Health is an intangible asset, and health preservation is like bank savings.
01
Basic Knowledge
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
1. Ma (麻): Indicates that Qi can flow, but blood cannot.
2. Mu (木): If the sensation of ma is severe, it indicates mu, meaning both Qi and blood cannot flow.
3. Suan (酸): Indicates that the meridians are open, but there is insufficient Qi and blood.
4. Zhang (胀): Indicates abundant Qi; individuals with this constitution tend to be irritable. If Qi cannot flow, it leads to zhang.
5. Tong (痛): Pure pain is due to blood stasis.
6. Yang (痒): Indicates that Qi and blood are flowing; itching occurs during wound healing, but this is different from generalized itching.
02
Functions of 10 Important Acupuncture Points
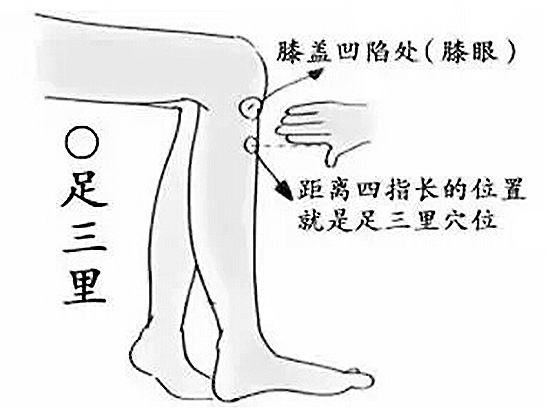
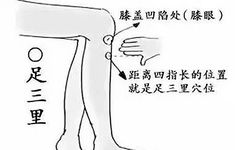
1. Zu San Li (足三里)
Function:
1. Strengthens the spleen and stomach, supports the body’s vital energy;
2. Promotes metabolism and strengthens the body;
3. Enhances endocrine function and boosts immunity.
Stimulation of Zu San Li has preventive and therapeutic effects on diseases of the digestive system, nervous system, blood system, circulatory system, endocrine system, urinary system, and reproductive system, especially for digestive disorders.
Indications:
Gastritis, chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, gastric prolapse, gastric spasms, indigestion, hepatitis; neurasthenia, epilepsy, insomnia, headaches, anemia, hemiplegia, hypertension, hypotension, arteriosclerosis; coronary heart disease; diabetes, enuresis; impotence, premature ejaculation, nocturnal emissions, menstrual irregularities, excessive menstruation; colds; knee arthritis, lower limb arthritis, etc.
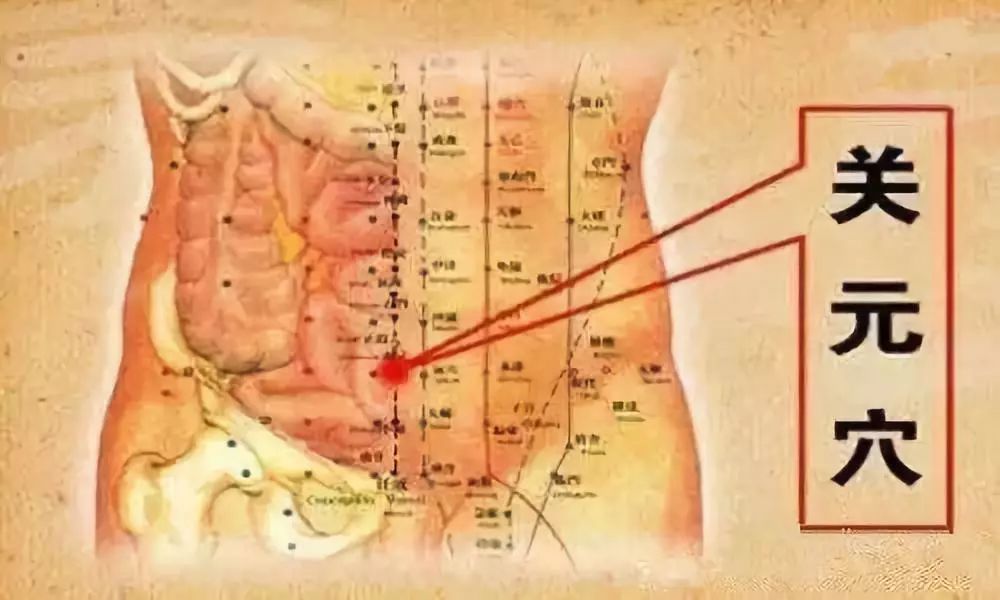
2. Guan Yuan (关元穴)
Function:
1. Nourishes the essence and strengthens the foundation;
2. Tonifies the kidneys, enhances yang, regulates menstruation, clears heat, and promotes dampness elimination. This point is essential for reproductive health and vital energy.
3. Supplements deficiency and strengthens the foundation. This point enhances reproductive system function, boosts immunity, prevents aging, and treats various deficiencies.
Indications:
Impotence, premature ejaculation, nocturnal emissions, menstrual irregularities, cervical erosion, uterine prolapse, pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, enuresis, urinary retention, urinary incontinence, cystitis, nephritis, urethritis, genital eczema; dysentery, hernia, prolapse, hypertension, diabetes; forgetfulness, neurasthenia; weakness, physical debility.
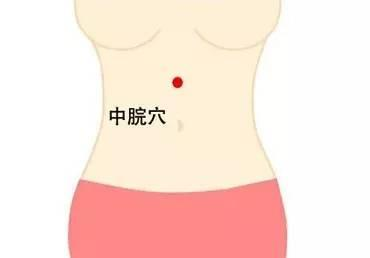
3. Zhong Wan (中脘穴)
Function:
1. Regulates the spleen and stomach;
2. Reduces counterflow and resolves stagnation. This point regulates the stomach, supplements deficiency, promotes digestion, and stops vomiting.
Indications:
Gastric spasms, gastric ulcers, gastric prolapse, gastric distension, indigestion, vomiting, halitosis, enteritis, duodenal ulcers, dysentery, appendicitis, constipation, hepatitis, cholecystitis, jaundice, hypertension, angina, heat stroke, epilepsy, hysteria, neurasthenia, insomnia, cough, asthma, hematemesis, uterine prolapse, menstrual irregularities. This point is particularly important for treating digestive system diseases.

4. Nei Guan (内关穴)
Function:
1. Regulates Qi and invigorates blood;
2. Calms the mind and stabilizes emotions.
Indications:
Angina, myocarditis, rheumatic heart disease, bradycardia, arrhythmia; shock, coma, syncope, motion sickness, insomnia, hysteria, epilepsy, mental disorders; gastric diseases, gastric spasms, vomiting, hiccups; diaphragm spasms, pregnancy sickness, hypotension, absence of pulse, etc. This point is particularly effective for various heart diseases and mental disorders.
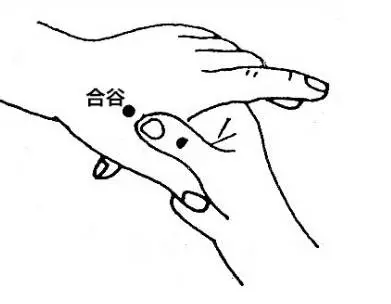
5. He Gu (合谷穴)
Function:
1. Clears heat and releases the exterior;
2. Relaxes muscles and dispels wind, regulates the intestines and stomach. Its primary function is to clear heat and relieve pain.
Indications:
Colds, cough, headaches, trigeminal neuralgia, facial nerve paralysis, epilepsy, schizophrenia; enteritis, dysentery, hemorrhoids, pediatric prolapse, toothache, rhinitis, epistaxis; tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, deafness, acute shoulder rheumatism, finger spasms, difficult labor, measles, excessive sweating, aphasia, etc. It is particularly effective for headaches caused by colds.

6. Yong Quan (涌泉穴)
Function:
1. Clears the mind and awakens the spirit;
2. Calms the mind and stabilizes emotions;
3. Clears heat and disperses wind.
Regular cupping on this point can guide the kidney’s deficient fire and clear the turbid Qi from the upper jiao, promoting liver function, improving vision, and calming the throat and mind. It can lower blood pressure and enhance local blood circulation, helping to prevent age-related numbness and edema.
Indications:
Shock, coma, dizziness, heat stroke, forgetfulness, headaches, trigeminal neuralgia; epilepsy, hysteria, mental disorders, pediatric convulsions; cerebral hemorrhage, functional paralysis, functional aphasia, facial spasms, hypertension, angina, myocarditis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, cough, epistaxis, jaundice, stomach pain, edema, impotence, low back pain, knee pain, chest pain, vision impairment, measles, hernia, etc.
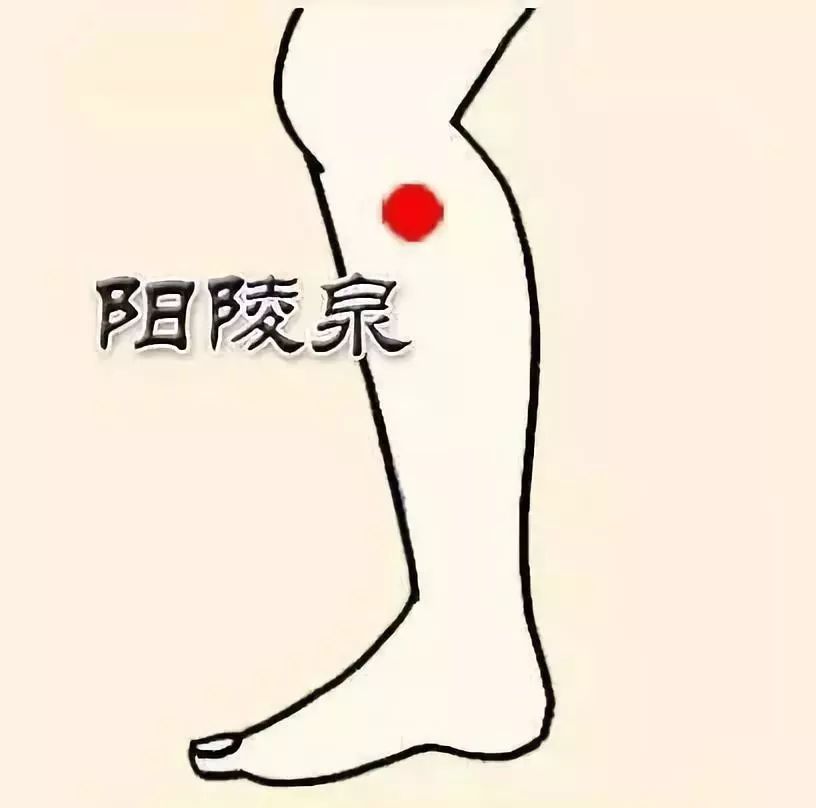
7. Yang Ling Quan (阳陵泉)
Function:
1. Opens the meridians and activates the collaterals;
2. Regulates the meridians and benefits the joints;
3. Clears heat and benefits the gallbladder.
Indications:
Diseases of the lower limbs and lower back, such as knee arthritis, ankle arthritis, sciatica, peroneal nerve paralysis, vasculitis, rheumatoid arthritis, low back pain, etc. This point is also crucial for treating liver and gallbladder diseases, with good effects on hepatitis, cholecystitis, and jaundice. Additionally, it is effective for hypertension, epilepsy, enuresis, and athlete’s foot.
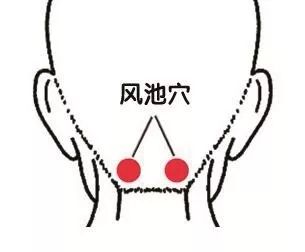
8. Feng Chi (风池穴)
Function:
1. Clears the heart and brightens the eyes;
2. Clears heat and disperses wind;
3. Opens the orifices and activates the collaterals.
Indications:
Cerebral thrombosis, concussion, meningitis, forgetfulness, epilepsy, mental disorders, migraine, insomnia, dizziness, hyperthyroidism, stiff neck, glaucoma, night blindness, optic neuritis, retinitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, hypertension, tinnitus, malaria, deafness, etc.
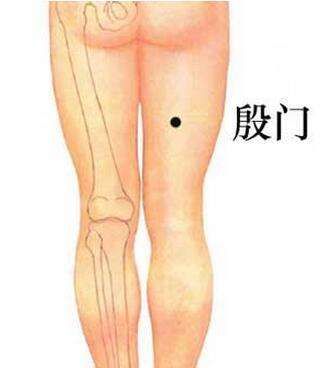
9. Yin Men (殷门穴)
Function:
1. Opens the meridians and activates the collaterals;
2. Unblocks the tendons and vessels.
Indications:
Low back pain, sciatica, herniated disc, lower limb muscular rheumatism, paralysis.
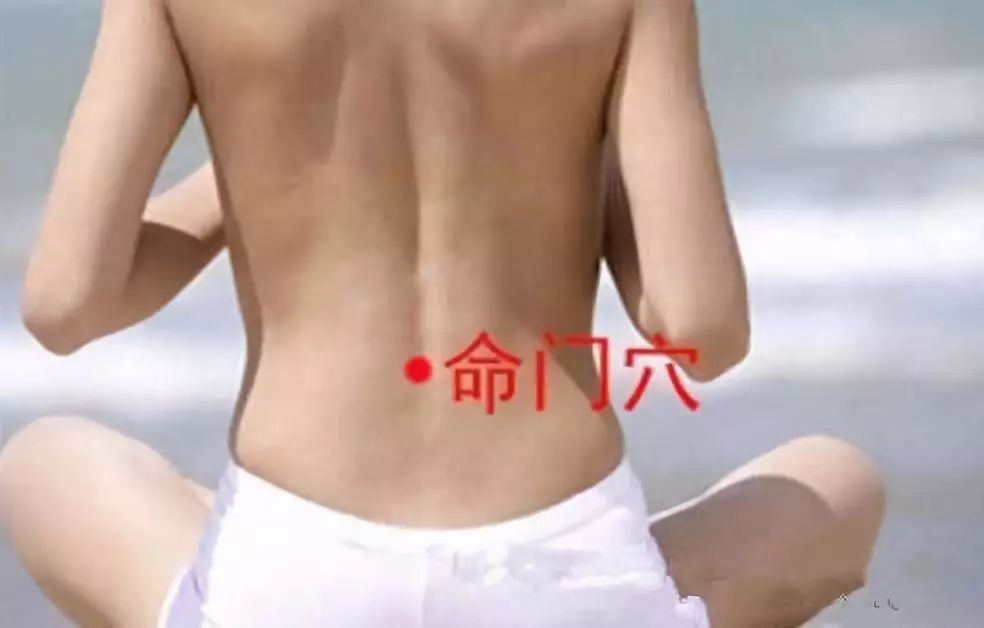

10. Ming Men (命门穴)
Function:
1. Nourishes the kidneys and regulates menstruation;
2. Regulates the intestines and prevents prolapse.
Indications:
Nocturnal emissions, impotence, menstrual irregularities, dysmenorrhea, enuresis, low back pain, headaches, tinnitus, hemorrhoids, constipation.
03
The Health Preservation Song

Health is an intangible asset, and health preservation is like bank savings;
Illness is a malignant overdraft, and serious illness can lead to financial ruin;
Everything else is false, only health is true;
Don’t wait until you’re sick to find a doctor; practice health preservation when you’re well;
Better to stand and maintain health than to lie down and take pills;
Health is always priceless; persist in health preservation and care.

>>Scan to follow<<
Reprinted from: Traditional Chinese Culture