Obesity is a problem that troubles a significant portion of the population today, especially among women. Previously, we discussed acupuncture methods for weight loss, but many people report that it takes courage to endure needles. Moreover, there are many methods available for weight loss, and acupuncture is not the only option. Today, we will discuss another method that is generally more acceptable—zou guan (walking cupping).
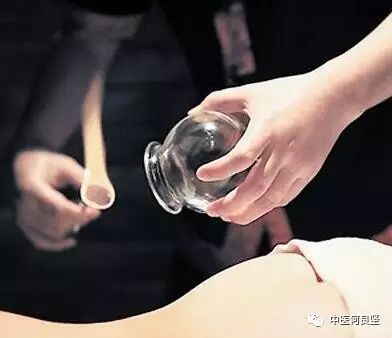
Zou guan, also known as you zou guan (moving cupping), is a type of cupping therapy in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that contrasts with xi ding guan (static cupping). Many people are familiar with cupping, often seeing men with bare backs or women in backless outfits displaying dark circular marks on their arms or backs during hot summer days. If you haven’t noticed, the black marks on swimmer Michael Phelps during the Olympics certainly left a deep impression, right? These are the marks left by static cupping, which typically fade within about a week.
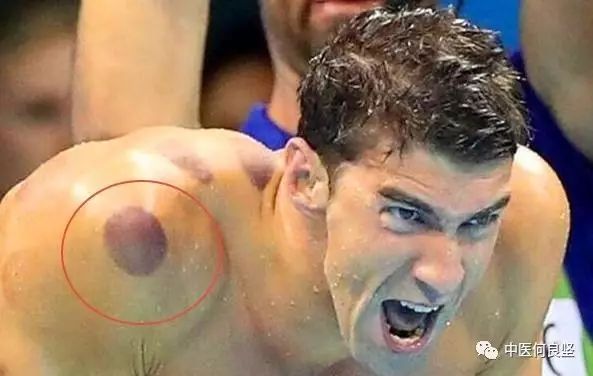
(Static cupping leaves marks that generally fade within a week)
In contrast, zou guan typically only causes temporary redness and warmth in the local skin without leaving marks that affect appearance.
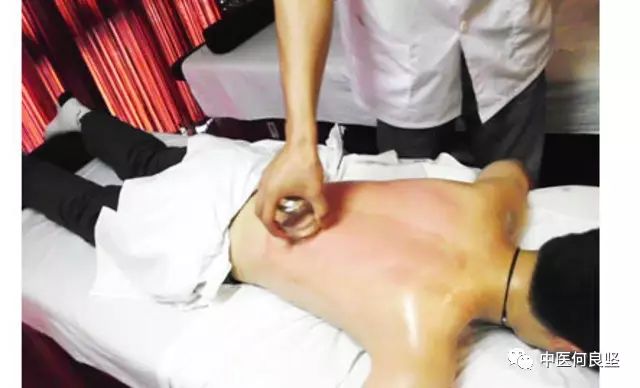
(Zou guan only leaves slight redness that easily fades)
The Medical Principles of Zou Guan for Weight Loss
From a Western medical perspective, the principles of moving cupping are as follows:
1. The strong suction force during cupping fully opens the sweat pores, stimulating the functions of sweat glands and sebaceous glands, leading to the shedding of aging skin cells and accelerating the expulsion of toxins and waste from the body.
2. It can also adjust endocrine functions and accelerate blood and lymph circulation.
3. It promotes gastrointestinal peristalsis, thereby improving digestive function and speeding up metabolism.
4. It increases heat production and fat consumption, reducing both superficial and deep-seated excess fat.
From a Traditional Chinese Medicine perspective, obesity often falls under the category of tan shi (phlegm-dampness). My treatment approach generally focuses on the pi (spleen) and dai mai (girdle vessel). TCM believes that the spleen’s function is to transport and transform water and dampness; if the spleen’s function is impaired, dampness cannot be transformed. The dai mai encircles the waist like a belt; if it is obstructed, dampness accumulates in the waist and abdomen, leading to abdominal obesity. Zou guan can help clear the meridians and strengthen the spleen to eliminate dampness, allowing qi and blood to flow, thus dispersing phlegm-dampness. Additionally, phlegm-dampness is cold in nature, and TCM principles state that “to treat phlegm and fluids, one should use warming herbs,” so combining it with warming ai jiu (moxibustion) to warm the meridians can yield even better results.

Advantages of Zou Guan for Weight Loss
The method of zou guan for weight loss differs from medications, which typically have a limited duration of effect. Zou guan works by adjusting the patient’s internal functions, thus its effects are generally sustained even after treatment stops, meaning weight regain is less likely. In other words, weight loss through zou guan typically does not rebound.
Indications for Zou Guan Weight Loss
Zou guan therapy is effective for obesity caused by endocrine disorders, simple obesity, etc., quickly reducing excess fat, tightening the skin without sagging or wrinkles, and without affecting overall health. Zou guan is suitable for those who have been ineffective in long-term weight loss efforts or have failed with medications, offering advantages such as no need for dieting, no intense exercise, and no surgical pain.
Method of Zou Guan
On the skin of the area to be treated, apply a layer of cupping oil, moxibustion oil, or petroleum jelly as a lubricant. Then, using the flash fire method, apply the cup to the selected area of skin. The suction strength should be moderate, starting small and gradually increasing. If the suction is too strong, the cup will be difficult to move or may cause pain; if too weak, it will not be effective. The practitioner should hold the cup with the right hand or support and stretch the skin with the left hand, moving it up and down, side to side, or in a circular motion along the meridians.
(Video of abdominal zou guan)
Precautions for Zou Guan Weight Loss
1. Individuals with anemia or heart disease should not undergo zou guan for weight loss.
2. Those with skin allergies, rashes, or eczema should avoid zou guan for weight loss.
3. Women should not undergo zou guan during menstruation.
4. Individuals with colds or diarrhea should not undergo zou guan for weight loss.
5. Those who are overly fatigued should avoid zou guan for weight loss.
6. The duration of zou guan should not exceed 10 minutes to avoid damaging the meridians and skin.
7. Zou guan tends to disperse qi; for individuals with a weak constitution, it is recommended to follow up with moxibustion to support the body and achieve the effect of warming and transforming cold dampness.
In conclusion, zou guan for weight loss requires selecting meridians and acupoints based on the patient’s constitution. Generally, local meridians and acupoints (areas of obesity) are chosen along with systemic regulating acupoints. It can also be combined with other therapies such as acupuncture, thread embedding, and auricular therapy for better results. Additionally, one should not relax dietary and exercise adjustments simply because they are undergoing zou guan or other TCM weight loss treatments. A healthy lifestyle, including appropriate exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, is also a crucial factor affecting weight loss efficacy.
Thank you for reading, and feel free to share this with those in need. Wishing you good health.
For more content, please long-press the following public account QR code to follow and view historical messages for more information.


