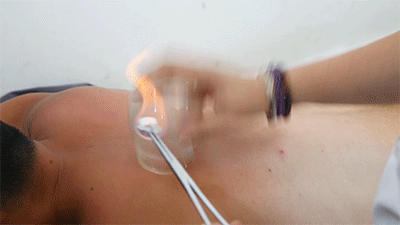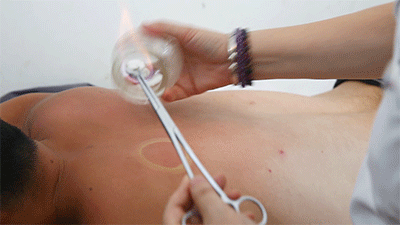 Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, then immediately lift it off.❸ Repeat the suction several times until the skin becomes reddened.Flash cupping typically does not leave marks on the skin and is the least stimulating of the four techniques.● Sliding Cupping
Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, then immediately lift it off.❸ Repeat the suction several times until the skin becomes reddened.Flash cupping typically does not leave marks on the skin and is the least stimulating of the four techniques.● Sliding Cupping Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. Apply a lubricating substance on the skin where cupping will be performed. The choice of lubricant varies based on the desired therapeutic effect. In this image, Zicao You (Lithospermum Oil) is used, which promotes blood circulation.
Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. Apply a lubricating substance on the skin where cupping will be performed. The choice of lubricant varies based on the desired therapeutic effect. In this image, Zicao You (Lithospermum Oil) is used, which promotes blood circulation.

 ❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, holding the cup and sliding it along the meridians. After sliding cupping, if there are issues in the body, there will be large areas of sha (petechiae) at the cupping site; if there are no issues, it will generally just leave cup marks that fade quickly.● Retained Cupping
❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, holding the cup and sliding it along the meridians. After sliding cupping, if there are issues in the body, there will be large areas of sha (petechiae) at the cupping site; if there are no issues, it will generally just leave cup marks that fade quickly.● Retained Cupping


 ❶ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, leaving it for 10-15 minutes before removing it and cleaning the skin with a cotton ball.● Bloodletting Cupping
❶ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then remove it instantly and place the cup on the skin, leaving it for 10-15 minutes before removing it and cleaning the skin with a cotton ball.● Bloodletting Cupping ❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.
❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. ❷ Use a disposable blood collection needle to prick the skin locally.
❷ Use a disposable blood collection needle to prick the skin locally. ❸ Retain the cup.
❸ Retain the cup. ❹ Remove the cup and clean the blood that has oozed out with a cotton ball.Cupping therapy has effects such as promoting meridian flow, invigorating qi and blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. The cup marks left after cupping indicate various health issues. Let’s explore the “diagnosis based on cup marks” together.Diagnosis Based on Cup Marks
❹ Remove the cup and clean the blood that has oozed out with a cotton ball.Cupping therapy has effects such as promoting meridian flow, invigorating qi and blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. The cup marks left after cupping indicate various health issues. Let’s explore the “diagnosis based on cup marks” together.Diagnosis Based on Cup Marks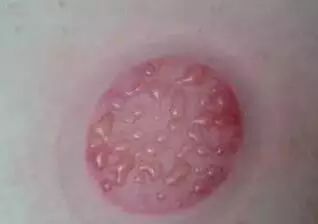
Red or black-red cup marks indicate a pathological response of long-term illness with dampness and blood stasis;
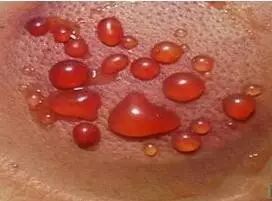
Petechiae that are purple-red or purple-black, without stasis or fever, indicate a condition of cold with blood stasis, varying in severity;
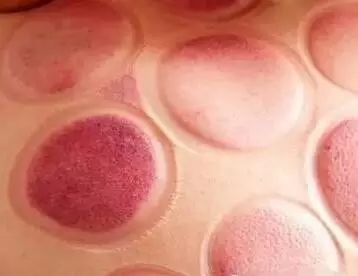
Petechiae that are purple-red or purple-black, or show signs of heat toxicity, indicate the presence of heat toxin in the patient;

Petechiae that are slightly itchy or show skin patterns indicate a wind condition;
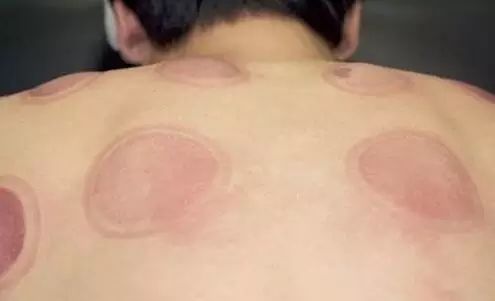
Petechiae with no color change and feel cool to the touch indicate a deficiency-cold condition.
If there are no cup marks or if the cup marks disappear quickly after removal, it indicates a relatively mild sub-health condition.
If the marks do not fade after a few days, it suggests a long-standing condition that requires more attention to treatment and care. As the condition improves, the cup marks will also fade, indicating recovery.
Indications, Main Points, and Contraindications for Cupping
1. Indications and Main Points:
Respiratory System Indications
Acute and chronic bronchitis, asthma, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pleuritis. Main points: Da Zhu (Dazhui), Feng Men (Fengmen), Fei Shu (Lung Shu), Ying Chuang (Yingchuang).
Digestive System Indications
Acute and chronic gastritis, gastric neuralgia, dyspepsia, hyperacidity. Main points: Gan Shu (Liver Shu), Pi Shu (Spleen Shu), Wei Shu (Stomach Shu), Ge Shu (Ge Shu), Zhang Men (Zhangmen).
Acute and chronic enteritis. Main points: Pi Shu (Spleen Shu), Wei Shu (Stomach Shu), Da Chang Shu (Large Intestine Shu), Tian Shu (Tianshu).
Circulatory System Indications
Hypertension. Main points: Gan Shu (Liver Shu), Dan Shu (Gallbladder Shu), Pi Shu (Spleen Shu), Shen Shu (Kidney Shu), Wei Zhong (Weizhong), Cheng Shan (Chengshan), Zu San Li (Zusanli). Focus on the back and lower limbs.
Arrhythmia. Main points: Xin Shu (Heart Shu), Shen Shu (Kidney Shu), Ge Shu (Ge Shu), Pi Shu (Spleen Shu).
Insufficient blood supply to the heart. Main points: Xin Shu (Heart Shu), Ge Shu (Ge Shu), Gao Huang Shu (Gao Huang Shu), Zhang Men (Zhangmen).
Musculoskeletal System Indications
Cervical joint pain, shoulder joint and scapular pain, elbow joint pain. Main points: Pressing points and surrounding joints for cupping. Back pain, lumbar pain, sacral pain, hip pain. Main points: Cupping based on the location of pain and surrounding joints. Knee pain, thigh pain, heel pain. Main points: Use small glass cups at the site of pain and surrounding joints.
Nervous System Indications
Neurogenic headache, occipital neuralgia. Main points: Da Zhui (Dazhui), Da Zhu (Dazhu), Tian Zhu (Tianzhu, with face cushion), Zhi Yang (Zhi Yang).
Intercostal neuralgia. Main points: Zhang Men (Zhangmen), Qi Men (Qimen), and intercostal pain areas for cupping.
Sciatica. Main points: Zhi Bian (Zhibian), Huan Tiao (Huantiao), Wei Zhong (Weizhong).
Peripheral nerve paralysis due to rheumatic damage. Main points: Da Zhui (Dazhui), Gao Huang Shu (Gao Huang Shu), Shen Shu (Kidney Shu), Feng Shi (Fengshi), and the affected areas.
Cervical muscle spasm. Main points: Jian Jing (Jianjing), Da Zhui (Dazhui), Jian Zhong Shu (Jianzhong Shu), Shen Zhu (Shenzhu).
Gastrocnemius muscle spasm. Main points: Wei Zhong (Weizhong), Cheng Shan (Chengshan), and the affected gastrocnemius area.
Facial nerve spasm. Main points: Xia Guan (Xia Guan), Yin Tang (Yintang), Jia Che (Jia Che), using small cups, only retain for 6 seconds, then remove, and repeat cupping 10 to 20 times.
Diaphragmatic spasm. Main points: Ge Shu (Ge Shu), Jing Men (Jingmen).
Gynecological Indications
Dysmenorrhea. Main points: Guan Yuan (Guanyuan), Xue Hai (Xuehai), A Shi points.
Amenorrhea. Main points: Guan Yuan (Guanyuan), Shen Shu (Kidney Shu).
Menorrhagia. Main points: Guan Yuan (Guanyuan), Zi Gong (Zigong).
Leukorrhea. Main points: Guan Yuan (Guanyuan), Zi Gong (Zigong), San Yin Jiao (Sanyinjiao).
Pelvic inflammatory disease. Main points: Zhi Bian (Zhibian), Yao Shu (Yaoshu), Guan Yuan Shu (Guanyuan Shu).
Indications for Surgical Wounds and Ulcers
Boils. Main points: Shen Zhu (Shenzhu), and the boil area, using small cups with face pads for cupping.
Multiple folliculitis. Main points: Zhi Yang (Zhi Yang), local small cups with face pads for cupping.
Lower limb ulcers. Main points: Local small cups with face pads for cupping.
Acute mastitis. Main points: After applying a warm towel soaked in hot water to the area, use medium or large cups for cupping, which can be repeated 5 to 6 times.

2. Contraindications for Cupping
High fever, convulsions, spasms; skin allergies or ulcerated areas; areas with thin muscles or uneven bones and excessive hair are not suitable for cupping; pregnant women should be cautious with cupping on the lumbar and abdominal areas.
3. Cupping Precautions
1. Do not take a cold shower or drink cold beverages within two hours after cupping; if taking a shower after two hours, use warm water.
2. Avoid using air conditioning or fans during cupping to prevent air convection.
3. Do not perform cupping when overly full, hungry, or after excessive drinking; wait at least one hour after meals before cupping.
Common Acupuncture Points and Their Functions and Benefits
[Understanding Acupuncture Points] A hundred points can treat a hundred diseases! You can find corresponding acupuncture points for various ailments!
Self-massage video for common acupuncture points
Comprehensive guide to facial acupuncture points with illustrations
Nine types of constitution identification and nurturing methods
Practical hand diagnosis (recommended for collection)
Acupuncture points for moxibustion therapy
Top ten effective acupuncture points for beauty and body shaping
To assess liver health, check the base of the middle finger! Symptoms of poor liver health
Four moxibustion sessions in a lifetime can prevent a hundred diseases
Hand Diagnosis / Facial Diagnosis / Tongue Diagnosis / Pulse Diagnosis
Pediatric Diagnosis and Treatment / Pediatric Tuina
Moxibustion / Gua Sha / Sanfu Moxibustion
Hand Acupuncture / Abdominal Acupuncture / I Ching / Dietary Therapy
Organ Regulation / San Jiao Regulation
Five Movements and Six Qi / Twelve Meridians / Fasting
Five Animal Exercises / Ear Diagnosis / Postpartum Care
Yi Jin Jing / Gynecological Diagnosis and Treatment / Eight Principles Diagnosis
Shang Han Lun / Zhu You Shu / Repairing the Root Chakra
Eight Methods of Ling Gui / Huang Di Nei Jing / Acupuncture
Five Elements in TCM / TCM Growth Promotion / TCM Diagnosis
Marketing Techniques for Wellness Centers
Membership Group + 800 TCM General Course Materials
Long press to recognize the QR code below to add WeChat for learning