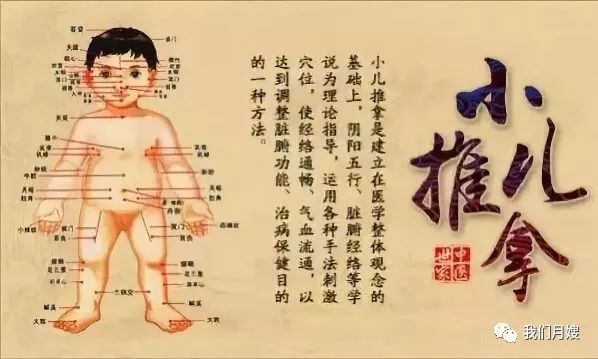
Pediatric Tuina is a manual therapy applied to children, stimulating acupuncture points and meridians to regulate qi, yin and yang, and the essence-spirit. It activates and mobilizes the child’s body to improve internal conditions through the body’s own mechanisms rather than relying on medication, achieving a balance between the organs and harmony between humans and nature.
Warm Reminder: Pediatric Tuina should only be used as an auxiliary treatment when the baby is unwell. If the baby is seriously uncomfortable, it is essential to go to the hospital for professional medical treatment before using Tuina to alleviate the baby’s symptoms.
1. Bu Pi Jing (Supplementing the Spleen Meridian), commonly used for digestive system diseases, also supplements the spleen and nourishes the lungs after respiratory infections, fostering the earth to generate metal.

2. Shun Yun Ba Gua (Following the Eight Trigrams), applicable for both spleen-stomach and respiratory system diseases.
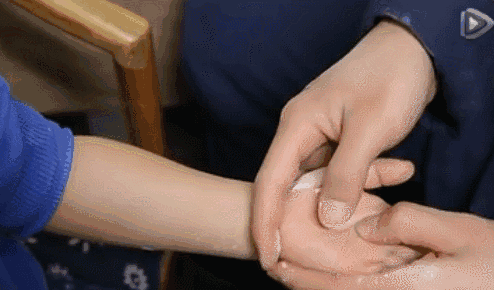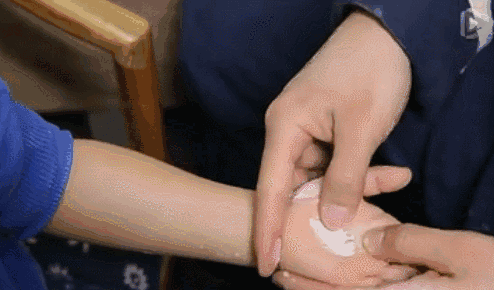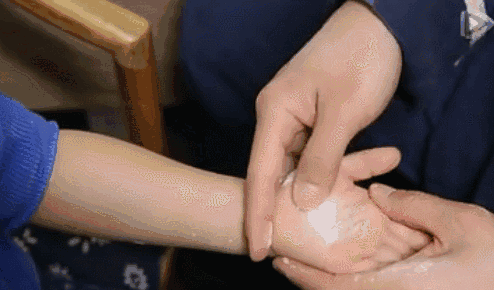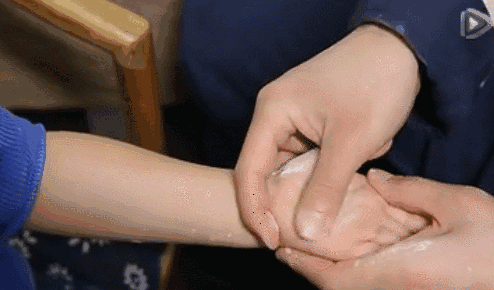
3. Qia Wu Zhi Jie (Pinching the Five Finger Joints), a common technique used after a baby is frightened.

4. Rou Yong Quan (Kneading the Yongquan Point), used for headaches, fever, vomiting, and diarrhea, to tonify kidney qi.

5. Diao Xiao Tian Xin (Pounding the Little Heavenly Heart), used for clearing heat and calming fright, applicable for convulsions, agitation, and restlessness.

6. Ping Gan Qing Fei (Smoothing the Liver and Clearing the Lungs), used for respiratory tract external pathogens.

7. Shun Shi Zhen Mo (Clockwise Abdominal Massage), used for constipation, food stagnation, and internal heat.

8. Na Feng Chi (Grasping the Wind Pool), used for colds, sweating, headaches, and fever.

9. Tui Liu Fu (Pushing the Six Fu Organs), used for high fever, cooling blood, and detoxification.
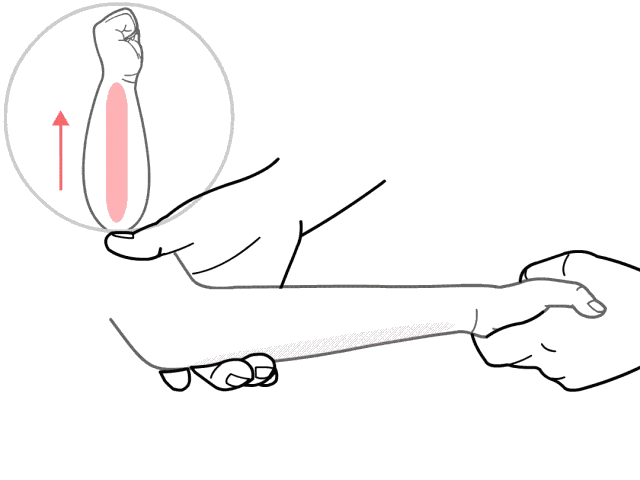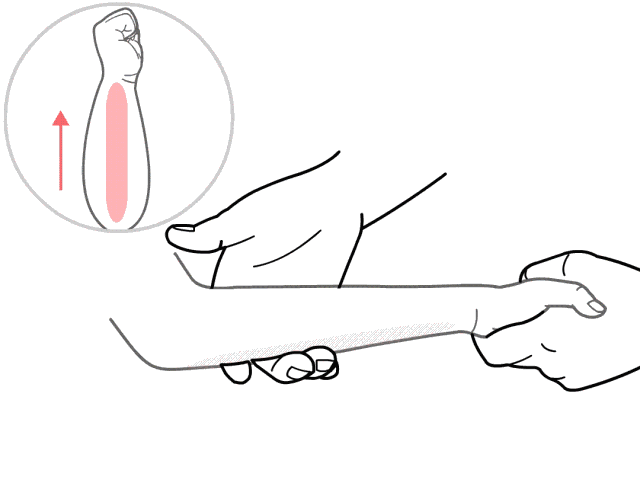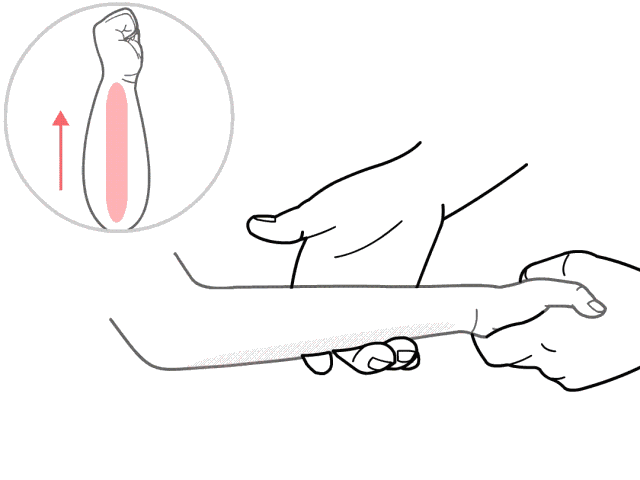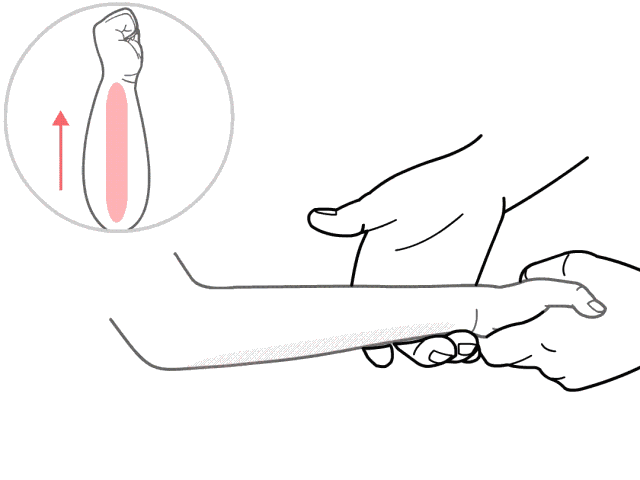
10. Nie Ji Da Zhui (Pinching the Great Vertebra), used for colds and fever.
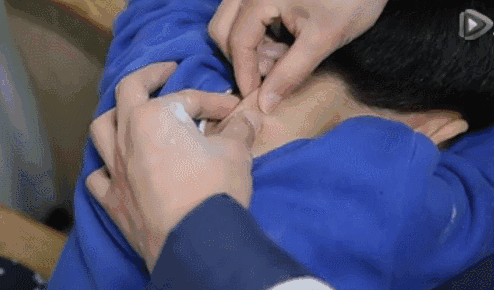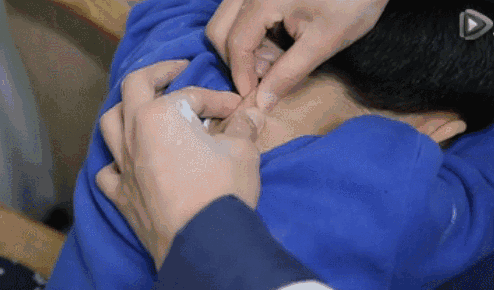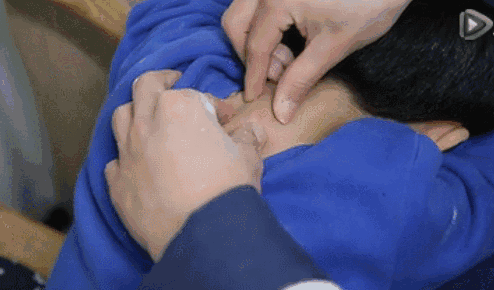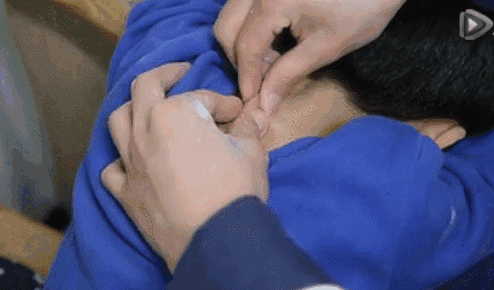
11. Fen Shou Yin Yang (Separating Yin and Yang of the Hands), used to regulate the balance of yin and yang, for mixed cold and heat, and persistent high fever.
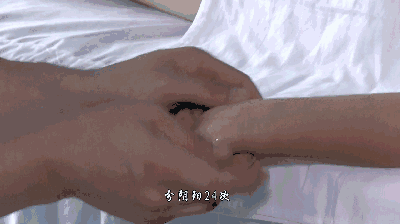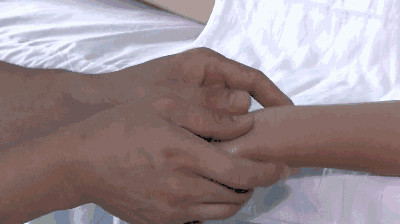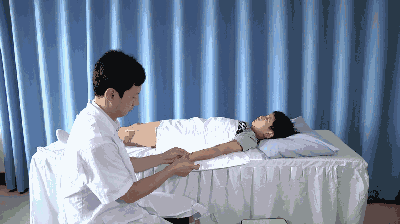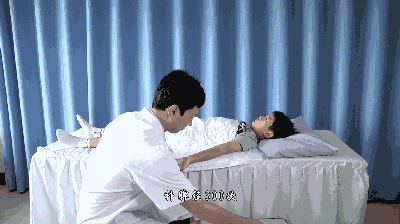
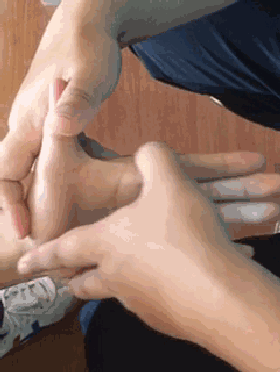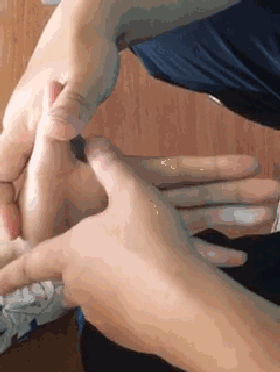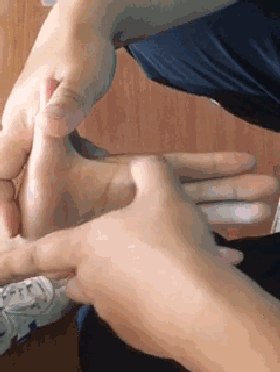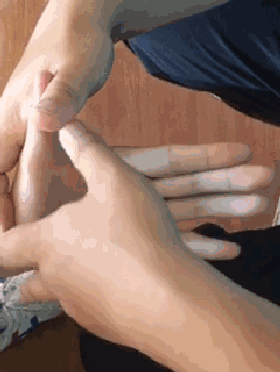
12. Qing Da Chang (Clearing the Large Intestine), used for constipation and food stagnation.
13. Qia Si Feng Xue (Pinching the Four Seam Points), used for anorexia and food stagnation.

14. Rou Fei Yu (Kneading the Lung Shu Point), used for pneumonia and cough.

15. Xia Tui Qi Jie Gu (Pushing Down the Seven Vertebrae), used for constipation and food stagnation.

16. Na Jian Jing (Grasping the Shoulder Well), used for colds and fright.
17. Fen Fu Yin Yang (Separating Yin and Yang of the Abdomen), used for diarrhea, food stagnation, and other digestive system diseases.
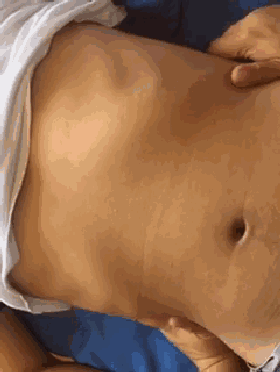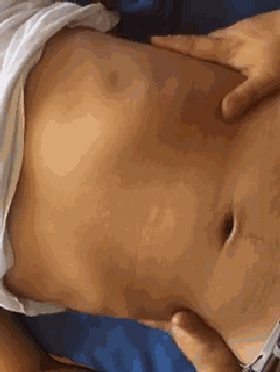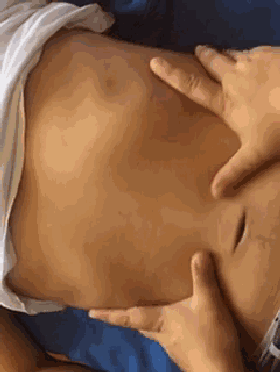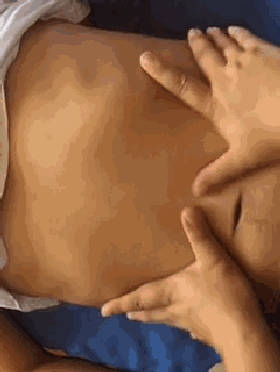
18. Heng Ca Si Heng Wen (Horizontal Rubbing of the Four Horizontal Lines), used for dry cough, light cough, or the initial stage of cough.
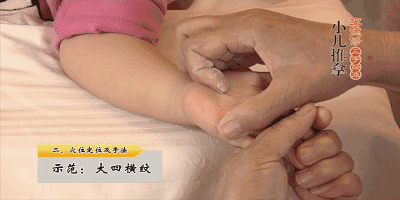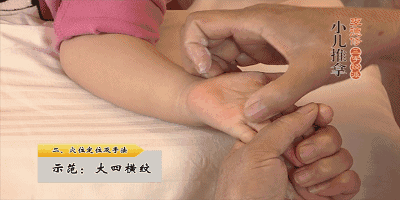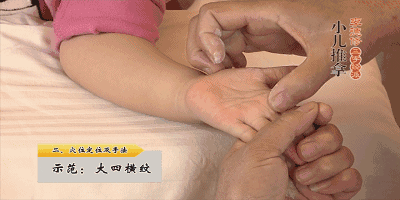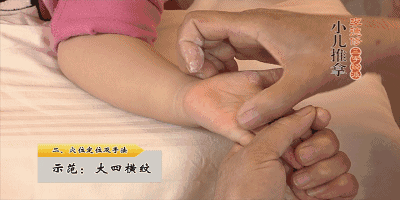
19. Rou Ban Men (Kneading the Ban Men Point), Ban Men is the gate of the spleen and stomach, can open the Sanjiao, clear both deficiency heat and excess heat, treating vomiting and diarrhea, and abdominal pain.

20. Rou Zu San Li (Kneading the Zu San Li Point), used for spleen and stomach diseases, often kneading Zu San Li is better than eating old hen; Zu San Li is a health point for the spleen and stomach.

21. Qing Tian He Shui (Clearing the Tian He Water), used for low fever and heat in the heart.
When the baby shows signs of discomfort, parents need not worry. At this time, simple pediatric Tuina techniques can be used to relieve the baby’s discomfort.
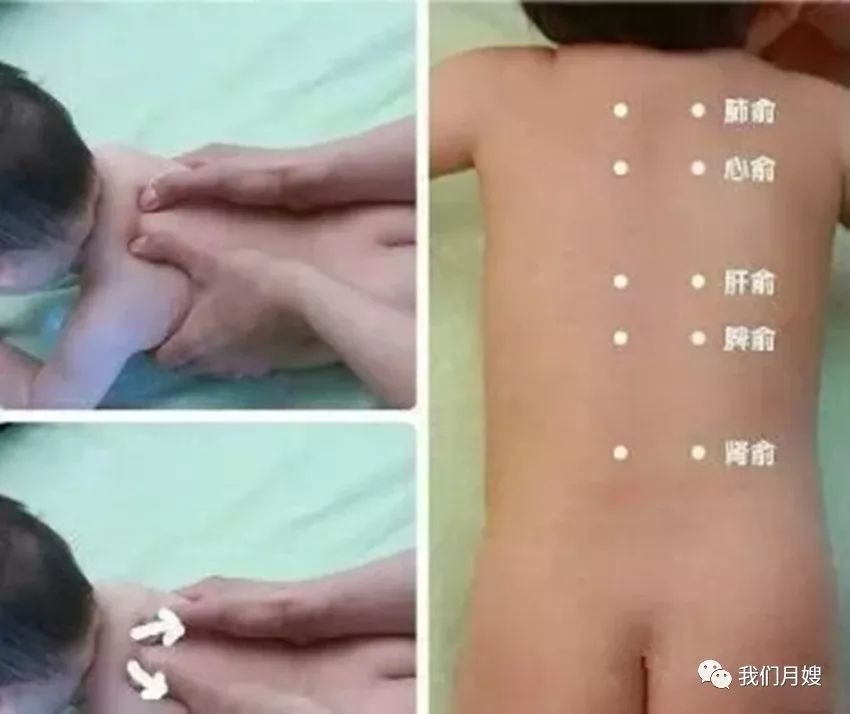
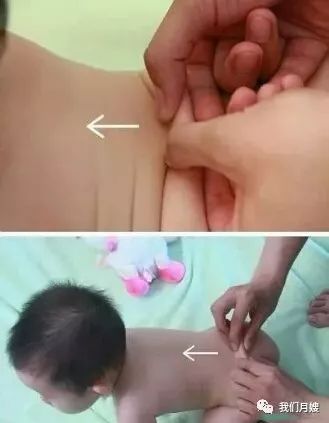
Lung Shu
[Location] Below the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra (between the 3rd and 4th thoracic vertebrae), 1.5 inches lateral, belonging to the Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian.
[Operation] Use both thumbs or the index and middle fingers to knead both sides of the Lung Shu point, called kneading the Lung Shu; use both thumbs to push down from the inner edges of the scapula 100 times, called separating the Lung Shu, or separating the scapula.
[Function] Benefits the lungs, regulates qi, stops cough, and transforms phlegm.
[Indications] Fever, cough, and all respiratory diseases.
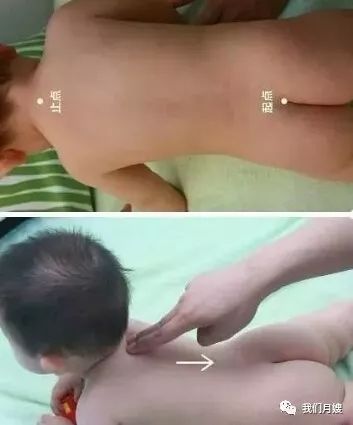
Spine
[Location] A straight line from Dazhui to Changqiang.
[Operation] Push straight down from top to bottom, called pushing the spine; use pinching from bottom to top, called pinching the spine. Pinch 3-5 times, and after every 3 pinches, lift the skin of the back once, called the three pinches and one lift method.
[Function] Regulates yin and yang, qi and blood, harmonizes the organs, opens the meridians, and cultivates the original qi, having a strengthening effect on the body.
[Indications] Fever, fright, night crying, malnutrition, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, etc.
Tian Shu
[Location] 2 inches (about one finger) beside the navel, one on each side.
[Operation] Use the index and middle fingers to press on both sides of the Tian Shu point, gently kneading 50-100 times.
[Function] Tian Shu is the gathering point of the large intestine, capable of guiding the large intestine and regulating qi to eliminate stagnation. Clinically used to treat digestive system diseases.
[Indications] Diarrhea, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, and digestive dysfunction.
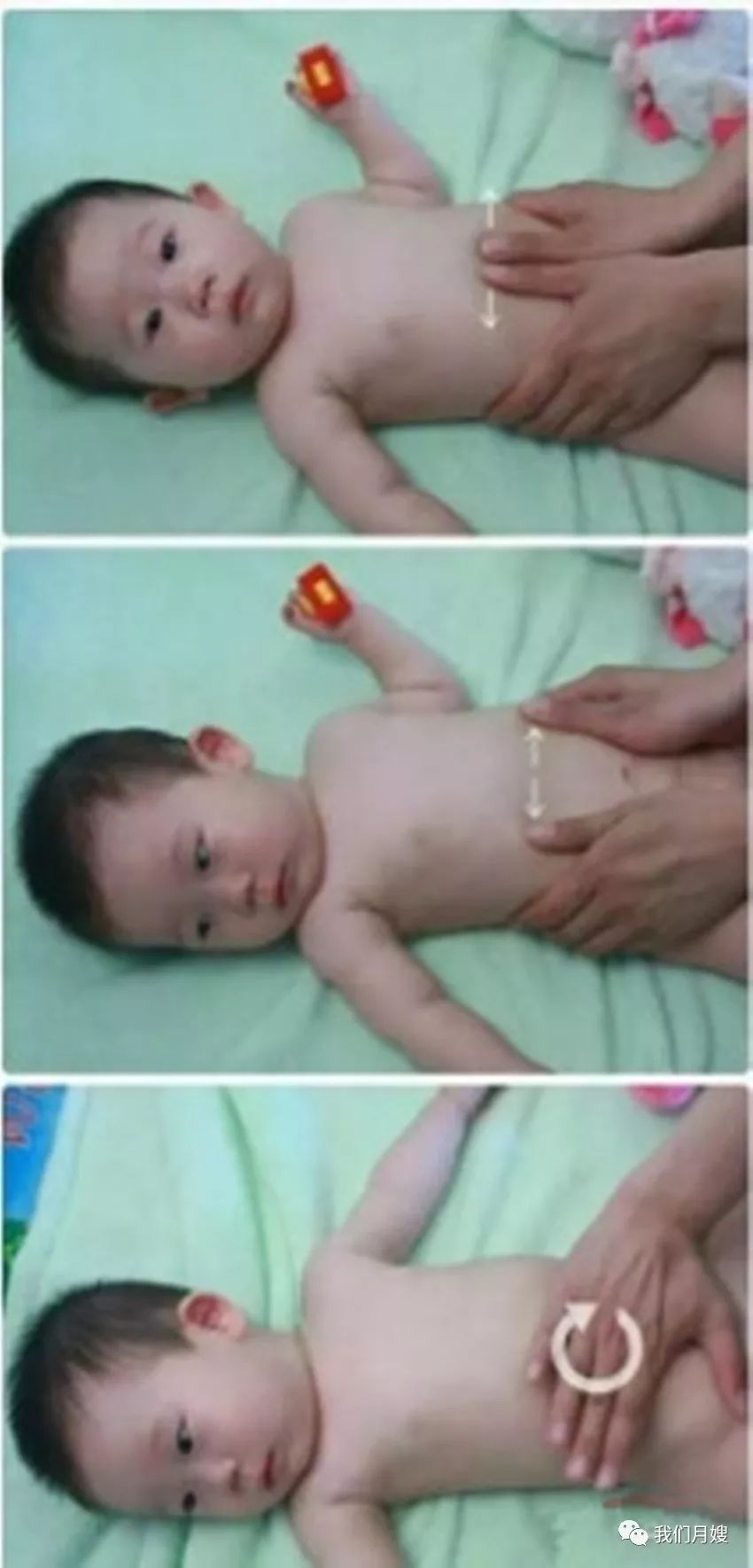
Abdominal Yin Yang
[Alias] Abdomen.
[Location] In the soft flesh below the middle point between the Zhongwan point and the two sides.
[Operation] Push along the edge of the rib arch or from Zhongwan to the navel, separating to both sides, called separating the abdominal yin and yang; rubbing with the palm or four fingers is called rubbing the abdomen.
[Function] Strengthens the spleen and stomach, regulates qi, and aids digestion.
[Indications] Abdominal pain, abdominal distension, borborygmi, etc. Clockwise abdominal massage can relieve constipation, while counterclockwise can stop diarrhea.
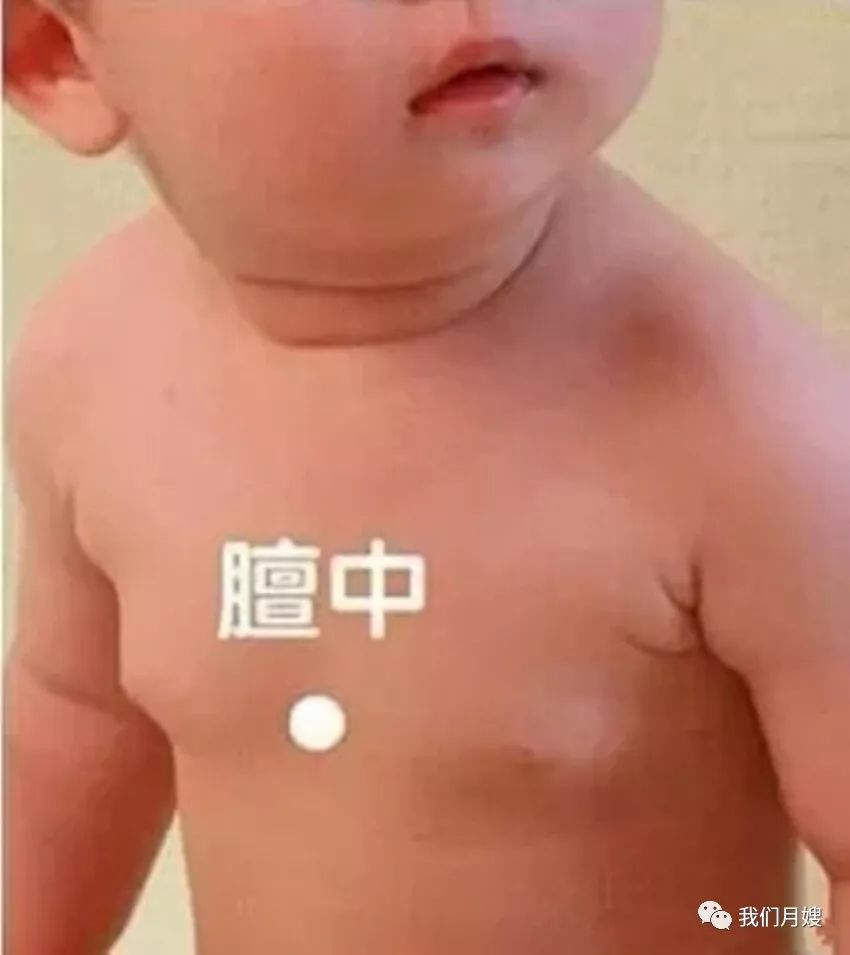
Dan Zhong
[Location] In the center of the line connecting the two nipples on the sternum, belonging to the Ren Meridian.
[Operation] Knead with the tip of the middle finger, called kneading Dan Zhong; use both thumbs to push from the point outward to the sides until reaching the nipples, called separating Dan Zhong.
[Function] Dan Zhong is the meeting point of qi, located in the chest; pushing and kneading Dan Zhong can widen the chest, regulate qi, and stop cough and transform phlegm.
[Indications] Chest tightness, vomiting, qi counterflow, cough, phlegm sounds, etc.
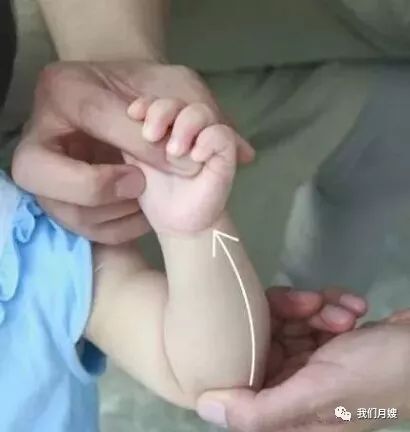
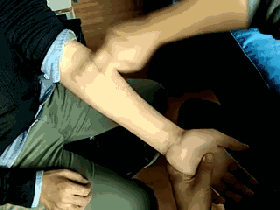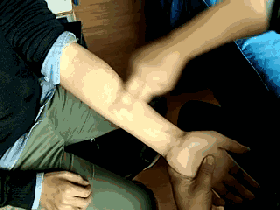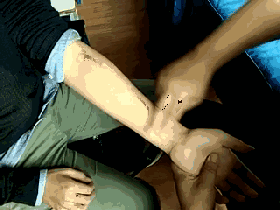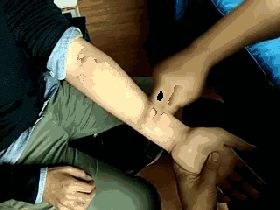
Tui Liu Fu
[Location] On the ulnar side of the forearm, a straight line from the elbow joint to the wrist crease.
[Operation] Use the thumb or index and middle fingers to push from the elbow towards the wrist, called Tui Liu Fu or pushing the six Fu organs.
[Function] Clears heat, cools blood, and detoxifies.
[Indications] All heat syndromes, high fever, thirst, fright, sore throat, oral thrush (white spots on the tongue resembling a goose’s mouth), mumps, and dry stools.

Yi Wo Feng
[Alias] External Yi Wo Feng.
[Location] On the back of the wrist, at the center of the wrist crease.
[Operation] Knead with the fingertips, called kneading Yi Wo Feng.
[Function] Kneading Yi Wo Feng can warm the middle, move qi, stop pain, and benefit the joints.
[Indications] All abdominal pain, colds, joint pain, acute and chronic fright.

Nei Lao Gong
[Location] In the center of the palm, at the point where the middle and ring fingers point when making a fist.
[Operation] Knead with the middle finger, called kneading Lao Gong. Knead 100-200 times.
[Function] Kneading the left induces sweating, while kneading the right drains heart fire and alleviates restlessness.
[Indications] Fever, thirst, mouth sores, gum erosion, internal heat, etc.
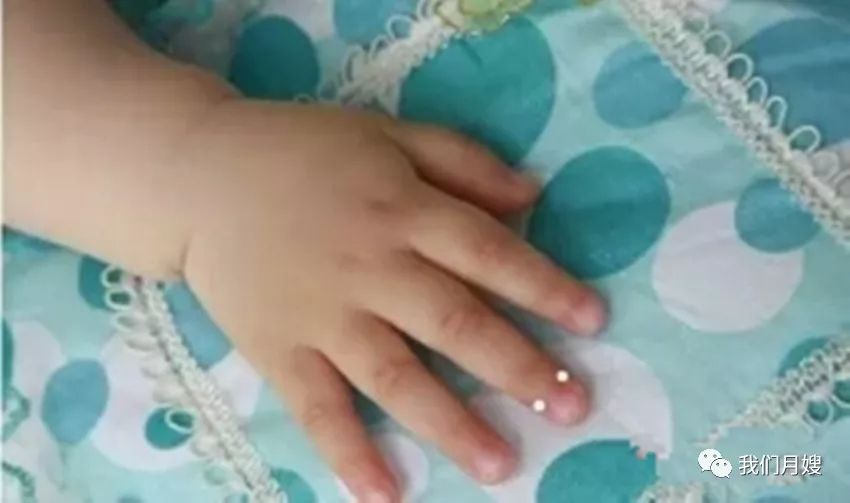

Duan Zheng
[Location] On both sides of the root of the middle finger nail, the radial side is called left Duan Zheng, and the ulnar side is called right Duan Zheng.
[Operation] Pinch with the thumb nail or knead with the thumb pad, called pinching or kneading Duan Zheng.
[Function] Pinching the right Duan Zheng treats vomiting and nosebleeds; pinching the left Duan Zheng has a lifting effect, mainly used for watery diarrhea and dysentery.
[Indications] Nosebleeds, fright, vomiting, diarrhea, dysentery.
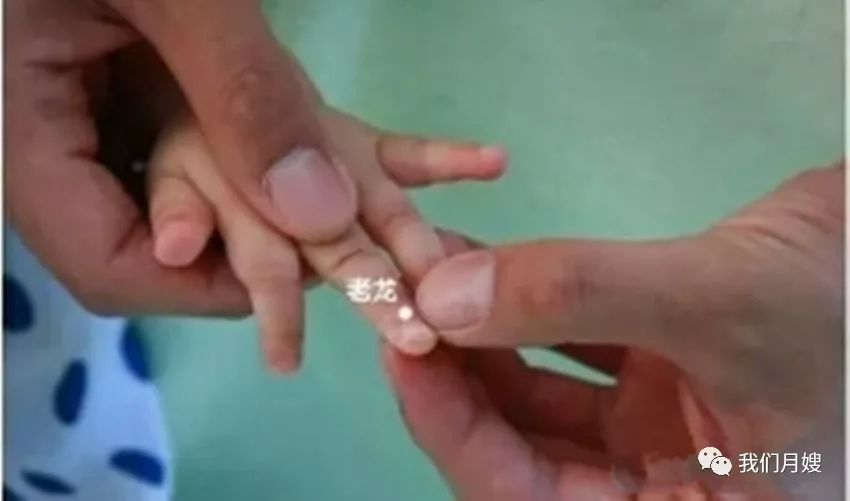
Lao Long
[Location] One fen below the center of the nail root of the middle finger.
[Operation] Pinch with the thumb nail, called pinching Lao Long.
[Function] Opens the orifices and awakens the spirit, reduces fever.
[Indications] Sudden fainting, exhaustion, qi closure, heart fire excess heat, acute fright.
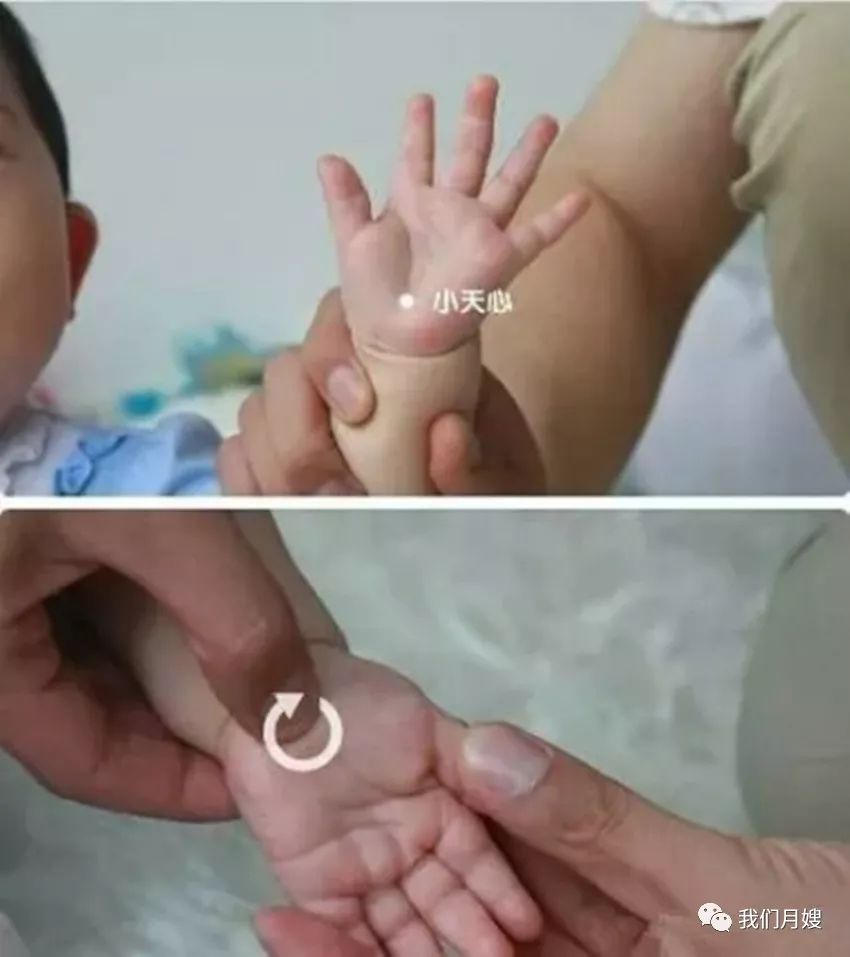
Xiao Tian Xin
[Alias] Fish Joint Intersection.
[Location] In the depression at the junction of the large and small fish joints.
[Operation] Knead with the fingertip, called kneading Xiao Tian Xin; pinch with the thumb nail, called pinching Xiao Tian Xin; pound with the tip of the middle finger or the bent interphalangeal joint, called pounding Xiao Tian Xin.
[Function] Kneading can clear heat and calm fright, promote urination, and brighten the eyes; pinching and pounding can calm the spirit and settle fright.
[Indications] Fright, convulsions, agitation, night crying, red and painful urination, red and swollen eyes, and unexpressed rashes.
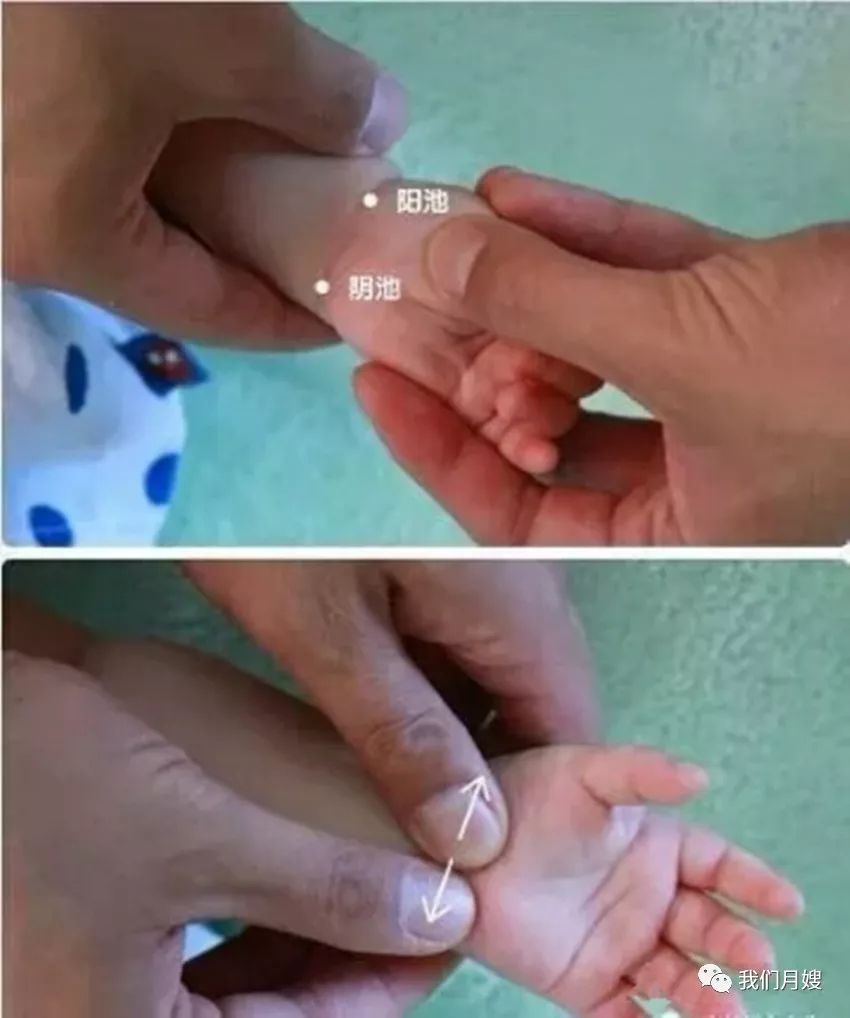
Shou Yin Yang
[Location] On the palm side of the wrist crease, also known as the Great Horizontal Line. The radial side (thumb side) is Yang Chi, and the ulnar side (little finger side) is Yin Chi.
[Operation] Both thumbs push from the center of the palm side wrist crease (Zong Jin point) to both sides, called separating the Great Horizontal Line, also known as separating the hands’ yin and yang.
[Function] Balances yin and yang, harmonizes qi and blood, and promotes digestion.
[Indications] Alternating cold and heat, abdominal distension, diarrhea, vomiting, food accumulation, and agitation.
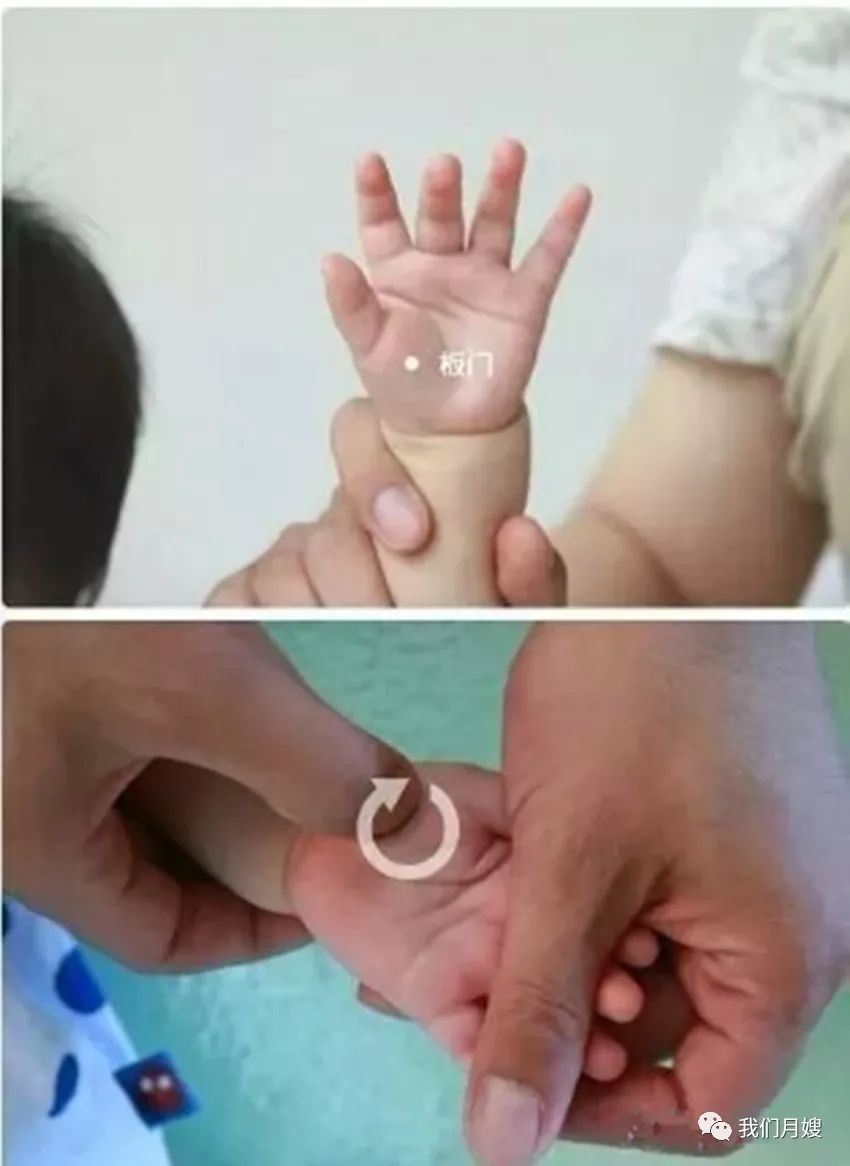
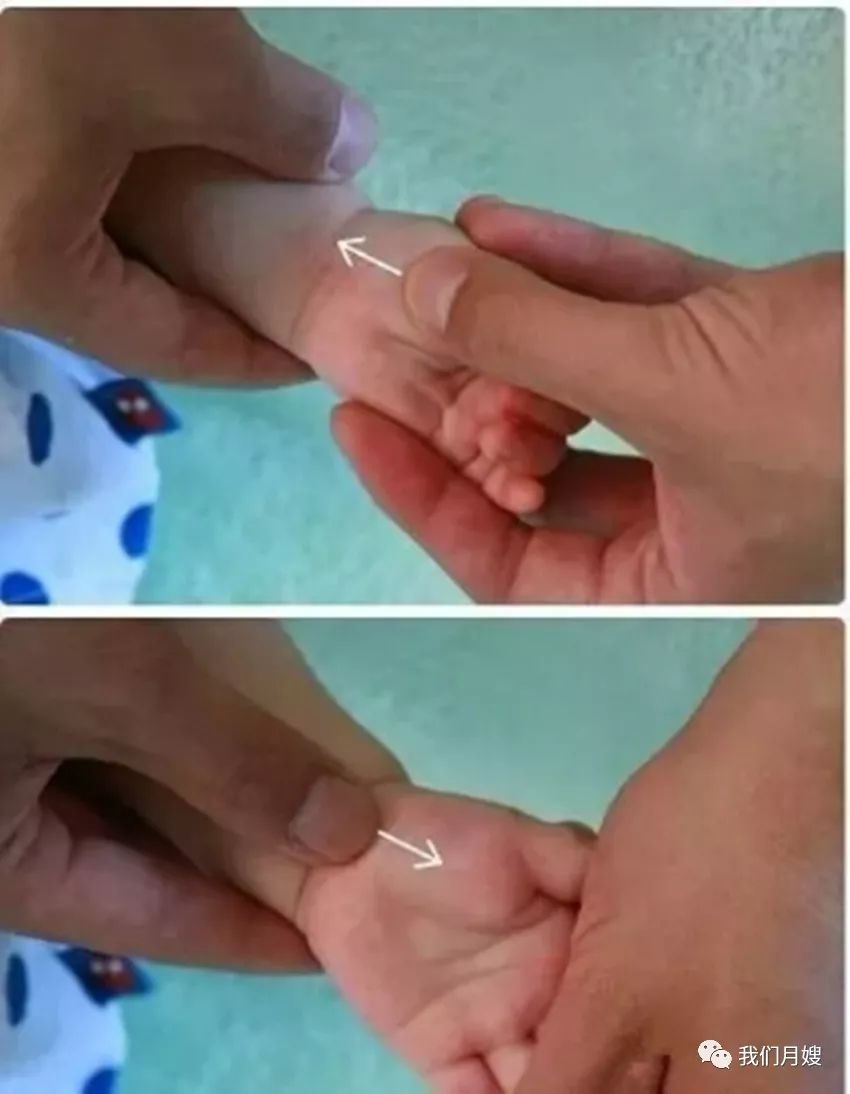
Ban Men
[Location] On the palm surface at the level of the large fish joint.
[Operation] Knead Ban Men with the thumb, which can be done clockwise or counterclockwise. Pushing from the wrist crease towards the base of the thumb is called pushing the horizontal line towards Ban Men, which can stop vomiting. Conversely, pushing from Ban Men towards the horizontal line can stop diarrhea.
[Function] Strengthens the spleen and stomach, aids digestion, and eliminates stagnation. Treats food stagnation, poor appetite.
[Indications] Food accumulation, abdominal distension, poor appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and dampness.
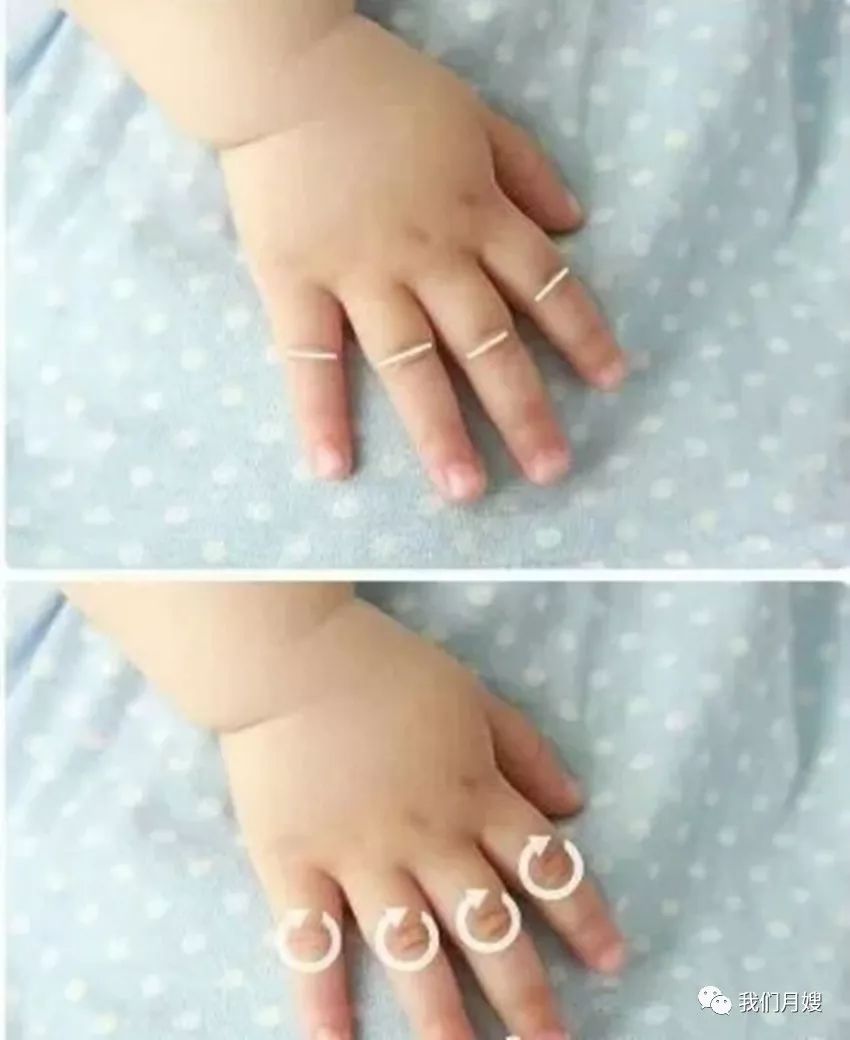
Wu Zhi Jie
[Location] On the back of the hand, at the first interphalangeal joint of the five fingers.
[Operation] Pinch with the thumb nail, called pinching Wu Zhi Jie, pinch 5-20 times; rub with the thumb and index finger, called rubbing Wu Zhi Jie, rub 100-200 times.
[Function] Pinching or rubbing Wu Zhi Jie can calm fright and settle the spirit, dispel wind-phlegm, and open the orifices; pinching Wu Zhi Jie is mainly used for agitation.
[Indications] Fright, agitation, convulsions, cough with phlegm, abdominal pain, etc.
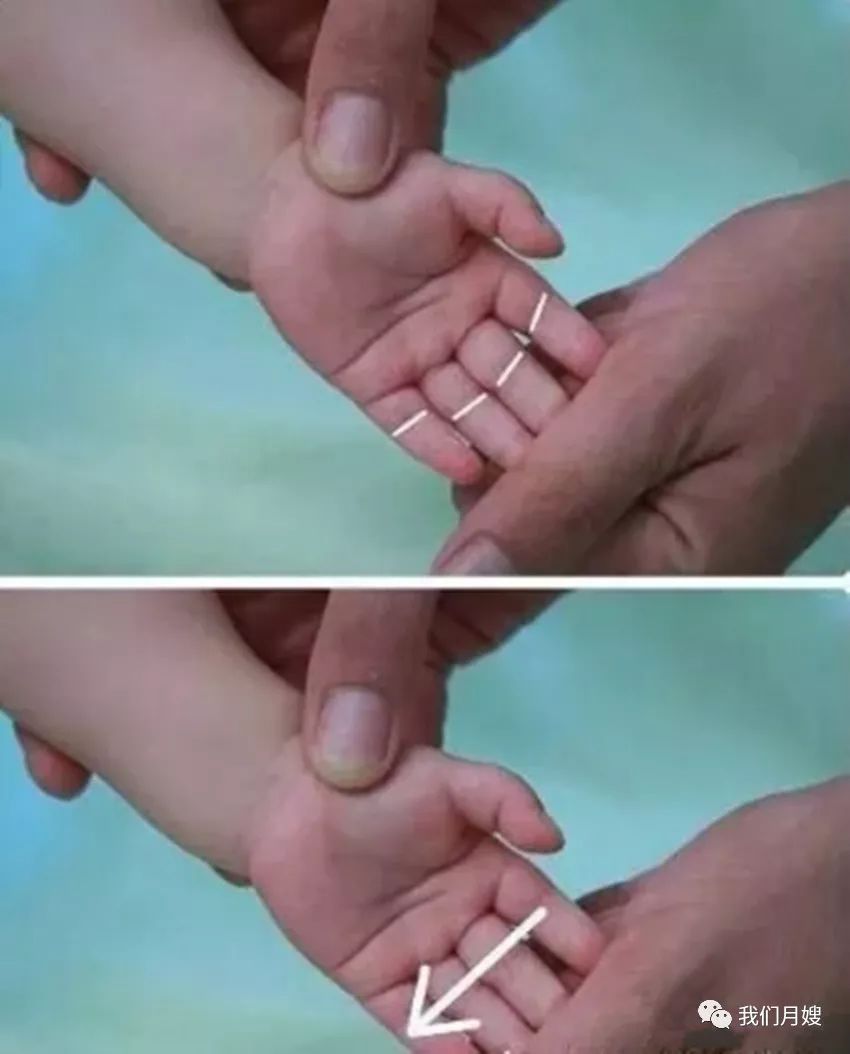
Si Heng Wen (Four Horizontal Lines)
[Location] On the palm surface, at the horizontal lines of the first interphalangeal joints of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers.
[Operation] Gather the four fingers together and push from the index finger’s horizontal line towards the little finger’s horizontal line, called pushing the four horizontal lines. Pinching with the thumb nail is called pinching the four horizontal lines.
[Function] Reduces fever and agitation, disperses stagnation, and harmonizes qi and blood. Treats abdominal distension, malnutrition, and loss of appetite.
[Indications] Abdominal distension, malnutrition, and digestive disorders.
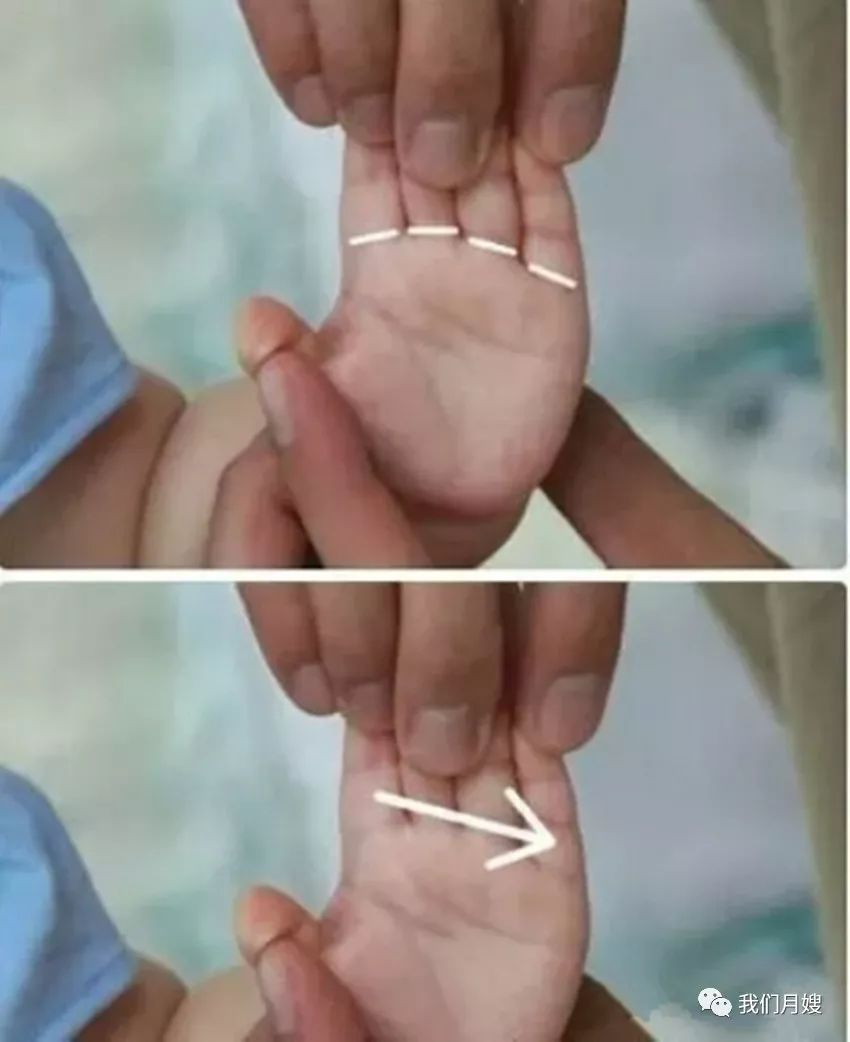
Xiao Heng Wen
[Location] At the horizontal lines of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers’ metacarpophalangeal joints.
[Operation] Pinch with the thumb nail, called pinching Xiao Heng Wen; push with the thumb, called pushing Xiao Heng Wen.
[Function] Opens the chest, disperses stagnation, and transforms phlegm.
[Indications] Bronchitis, whooping cough, pneumonia, and all respiratory diseases.
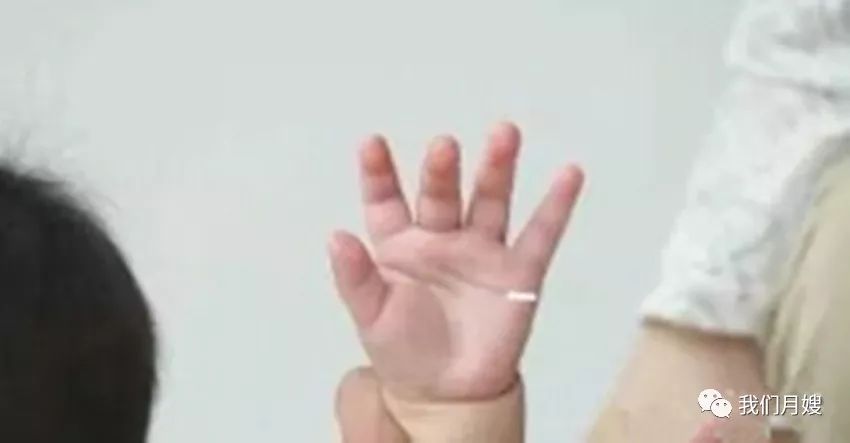

Zhang Xiao Heng Wen
[Location] At the base of the little finger, on the ulnar side of the palm.
[Operation] Knead with the middle or index finger, called kneading Zhang Xiao Heng Wen.
[Times] 100-500 times.
[Function] Clears heat, disperses stagnation, and transforms phlegm to stop cough.
[Indications] Commonly used for phlegm-heat cough, mouth and tongue sores, sudden cough, and drooling, effective for infants with severe drooling.
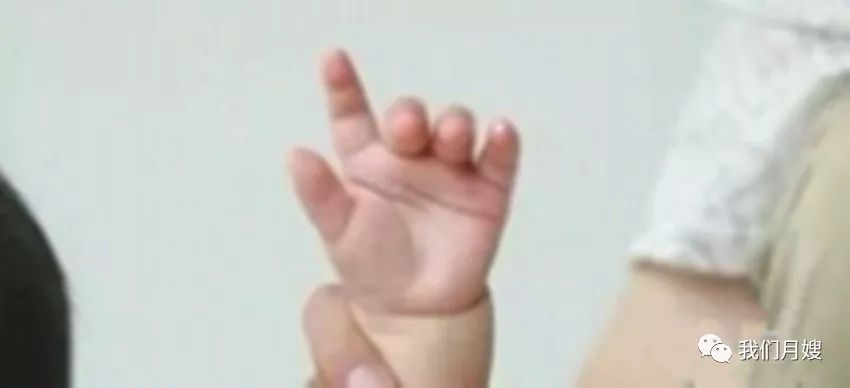
Shen Ding
[Location] At the tip of the little finger.
[Operation] Knead with the index or thumb tip, called kneading Shen Ding.
[Function] Kneading Shen Ding can consolidate kidney qi and stabilize the exterior to stop sweating.
[Indications] Spontaneous sweating or night sweats, and cranial closure (indicating whether the fontanelle is open or closed).
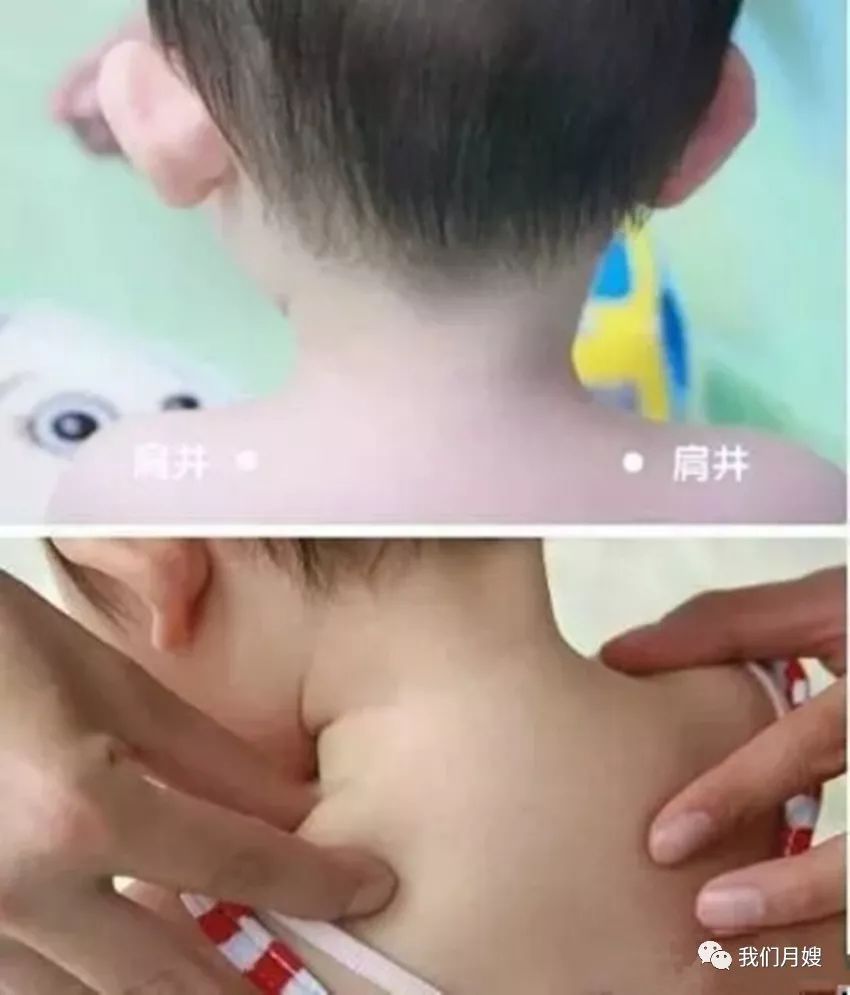
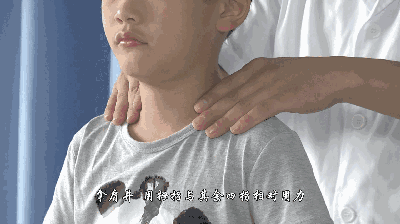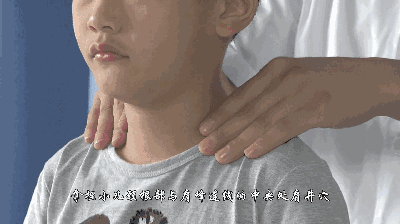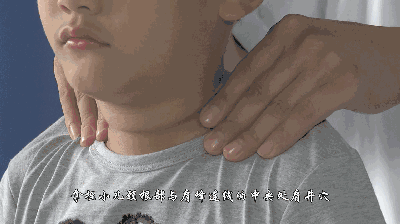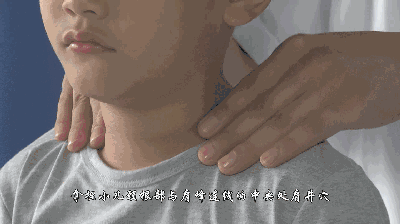
Jian Jing
[Location] At the midpoint of the line connecting Dazhui and the acromion, in the shoulder muscle area, belonging to the Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian.
[Operation] Use the thumb and index and middle fingers symmetrically to lift Jian Jing, called lifting Jian Jing, generally lifting 5 times; press on Jian Jing with the fingertip, called pressing Jian Jing, generally pressing for two minutes.
[Function] Induces sweating, releases the exterior, and tonifies qi and blood.
[Indications] Colds, fainting, and limited upper limb movement.
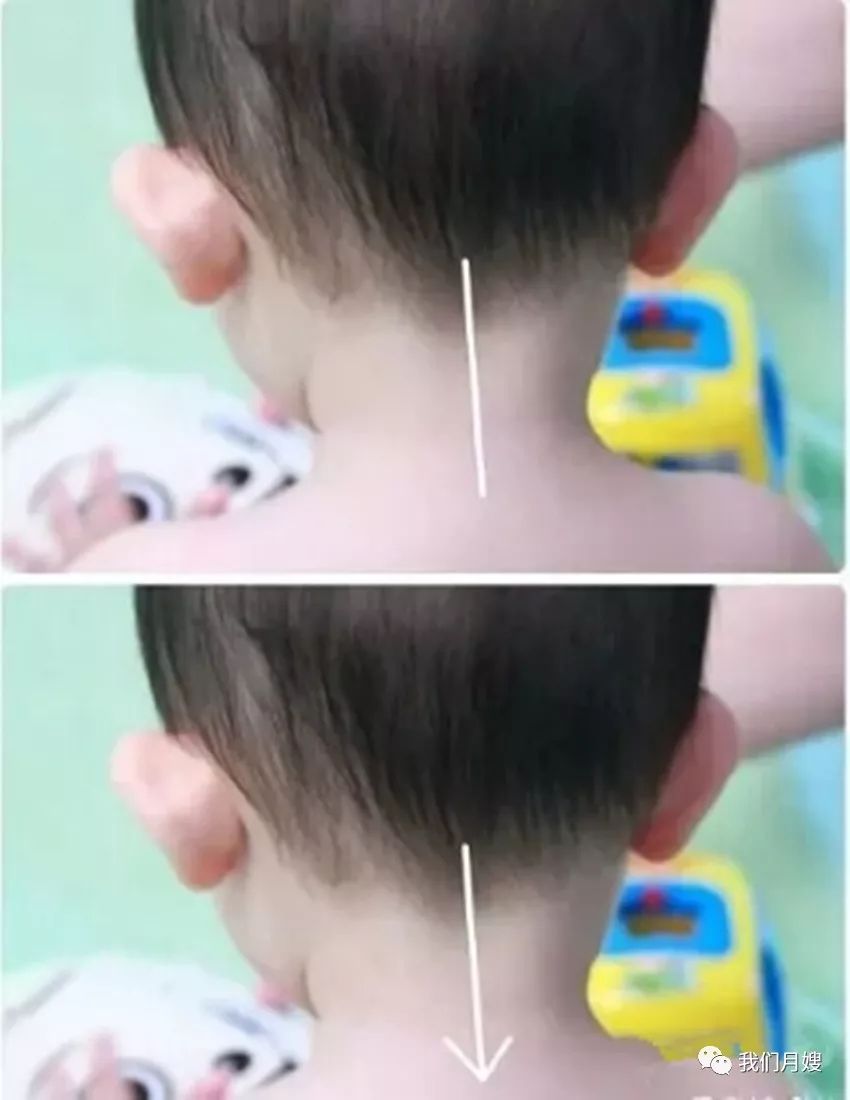
Tian Zhu Gu
[Location] A straight line from the hairline at the back of the neck to the Dazhui point.
[Operation] Use the thumb or index and middle fingers to push straight down, called pushing Tian Zhu; or scrape from top to bottom with a spoon dipped in water.
[Function] Stops nausea, dispels wind, and scatters cold.
[Indications] Nausea, stiff neck, fever, fright, sore throat, etc.
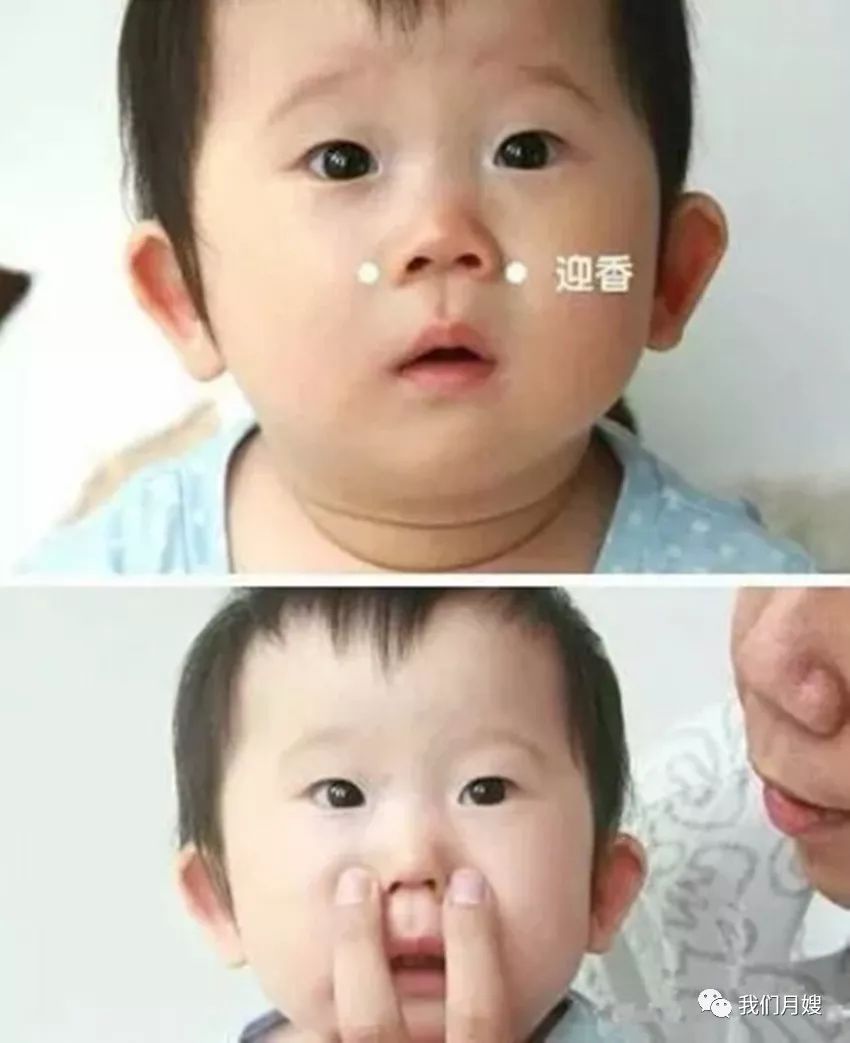
Ying Xiang
[Location] Five fen beside the nostrils, in the nasolabial groove.
[Operation] Knead with the index and middle fingers, called kneading Ying Xiang.
[Function] When the nose is blocked and unable to smell, pressing it can open the nasal passages, allowing scents to be detected, hence the name Ying Xiang.
[Indications] Nasal congestion and runny nose.