
In dermatology clinics, we use fire needling almost every day. Why is fire needling so widely applied in the treatment of skin diseases?
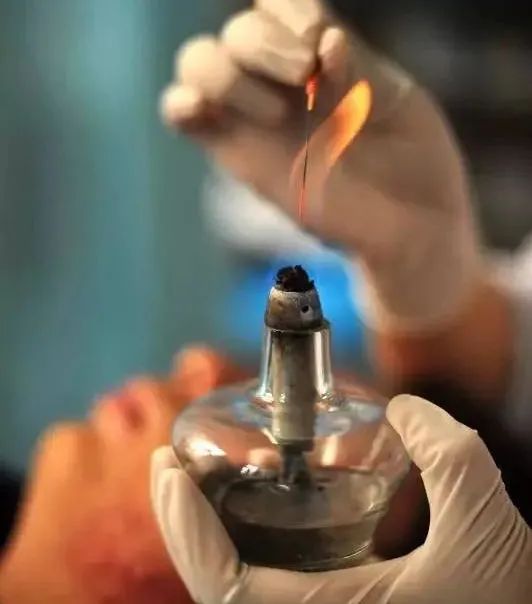

 ▲ First, we need to understand what fire needling is.Fire needling, also known as “white needling” or “burning needling,” involves heating a needle until it turns red and then quickly inserting the heated needle into acupuncture points or affected areas to treat diseases.
▲ First, we need to understand what fire needling is.Fire needling, also known as “white needling” or “burning needling,” involves heating a needle until it turns red and then quickly inserting the heated needle into acupuncture points or affected areas to treat diseases.


 ▲ What are the effects of fire needling?1. Fire needling directly punctures the affected area and reflex points, which can quickly eliminate or improve local tissue edema, congestion, exudation, adhesion, calcification, contraction, ischemia, and other pathological changes, thereby accelerating circulation, enhancing tissue metabolism, and promoting the recovery of damaged tissues and nerves. It also promotes the exudation of white blood cells and enhances their phagocytic function, helping to reduce inflammation;2. It can eliminate free radicals in the body, combat tissue oxidation, and promote the repair of inflamed tissues;3. It can increase the trace element content in damaged tissues and regulate peripheral blood white blood cell and platelet counts, achieving infection control.
▲ What are the effects of fire needling?1. Fire needling directly punctures the affected area and reflex points, which can quickly eliminate or improve local tissue edema, congestion, exudation, adhesion, calcification, contraction, ischemia, and other pathological changes, thereby accelerating circulation, enhancing tissue metabolism, and promoting the recovery of damaged tissues and nerves. It also promotes the exudation of white blood cells and enhances their phagocytic function, helping to reduce inflammation;2. It can eliminate free radicals in the body, combat tissue oxidation, and promote the repair of inflamed tissues;3. It can increase the trace element content in damaged tissues and regulate peripheral blood white blood cell and platelet counts, achieving infection control.


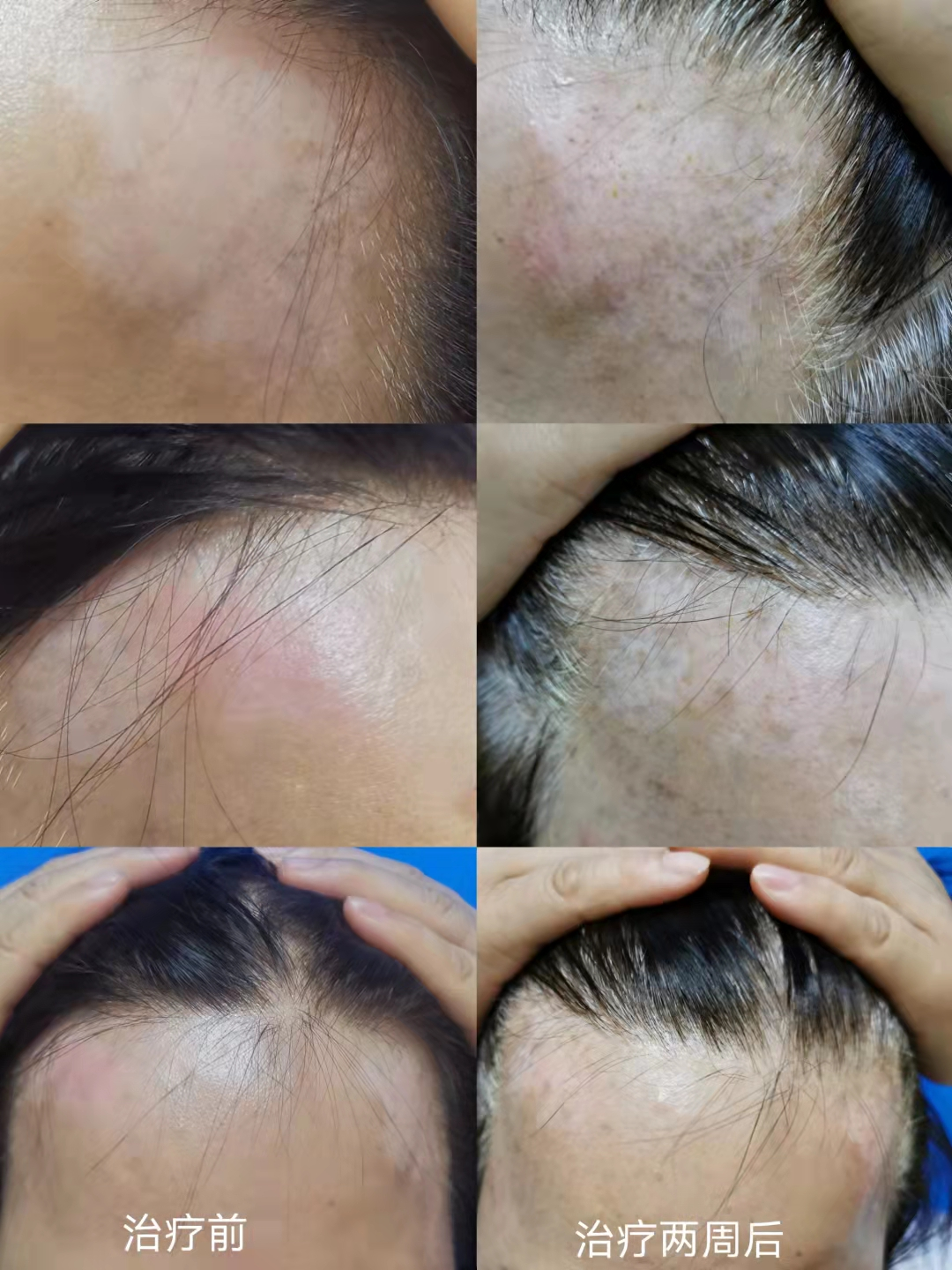
 ▲ What are the specific applications of fire needling in the treatment of skin diseases?1. Chronic EczemaPatients should take a comfortable position (such as supine, prone, or lateral), fully exposing the affected area, disinfecting with iodine or 75% ethanol, selecting the puncture points, holding an alcohol lamp in one hand, and using the thumb, index, and middle fingers of the other hand to hold the needle handle (if necessary, an assistant can hold the lamp while the practitioner operates with both hands, one hand on the local area and the other holding the needle). During needling, heat the needle tip until it turns red or white, quickly puncture the selected area, and then swiftly withdraw the needle. The depth of needling should be adjusted according to the thickness of the skin lesion.2. AcneAfter routine disinfection, select the puncture points at the center and base of the lesions, heat the needle tip until it turns white, quickly puncture the selected area, swiftly withdraw the needle, and then use a cotton swab to gently press and expel any debris or pus from the lesions. Treatment is performed 1-2 times a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.3. Herpes ZosterIn the acute phase, puncture the vesicular or non-vesicular lesions, clean the vesicular fluid with a cotton swab, ensure precise and shallow needling; if pain persists after the vesicles have receded, surround the painful area with needling, performing rapid local punctures. The depth of needling can be slightly deeper than before; if pain does not significantly alleviate, continue needling in the previously painful area after 2-3 days.4. VitiligoDisinfect the white patches with iodine, heat the needle tip until red, and quickly puncture the lesion area, lightly breaking the skin until the entire affected area is covered with needle points, ensuring that over 80% of the lesion is treated; if the lesion area is large or there are multiple lesions, needle in batches. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 10 weeks.
▲ What are the specific applications of fire needling in the treatment of skin diseases?1. Chronic EczemaPatients should take a comfortable position (such as supine, prone, or lateral), fully exposing the affected area, disinfecting with iodine or 75% ethanol, selecting the puncture points, holding an alcohol lamp in one hand, and using the thumb, index, and middle fingers of the other hand to hold the needle handle (if necessary, an assistant can hold the lamp while the practitioner operates with both hands, one hand on the local area and the other holding the needle). During needling, heat the needle tip until it turns red or white, quickly puncture the selected area, and then swiftly withdraw the needle. The depth of needling should be adjusted according to the thickness of the skin lesion.2. AcneAfter routine disinfection, select the puncture points at the center and base of the lesions, heat the needle tip until it turns white, quickly puncture the selected area, swiftly withdraw the needle, and then use a cotton swab to gently press and expel any debris or pus from the lesions. Treatment is performed 1-2 times a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.3. Herpes ZosterIn the acute phase, puncture the vesicular or non-vesicular lesions, clean the vesicular fluid with a cotton swab, ensure precise and shallow needling; if pain persists after the vesicles have receded, surround the painful area with needling, performing rapid local punctures. The depth of needling can be slightly deeper than before; if pain does not significantly alleviate, continue needling in the previously painful area after 2-3 days.4. VitiligoDisinfect the white patches with iodine, heat the needle tip until red, and quickly puncture the lesion area, lightly breaking the skin until the entire affected area is covered with needle points, ensuring that over 80% of the lesion is treated; if the lesion area is large or there are multiple lesions, needle in batches. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 10 weeks.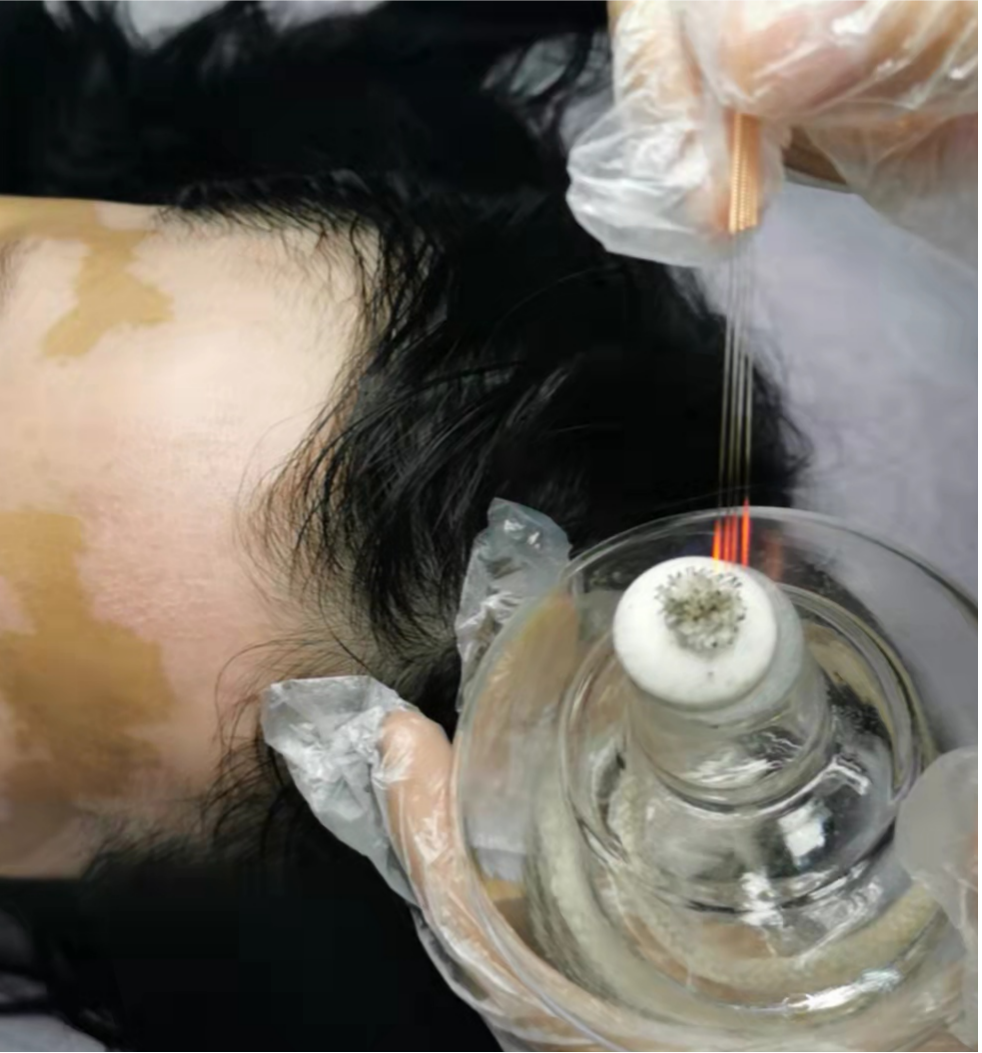
 5. Nodular Prurigo, FolliculitisDisinfect the lesion area, puncture the center of papules or small nodules; for hard nodules, use a 1ml syringe needle, heat it until red or white, and quickly puncture vertically into the lesion, ensuring the depth reaches just the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle. For larger nodules, perform surrounding punctures. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.6. Flat Warts, Common WartsAfter heating the needle tip until red, quickly puncture the top of the wart vertically; for small warts, one puncture is sufficient; for larger warts, 2-3 punctures are needed; the depth should just reach the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle. Generally, scabbing begins the next day, and the scab falls off after about a week. If the wart disappears after the scab falls off, treatment can be repeated.
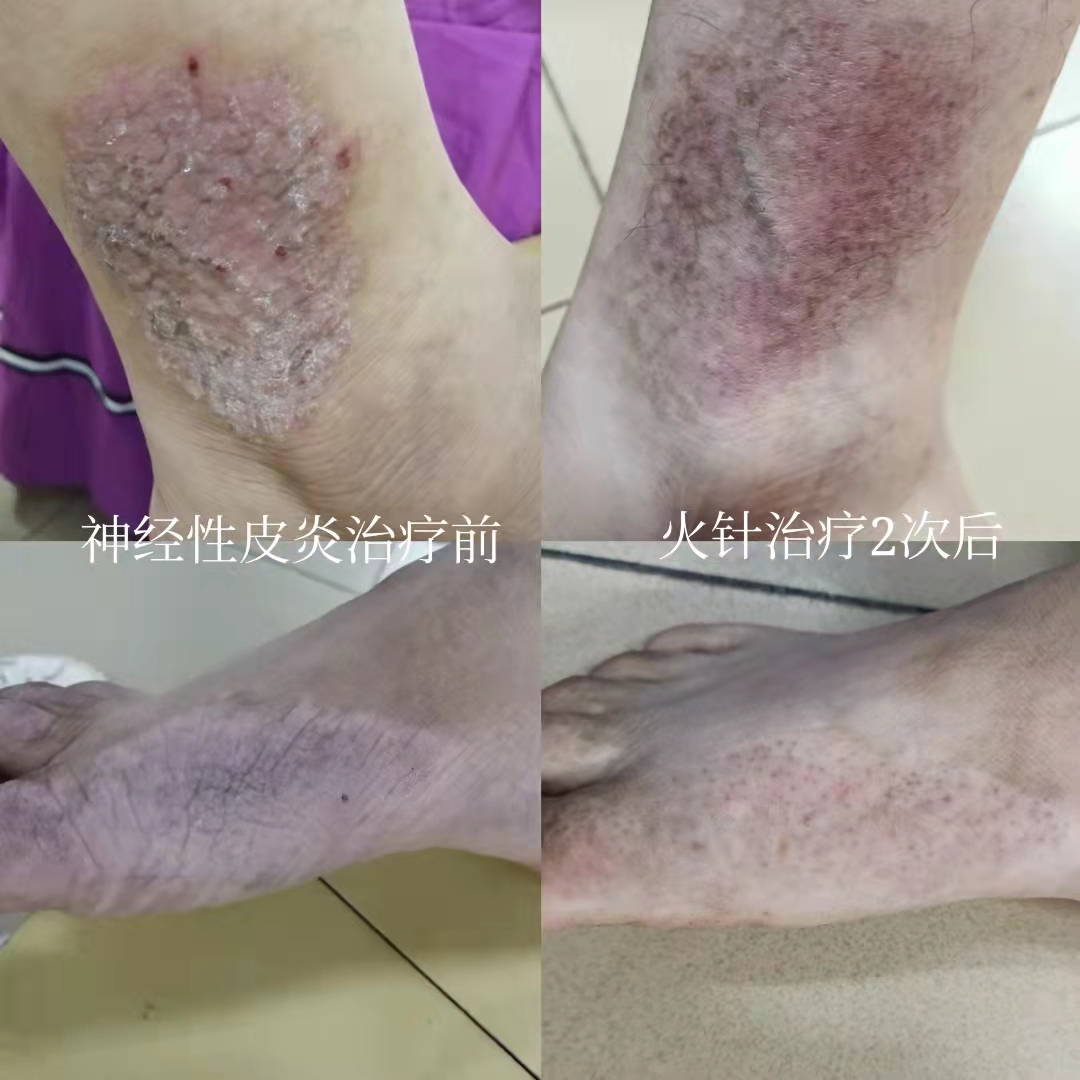
5. Nodular Prurigo, FolliculitisDisinfect the lesion area, puncture the center of papules or small nodules; for hard nodules, use a 1ml syringe needle, heat it until red or white, and quickly puncture vertically into the lesion, ensuring the depth reaches just the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle. For larger nodules, perform surrounding punctures. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.6. Flat Warts, Common WartsAfter heating the needle tip until red, quickly puncture the top of the wart vertically; for small warts, one puncture is sufficient; for larger warts, 2-3 punctures are needed; the depth should just reach the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle. Generally, scabbing begins the next day, and the scab falls off after about a week. If the wart disappears after the scab falls off, treatment can be repeated.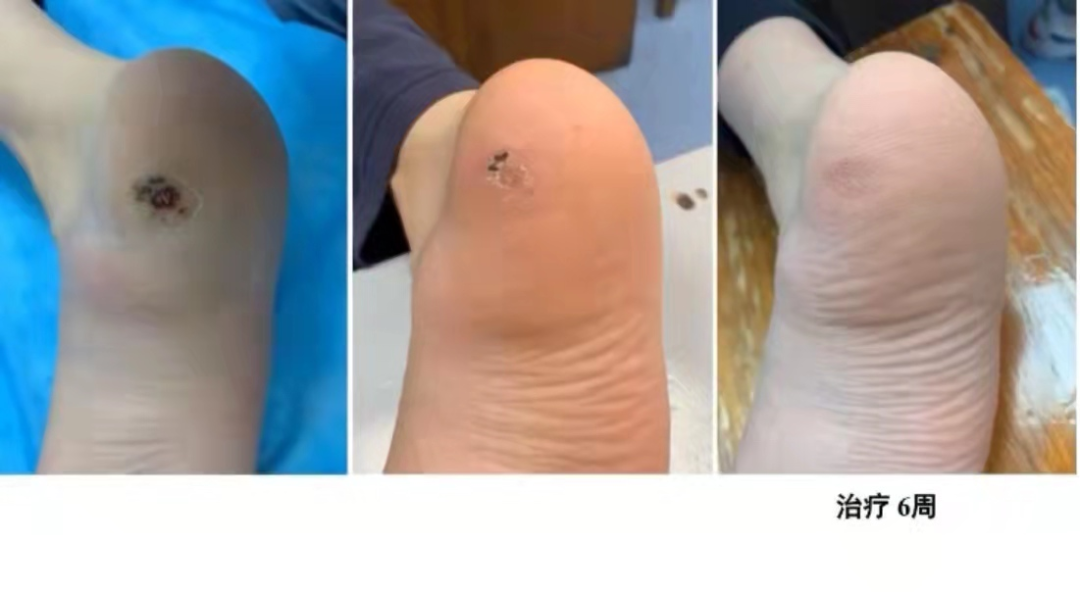 7. NeurodermatitisDisinfect the lesion area, and puncture the lesion area with fire needling. Choose the needle according to the thickness of the lesion, heat it until red or white, and quickly puncture vertically into the lesion, ensuring the depth just reaches the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle, ensuring the entire lesion area is treated. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.
7. NeurodermatitisDisinfect the lesion area, and puncture the lesion area with fire needling. Choose the needle according to the thickness of the lesion, heat it until red or white, and quickly puncture vertically into the lesion, ensuring the depth just reaches the base of the lesion, then swiftly withdraw the needle, ensuring the entire lesion area is treated. Treatment is performed once a week, generally for a course of 4 weeks.


Contributed by/Rheumatology Dermatology
Edited by/Yan Jing
Reviewed by/Qiu Yuxing
Chief Editor/Lin Maoru


